Select Language:
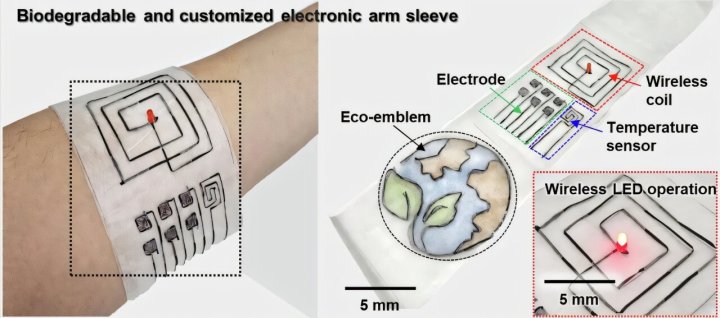

What’s the latest? A team from Seoul National University, under the guidance of Professor Seung-Kyun Kang and Dr. Jae-Young Baehave, has developed an innovative biodegradable fiber that could transform textile electronics and address the escalating issue of electronic waste. This sustainable material, explored in a July 2025 study in npj Flexible Electronics, naturally degrades without causing environmental harm, in contrast to conventional electronic textiles that contribute to pollution. Composed of renewable polymers, these fibers can function in wearable technology while breaking down in soil and compost, showcasing a commitment to making sustainable electronics accessible.
Why is this significant? Electronic waste represents a major global challenge, with over 50 million metric tons generated each year, much of which includes non-recyclable textiles mingled with metals and plastics. These new fibers present a significant advantage: they support advanced wearable technologies—such as smart fabrics for health monitoring—while minimizing ecological damage. Unlike traditional e-textiles, which can remain in landfills for hundreds of years, these biodegradable options decompose in a matter of months, contributing to the goals of a circular economy. This innovation has the potential to change various sectors, from fashion to healthcare.
Why should you care? If you use smartwatches, fitness trackers, or other wearables, this new technology could considerably enhance the sustainability of your next device without compromising functionality. It’s a move towards eco-conscious tech use, lessening the environmental impact of discarded devices. Furthermore, it enables the development of comfortable smart clothing that could monitor health or connect to other devices without polluting the environment. Envision a future where your clothing powers your devices and is compostable once it’s no longer needed.
What’s on the horizon? The team is actively enhancing production capabilities, targeting commercial availability within five years. They face challenges like ensuring the durability of the materials meets industry standards and keeping production costs competitive. Expect pilot programs in medical wearables and sustainable fashion shortly. Researchers are also investigating applications for soft robotics and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Keep an eye out for brands like Patagonia or Nike incorporating this innovative technology into their eco-friendly products.
How long will they last? This question is a common concern among potential users. Research indicates that various factors—such as exposure to soil and conditions like bending and rubbing—can influence the lifespan of biodegradable electronics.






