Select Language:
Google’s investment in artificial intelligence is well-known and becomes apparent as soon as you open any of its applications. One of the earliest beneficiaries of this AI focus has been the Google Photos app. Now, the company is introducing a new level of transparency.
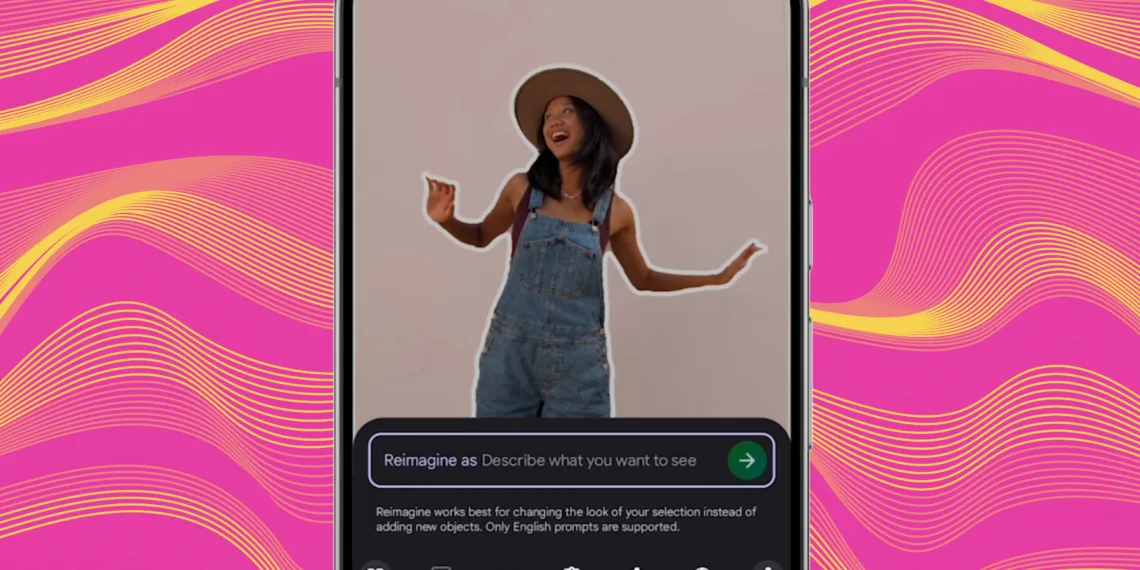
Do you remember the Magic Editor, which allows you to utilize AI-assisted editing within Google Photos? Moving forward, images enhanced by the Reimagine tool found in Magic Editor will include an invisible watermark.
The Reimagine feature enables you to edit photos using everyday language. Just select the elements you wish to modify and describe your desired changes in a single sentence. You can alter backgrounds, eliminate unwanted objects, and introduce new elements seamlessly.
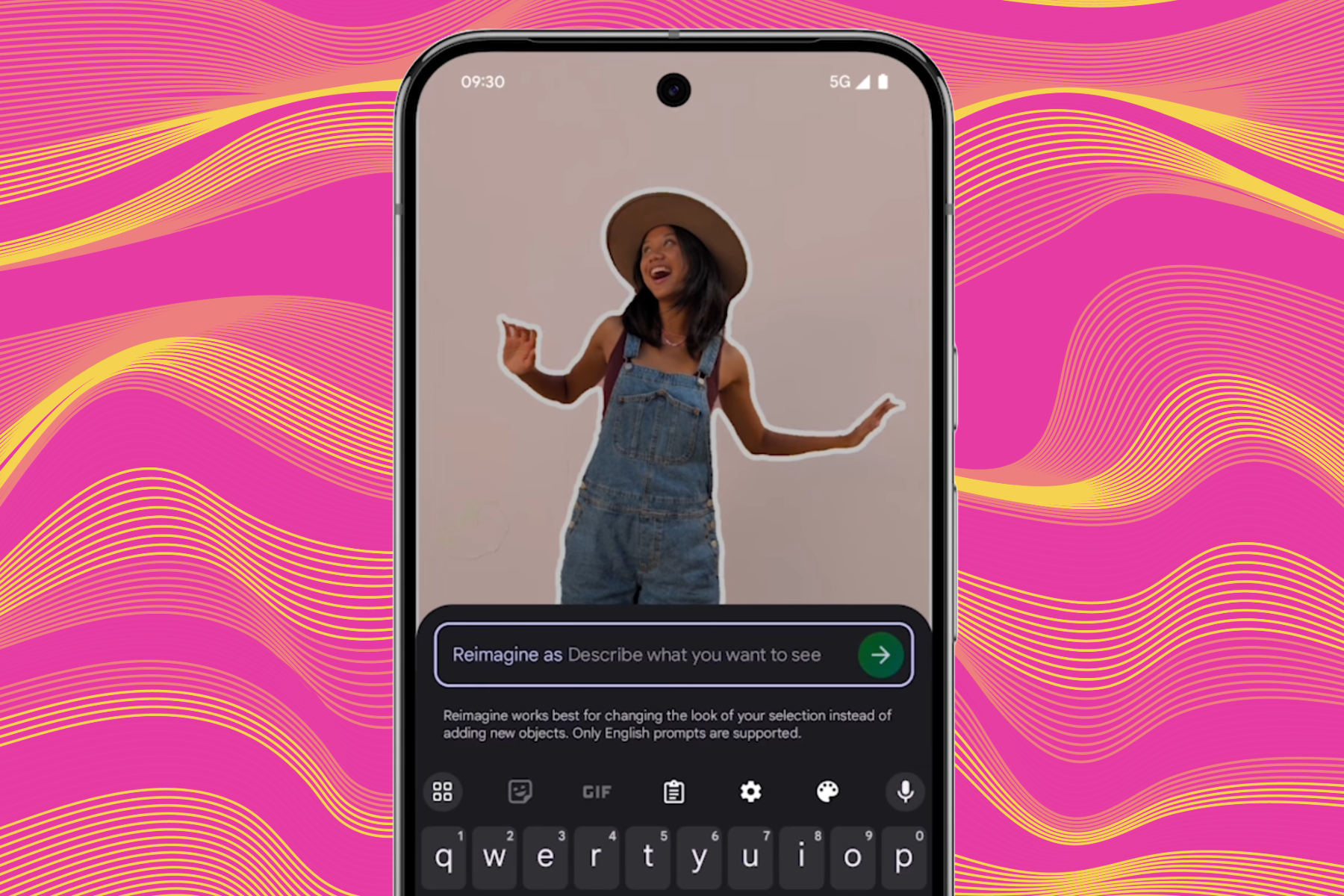
Although you won’t physically observe the watermark, it operates at the pixel level within the AI-edited images. Google utilizes a digital watermarking tool named SynthID to identify photos that have undergone AI enhancements.
While SynthID is designed to mark images accurately, it may not always succeed, especially with subtle modifications. According to Google, “In some instances, edits made with Reimagine may be too minor for SynthID to detect, like changing the color of a small flower in a photograph.”
Developed by Google DeepMind, SynthID serves as a digital watermarking solution for AI-generated visual content. While it remains invisible to human eyes, it can still be detected by machines and online platforms, including Google Search.
Even when the watermark is applied, the quality of the image remains intact. Modifications like cropping, changing color profiles, adding filters, or compressing images will not eliminate the SynthID signature.
SynthID has not only been integrated into images produced by Google’s Imagen model but is also a core component of video content generated by the Veo video generation model.
The role of AI effects on an image’s editing can be verified through the “About this image” feature. Users can explore this section for online images via Chrome or through Google Image Search.

This feature reveals information such as the date the image was first indexed by Google Search and its initial appearance online, along with details about its AI origins.
The “About this image” section can also be accessed through the Circle to Search feature on mobile devices and via Google Lens in the smartphone app for both Android and iOS. Copyright protection for these images may vary based on the level of AI involvement.
Google’s method of transparency differs from emerging standards like C2PA, which use cryptographic techniques to modify image metadata. Notably, Google is a participating member of the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA), alongside companies such as Amazon, Meta, OpenAI, and Microsoft.