Select Language:
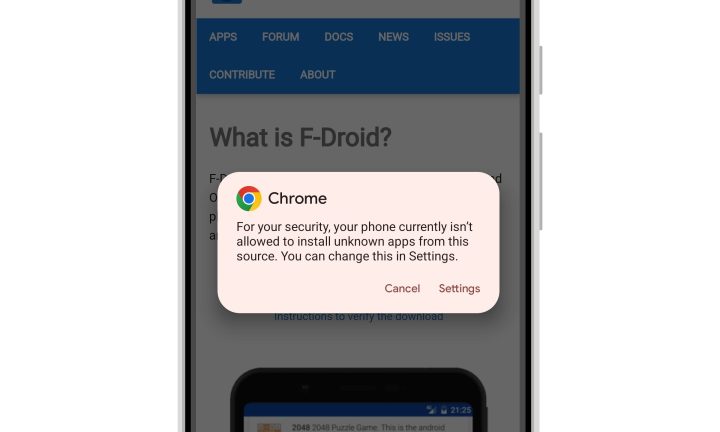
Malware-infected applications have long been a concern on Android devices, primarily due to the open nature of the platform. Unlike iOS, which restricts app installs to the official App Store, Android allows users to run apps from virtually any source on the internet, increasing the risk of malicious software.
What’s New for Android?
Google is now implementing a policy that requires all apps to be registered with verified developers before they can be installed on certified Android devices. This means that if you have a genuine Android phone from a reputable manufacturer, it most likely qualifies as a certified device. Certification indicates that Google has tested the device for security compliance and it comes equipped with protections like Google Play Protect, which scans for viruses and other threats.
The key change involves developer verification. Google will now verify the identity of developers or businesses responsible for apps before they appear on your device. If a developer remains unverified, the app will be blocked from installation. This move is part of Google’s efforts to tighten control over app sources and reduce the distribution of harmful software.
Why is this Important?
Previously, developers could distribute apps without verification, creating an opportunity for malicious actors to exploit the system. They often uploaded malware-laden apps, containing anything from trackers to data theft tools. Now, with the new policies, Google will verify developer identities, making it easier to hold malicious developers accountable and ensuring that users are downloading apps from legitimate sources.
What Does This Mean for Users?
Starting in March next year, Google will begin verifying developers for apps listed on the Google Play Store. By September, the verification process will expand to several Asian markets, with plans to further extend in subsequent years. The goal is to prevent harmful apps from spreading through unofficial channels, ultimately providing a safer app ecosystem.
Since implementing these identity checks, Google reports it has significantly reduced the number of malicious apps, which previously made up a tiny fraction of downloads from third-party sources. The verification process helps stop bad actors from hiding behind anonymity to distribute malware, conduct scams, or steal sensitive data.
Additional Measures
Google continues to leverage artificial intelligence to combat threats. Since 2017, they’ve used machine learning algorithms to identify malicious apps and are now deploying on-device AI to detect scams through calls and messages. The company also offers enhanced security features, like Advanced Protection, to safeguard devices against evolving threats.
In essence, these changes are designed to make Android devices more secure by ensuring that only verified developers can distribute apps, thereby protecting users from the increasing threat of malicious software.