Select Language:
A team of Chinese scientists has developed the world’s first prototype battery utilizing hydride ions, which possess the highest electron density among all hydrogen forms, opening a new avenue for renewable energy advancement.
The researchers from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, affiliated with the Chinese Academy of Sciences, created an all-solid-state rechargeable hydride ion battery. This innovative design employs sodium aluminum hydride—a hydrogen storage material—as the positive electrode, and cerium dihydride, a hydrogen-deficient compound, as the negative electrode, according to findings published in a renowned UK scientific journal.
The battery initially offers a specific capacity of 984 milliampere-hours per gram and retains 402 mAh per gram after 20 charge-discharge cycles.
Similar to lithium-ion batteries, a hydride ion battery stores and releases energy through the movement of hydride ions. These ions possess higher electron density compared to hydrogen cations or atoms and are highly reactive and polarizable, making them promising candidates for energy storage.
Until now, such batteries remained theoretical because of the lack of suitable electrolyte materials. An effective electrolyte must have high ionic conductivity, low electronic conductivity, strong thermal and electrochemical stability, and compatibility with electrode components.
To overcome this hurdle, the team developed a novel composite electrolyte featuring a core-shell structure. This material comprises a thin layer of barium hydride coating cerium trihydride, resulting in excellent hydride ion conduction at room temperature, along with superior thermal and electrochemical stability—ideal qualities for electrolyte performance.
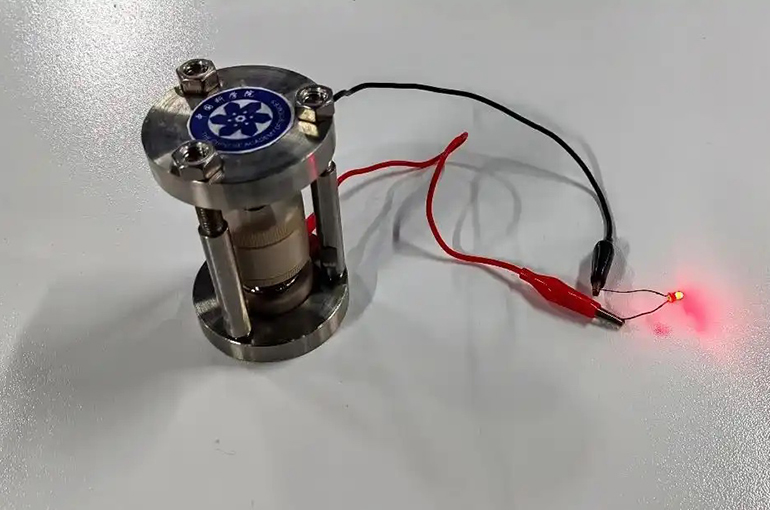
Using this setup, the scientists assembled a stacked battery, which increased the output voltage to 1.9 volts, successfully powering a light-emitting diode.
This breakthrough demonstrates the potential for hydride ion batteries to power electronics and marks a significant move from theoretical concepts to practical experiments.
The development represents a new approach to energy storage technology, with promising applications in large-scale energy systems, hydrogen storage, portable power sources, and specialized energy solutions.