Select Language:
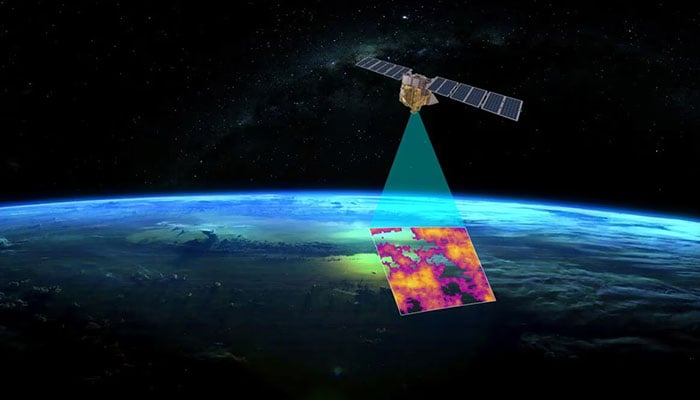

In a groundbreaking partnership with its AI technology collaborators, Google has launched FireSat, the inaugural satellite of an innovative constellation aimed at transforming how wildfires are detected and managed.
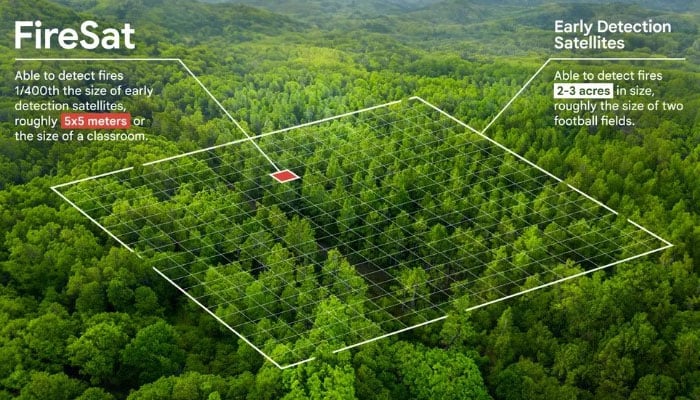
The FireSat initiative is a joint effort involving Google Research, Muon Space, Earth Fire Alliance, and the Moore Foundation, along with international wildfire management agencies. This satellite has the remarkable ability to detect wildfires as small as 5 by 5 meters within just 20 minutes, according to ESG News.
The tech giant has committed $13 million to this initiative through its AI Collaborative: Wildfires program.
In contrast to conventional methods that depend on infrequent, low-resolution satellite imagery—which can lead to slow responses—FireSat offers near real-time data to firefighting agencies.

This technological advancement significantly improves response strategies, underscoring the pressing demand for quick detection, as noted by Juliet Rothenberg, who experienced a wildfire evacuation in California.
“We received only updated satellite images every 12 hours while the sky over the Bay Area was filled with smoke and tinged red. It was shocking to realize that wildfire agencies didn’t have access to much better data than we had,” Rothenberg explained.
The first of 50 satellites was successfully launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base.
The decision to use satellites instead of high-altitude drones for wildfire monitoring is largely attributed to the decreasing costs of satellite technology and their capacity to cover remote mountainous areas prone to wildfires.
Chris Van Arsdale, co-founder and part of the FireSat team, mentioned that they encountered several challenges in making this innovation a reality.
“A significant challenge was distinguishing between actual fires and random environmental ‘noise.’ We had to find a way to differentiate genuine fires from sensor malfunctions or misaligned pixels,” he noted.
FireSat’s early warning capabilities could help minimize economic and humanitarian losses caused by wildfires while providing greater protection for vulnerable communities and ecosystems worldwide.
Moreover, the data collected by FireSat will create a comprehensive historical record of fire behavior, assisting scientists in forecasting future wildfires.
“FireSat serves not only as an emergency response tool but also as a powerful mechanism for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. It’s inspiring that this satellite constellation contributes to combating climate change while actively engaging in response efforts,” Rothenberg added.