Select Language:
Understanding the Impact of Tariffs on Global Trade Dynamics
The World Trade Organization (WTO) has recently published its Global Trade Outlook, shedding light on the complex and evolving landscape of international trade amidst tariff fluctuations. The report attempts to navigate the murky waters of trade forecasts during a time of heightened uncertainty characterized by myriad tariff announcements, suspensions, exceptions, and ongoing negotiations.
The Dual Scenarios Defined
To provide a comprehensive forecast, the WTO constructed two distinct scenarios:
-
Baseline Scenario: This assumes a continuation of the prior low-tariff environment coupled with relatively low trade uncertainty. In this context, global trade was initially projected to grow by 2.7 percent for the year.
- Tariff Scenario: Reflecting the real-time measures in place as of April 14, this scenario incorporates the suspension of reciprocal tariffs, which partially mitigated the effects of the Trump administration’s tariff policies.
Under the tariff scenario, the WTO has adjusted its outlook for global merchandise trade, predicting a decline of 0.2 percent for the year. This translates to a significant 2.9 percentage-point reduction compared to the more optimistic baseline forecast.
Consequences of Tariff Resumption
The WTO has issued a stark warning regarding the potential for further decline in global trade volume. Should reciprocal tariffs be reinstated and economic uncertainty continue to spread, projections indicate an even steeper drop. The organization’s worst-case outlook anticipates a decline of 1.6 percent in global trade volume by 2025.
Insights from WTO Leadership
WTO Director-General Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala expressed serious concerns regarding the enduring uncertainty that surrounds trade policy — particularly the escalating tensions between the United States and China. “The recent de-escalation of tariff tensions has temporarily relieved some of the pressure on global trade,” she noted. However, she underscored that ongoing uncertainty likely hampers global growth, leading to significant adverse effects worldwide.
Regional Impact of U.S. Tariffs
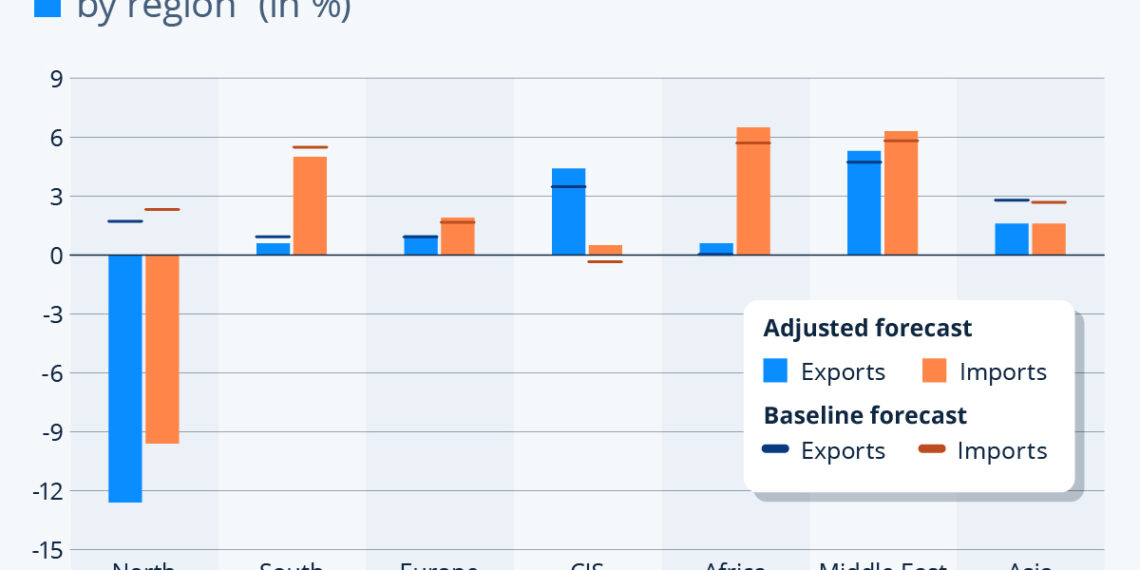
The ripple effects of tariffs, particularly those imposed by the United States, are markedly pronounced in North America. The WTO’s regional forecast reveals a stark disparity between the baseline and the tariff scenario. Instead of a projected growth of 2.2 and 2.8 percent in exports and imports, respectively, North America is now facing sobering predictions—a 12.6 percent drop in exports and a 9.6 percent decline in imports.
Asia: A Secondary Victim
With China at the epicenter of trade conflicts, the Asian continent is projected to experience the second-largest repercussions. Forecasts indicate that im- and exports in the region would witness a downward adjustment, with growth rates anticipated at 1.6 percent in 2025, down from earlier projections of 3.2 and 3.3 percent, respectively.
Potential Outcomes for U.S.-China Trade Relations
The tension between the U.S. and China could lead to drastic changes in the trading patterns between the world’s largest economies. The WTO predicts that U.S. imports from China could potentially plunge by as much as 77 percent. This anticipated downturn could trigger a significant reorientation in global trade flows, as Chinese exports may find new avenues through third countries. Consequently, other producers would face intensified competition as they adapt to an altered trading landscape shaped by the tariff onslaught.
Summary of Trade Predictions
The WTO’s assessments signal not only a short-term decline in trade but also lingering uncertainties that could cast shadows over global growth in the coming years. As countries navigate the complexities of tariffs and trade relationships, the ramifications for both exporters and importers will require careful consideration and strategic adaptation to foster resilience in these challenging times.
The unfolding scenario suggests that stakeholders should remain vigilant, as the global trade environment may shift rapidly in response to policy changes and economic dynamics.