Select Language:
USA or China: Who Dominated Global Trade in 2024?
1. The Fight for Market Leadership: U.S. and China in 2024
As 2024 wraps up, the ongoing rivalry between the United States and China for global trade supremacy continues to capture headlines. Both nations have reinforced their positions, but subtle shifts suggest one may have edged ahead in terms of trade volume and economic influence. Understanding what defined their trade dominance this year requires a detailed look into trade flows, policy impacts, and emerging trends.
2. U.S. Trade Volume Stays Steady Amidst Challenges
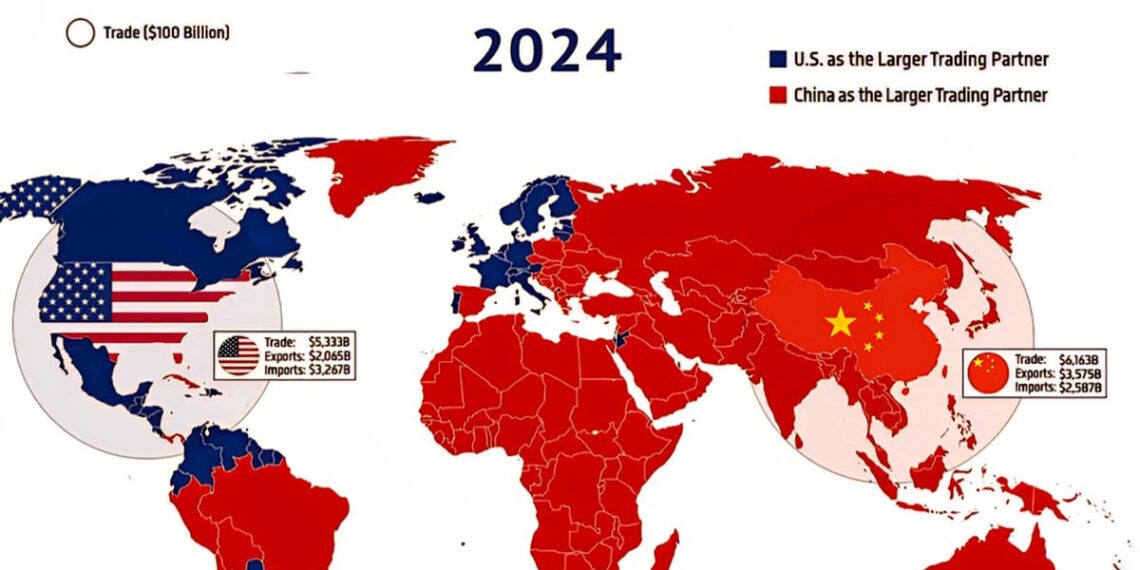
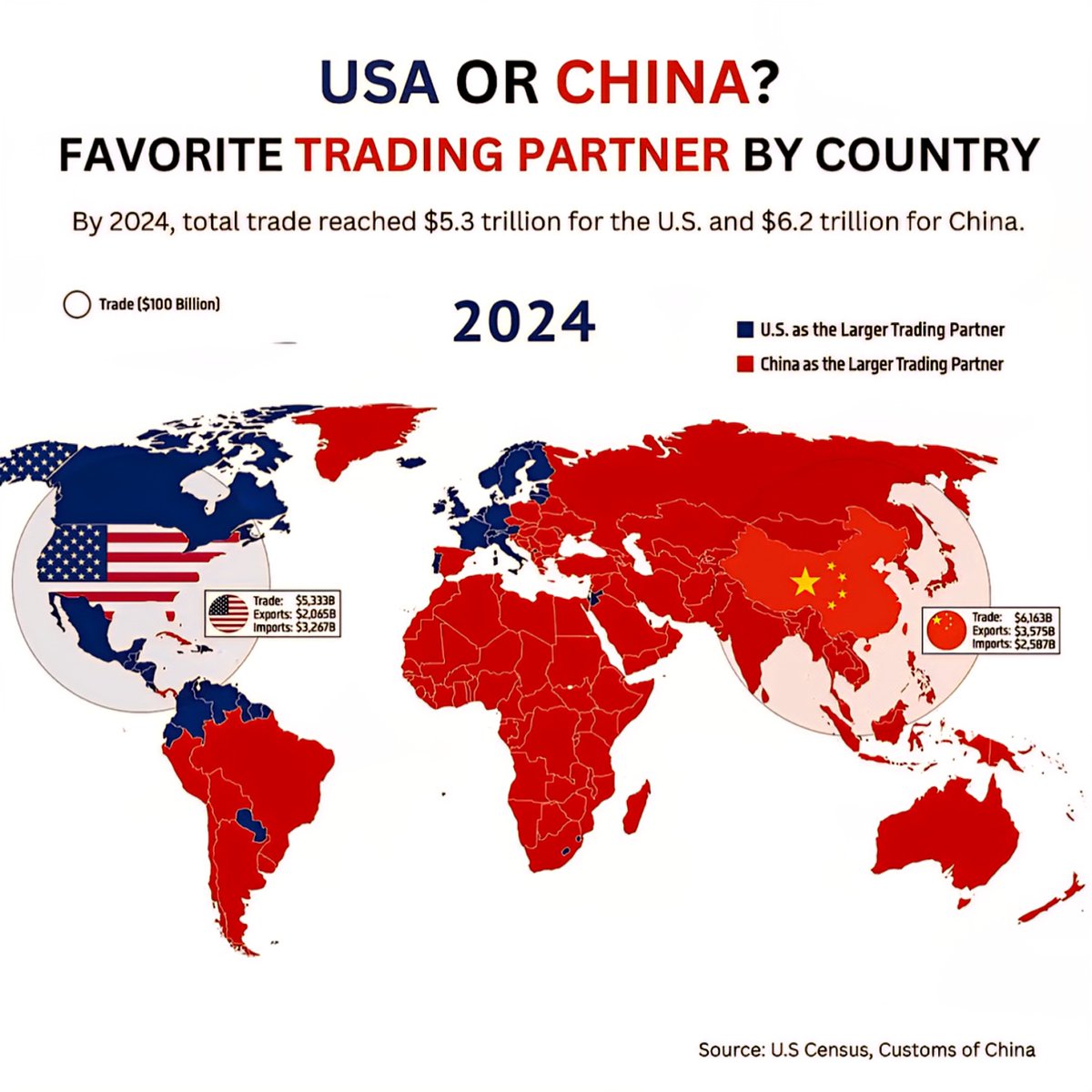
The United States maintained its position as one of the top global traders in 2024, with total trade volume reaching approximately $6.2 trillion. Despite facing headwinds such as inflation, global supply chain disruptions, and shifts in domestic policy, the U.S. managed to preserve its extensive trade relationships, particularly with Canada, Mexico, and key Asian partners like Japan and South Korea.
Recent trade agreements and strategic partnerships aimed at bolstering supply chain resilience contributed significantly to the nation’s stability in international trade. However, America’s focus on technological export controls and strengthening its semiconductor industry marked a shift toward safeguarding critical sectors.
3. China’s Continued Rise and Expanding Global Reach
China’s trade figures for 2024 tell a story of persistent growth and expanding global influence, with total trade roughly surpassing $5.5 trillion. The nation demonstrated resilience in the face of global economic uncertainties, including inflationary pressures and shifting trade tensions.
A notable aspect of China’s trade strategy this year was diversification—expanding into emerging markets in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America. The Belt and Road Initiative continued to play a role in enhancing China’s trade corridors, facilitating more efficient routes for exports and imports. Moreover, China’s technological sectors, particularly electronics and green energy products, led the growth trajectory.
4. Key Trade Partnerships and Regional Dynamics
United States
The U.S. expanded its trade alliances through new agreements with the Indo-Pacific region, bolstering economic ties with India and fostering closer collaboration with Australia. Meanwhile, efforts to replace dependence on Chinese imports by boosting manufacturing in North America gained momentum, especially in electronics and automotive sectors.
China
China’s trade partnerships with Russia intensified, especially in energy and raw materials, as mutual sanctions and geopolitical factors reshaped global trade dynamics. Additionally, China’s push to dominate the green energy market by expanding exports of solar panels and EV batteries increased its market share worldwide.
5. Technology and Trade: The Battle of Innovation
Innovation remained a critical battleground for U.S.-China trade dominance in 2024. The U.S. chipped away at China’s technological advancements through export restrictions and investment screening, aiming to protect its leadership in AI, semiconductor manufacturing, and quantum computing.
Conversely, China accelerated its own technological development, particularly in 5G infrastructure, electric vehicles, and green energy technologies. The race for technological supremacy underscored broader economic and geopolitical strategies, shaping global trade patterns for years to come.
6. Economic Policies and Sanctions
Trade policies in 2024 reflected a broader geopolitical contest. The U.S. continued to use sanctions as a tool to pressure China on issues ranging from intellectual property to environmental standards. Meanwhile, China responded with retaliatory measures and efforts to reduce reliance on American technology and investment.
Despite these tensions, both nations kept their trade channels open, recognizing that economic stability and growth were vital to maintaining their influential positions globally.
7. The Future Outlook: Who Will Lead in 2025?
As we look ahead to 2025, the competition between the U.S. and China remains fierce but also deeply interconnected. While the U.S. still holds a slight edge in overall trade volume and technological innovation, China’s rapid growth and strategic expansion suggest it could overtake the U.S. in the coming years.
Economic analysts believe that the winner of this rivalry will depend on various factors, including policy decisions, geopolitical developments, and the ability to innovate and diversify markets. For businesses and consumers worldwide, the outcome will significantly influence global supply chains, prices, and economic stability.
Conclusion:
The trade landscape in 2024 showcased a tug-of-war between two economic giants. The United States and China continue to shape the future of global commerce — a dynamic that will undoubtedly steer international markets in years to come. Stakeholders worldwide are closely watching these developments, understanding that today’s decisions will influence tomorrow’s trade routes, technology, and economic power balance.