Select Language:
The U.S. Labor Market: Recent Trends and Insights
The United States labor market has undergone significant shifts in recent years, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Recent data suggests that this vital sector is finally finding its balance again, marking a significant development for both job seekers and employers.
Current Job Openings and Unemployment Figures
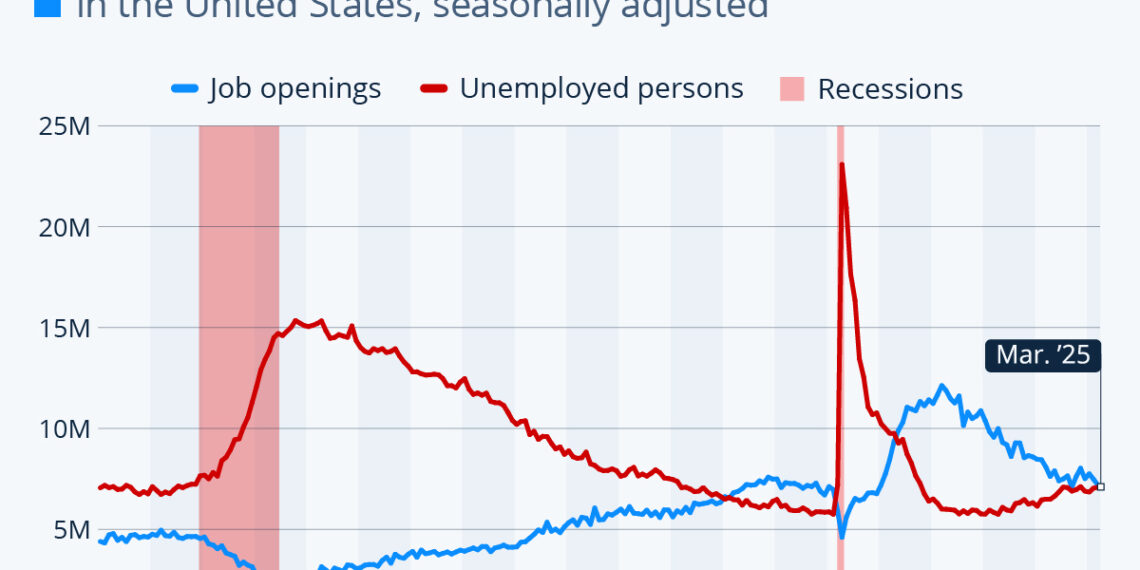
According to the latest Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey (JOLTS), as of March 2023, the number of job openings fell to approximately 7.19 million. This figure represents the second lowest recorded since January 2021. The unemployment rate during the same period was around 7.08 million, which indicates a ratio of roughly 1.02 unfilled positions for every job seeker. This data unveils an essential insight: the significant imbalance between labor demand and supply that had previously characterized the market is beginning to equalize.
Historical Context of Job Openings
To understand the current situation, it is essential to consider historical trends:
- Pre-Pandemic Levels: Before the pandemic struck in March 2020, there were approximately 1.2 job openings for each unemployed person.
- Pandemic Impact: With the onset of the pandemic, this ratio plummeted to 0.2 in April 2020 amidst extensive layoffs across various sectors.
- The Great Resignation: By March 2022, during the height of the so-called "Great Resignation," the ratio soared to 2.02 job openings for every unemployed individual.
Comparison Over Time
The gradual recovery is noteworthy. In April 2021, the ratio stood at about 1.02, the same as it is now, following a significant spike during the turbulent times of the pandemic. This recent stabilization suggests that businesses are finding their footing while job seekers are also adapting to a more balanced labor market.
Implications for Inflation
The Federal Reserve, particularly under the leadership of Chair Jerome Powell, has long emphasized the need for a balanced labor market to mitigate upward pressure on wages, a key driver of inflation.
Federal Reserve’s Acknowledgment
In the most recent FOMC meeting, the committee recognized that the balancing act in the labor market has largely been restored. This acknowledgment signals a hopeful trajectory for the economy, as it implies that labor market conditions are less likely to contribute to inflationary pressures moving forward.
The Broader Economic Outlook
With the latest figures indicating a return to balance, there is optimism among economists and policymakers about future economic stability. As job openings align closely with unemployment figures, businesses may regain confidence in hiring, which could foster job growth and ultimately support economic health.
Conclusion
The U.S. labor market is gradually balancing out, reflecting a critical transition from the disruptions caused by the pandemic. As job openings and unemployment figures begin to stabilize, both job seekers and employers stand to benefit from a more equitable labor environment. This balance not only aids in reducing wage pressures but also fosters a more robust economic landscape moving forward.