Select Language:
U.S. Economy Faces Challenges: A Deep Dive into Q1 2025’s Economic Shrinkage
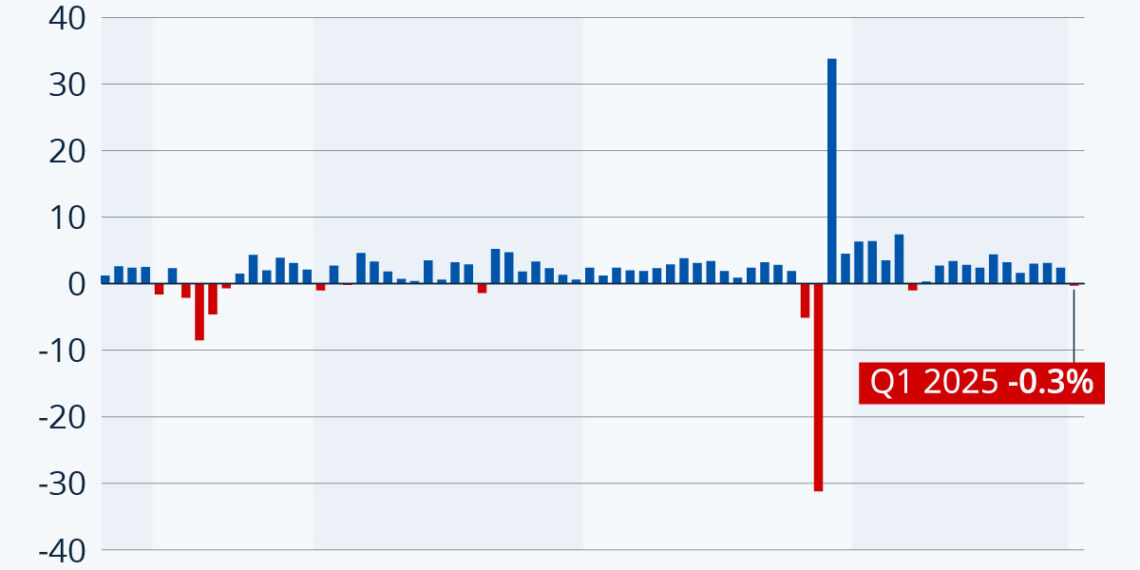
The latest data from the Bureau of Economic Analysis has revealed a concerning trend in the U.S. economy: a contraction of 0.3 percent in the first quarter of 2025. This is particularly striking in light of the 2.4 percent growth experienced in the previous quarter. Let’s explore the factors driving this economic downturn and the broader implications for the country.
The Economic Landscape in Q1 2025
Contraction Overview
In Q1 2025, the economy experienced an unexpected shrinkage, falling short of economists’ projections, which anticipated a modest growth of 0.4 percent. The shift from growth to contraction is alarming, especially after a period of relative stability where the GDP had shown positive signs.
Stock Market Response
In reaction to the economy’s slump, stock markets took a downturn. Investor sentiment often reflects concerns over economic health, and this drop underscores the unease surrounding the latest GDP figures.
Key Contributing Factors
Surge in Goods Imports
One of the most significant contributors to the GDP contraction was a remarkable 50 percent increase in goods imports during the first quarter. Analysis suggests that importers were proactively stocking up in anticipation of upcoming tariffs announced by the Trump administration. This strategic move, while aimed at mitigating costs, ultimately had the unintended consequence of negatively impacting GDP figures for the quarter.
The Zero-Sum Game
Although the surge in imports is detrimental to GDP in the short term, it is essential to note that once these goods are sold domestically, they will contribute positively to GDP. This scenario presents a classic zero-sum dynamic in economic reporting, where the immediate negative impact could be offset in the longer term.
Weaker Consumer and Government Spending
Another significant factor leading to the economic shrinkage was a notable decline in consumer spending. This trend reflects consumers’ hesitation to spend amid rising inflation and uncertainty. Coupled with decreased government spending under the current administration, the contraction in GDP gains momentum.
The Role of Consumer Confidence
Consumer spending is a major driver of economic growth, and any dip can have ripple effects throughout the economy. The weakened consumer confidence may stem from various factors, including inflation, job market instability, and global economic uncertainties.
Positive Contributions: Investment Trends
Amid the gloomy economic indicators, one area showed strong growth: investment spending. Equipment investment surged, possibly linked to the impending tariffs. This uptick in investment represents a flicker of optimism in an otherwise troubling economic environment, providing a counterbalance to the declines observed in other areas.
Lessons from Recent Economic History
Comparing Past Contractions
The U.S. economy’s latest contraction echoes past instances of economic downturns. A notable comparison can be drawn with the first quarter of 2022, when the economy contracted by 1 percent in response to global disruptions caused by the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Fortunately, the economy demonstrated resilience with a subsequent recovery.
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
The economic landscape of the U.S. has been particularly volatile in recent years. The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in the steepest recorded decline during the first half of 2020, followed by a notable rebound. The lessons learned from these episodes highlight the importance of adaptability and strategic planning in both consumer and governmental spending.
Future Implications
As we analyze the implications of Q1 2025’s economic conditions, it is vital for policymakers, businesses, and consumers to remain vigilant. With the potential for future tariffs, changes in consumer behavior, and investment dynamics, the road ahead may involve complex navigational decisions for all stakeholders involved in the economy.