Select Language:
Key Factors Influencing Global Quality of Life in 2025

1. Economic Stability and Income Levels
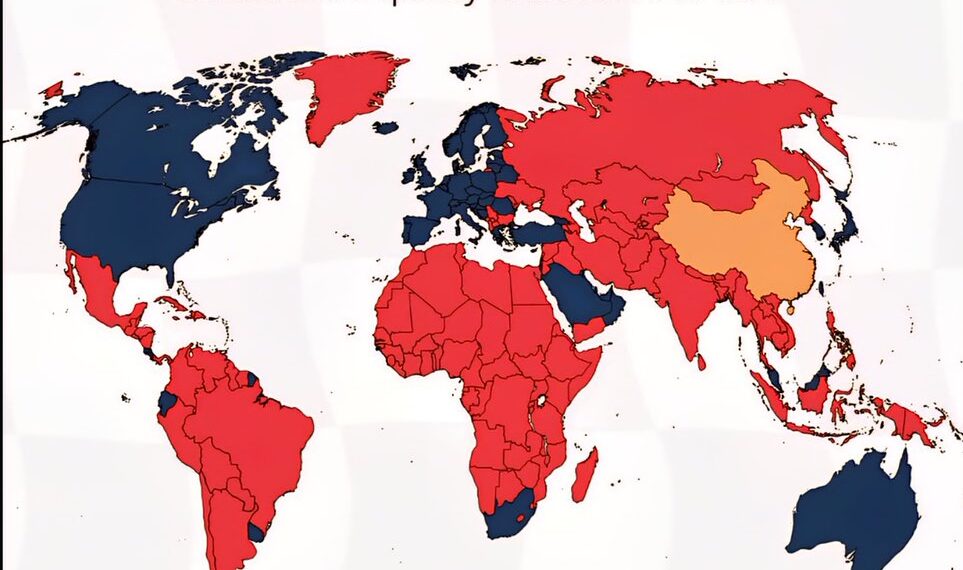
By 2025, many countries have seen a shift in economic stability, which directly impacts residents’ quality of life. While China continues to experience rapid economic growth, several Western nations have maintained high-income levels thanks to innovation sectors like technology and finance. Countries such as the United States, Canada, and Germany now enjoy a high average income per capita, leading to better access to healthcare, education, and leisure activities. Conversely, some developing nations still struggle with income inequality, which hampers social mobility and access to essential services, underscoring the importance of economic policies that promote inclusivity.
2. Healthcare Systems and Life Expectancy
Healthcare accessibility remains a pivotal factor in global quality of life assessments. In 2025, nations including the Scandinavian countries and Japan have advanced healthcare systems that contribute to longer average life expectancies. Meanwhile, China continues to make significant investments in its healthcare infrastructure, narrowing gaps in rural versus urban health outcomes. However, disparities persist, especially in low-income regions, highlighting the ongoing challenge of ensuring comprehensive healthcare access for all populations.
3. Educational Opportunities and Literacy Rates
Educational attainment continues to influence quality of life, with countries boasting high literacy rates and robust education systems seeing positive impacts on societal well-being. The United States, South Korea, and Australia lead in providing accessible, quality education, fostering innovation and economic growth. China, leveraging its massive investment in education, has made strides in expanding its high-quality universities and vocational training programs. Yet, gaps remain in rural and underserved communities, emphasizing the need for educational reforms that prioritize equity.
4. Environmental Sustainability and Quality of Air and Water
Environmental health significantly affects daily life, especially as climate change accelerates. In 2025, Scandinavian nations, Canada, and New Zealand have successfully implemented policies ensuring cleaner air, water, and sustainable living environments. China has made notable progress in reducing pollution, especially in major cities, thanks to strict regulations on industrial emissions and green initiatives. However, many countries continue grappling with pollution and resource management challenges, highlighting the importance of global cooperation on climate issues.
5. Technological Advancement and Digital Connectivity
Access to cutting-edge technology shapes modern living standards. Western countries with advanced broadband infrastructure—like the United States, South Korea, and Australia—offer residents unparalleled digital connectivity, facilitating remote work, education, and healthcare. China’s rapid advancements in 5G and AI technologies position it as a competitive leader in digital innovation. Nonetheless, digital divides still exist within nations, emphasizing the need for policies that bridge the gap between urban and rural digital access.
6. Food Security and Nutrition
Ensuring consistent access to nutritious food remains vital for quality of life. Countries like Australia, Japan, and Germany maintain high standards for food safety and nutrition, thanks to rigorous food regulation systems. China has significantly improved its food supply chains, reducing malnutrition and food shortages. However, climate-related disruptions threaten agricultural stability worldwide, underscoring the ongoing need for resilient food systems in the face of global environmental changes.
7. Personal Safety and Security
Perceptions of safety are integral to life quality. Countries such as Switzerland, Singapore, and Japan benefit from low crime rates and effective law enforcement, fostering secure environments for residents. While China has made progress in urban safety initiatives, rural areas sometimes face security challenges. The global trend indicates that investing in community policing and social programs contributes to overall safety and well-being.
8. Social Cohesion and Cultural Inclusivity
A society’s ability to foster social cohesion influences mental health and overall happiness. Nations promoting inclusivity, tolerance, and cultural diversity—like Canada, New Zealand, and the Netherlands—report higher levels of happiness among their populations. China’s multicultural policies and ethnic integration efforts have improved social stability, yet disparities persist in some regions. Encouraging dialogue and inclusion remains essential for building resilient, harmonious communities.
As 2025 unfolds, the landscape of global quality of life continues to evolve, shaped by economic, social, and environmental factors. While some countries like China are rapidly closing gaps in health, technology, and infrastructure, others maintain longstanding advantages through innovation and social policies. Moving forward, the key to enhancing quality of life worldwide lies in balanced growth, sustainable practices, and inclusive policies that ensure no one is left behind.