Select Language:
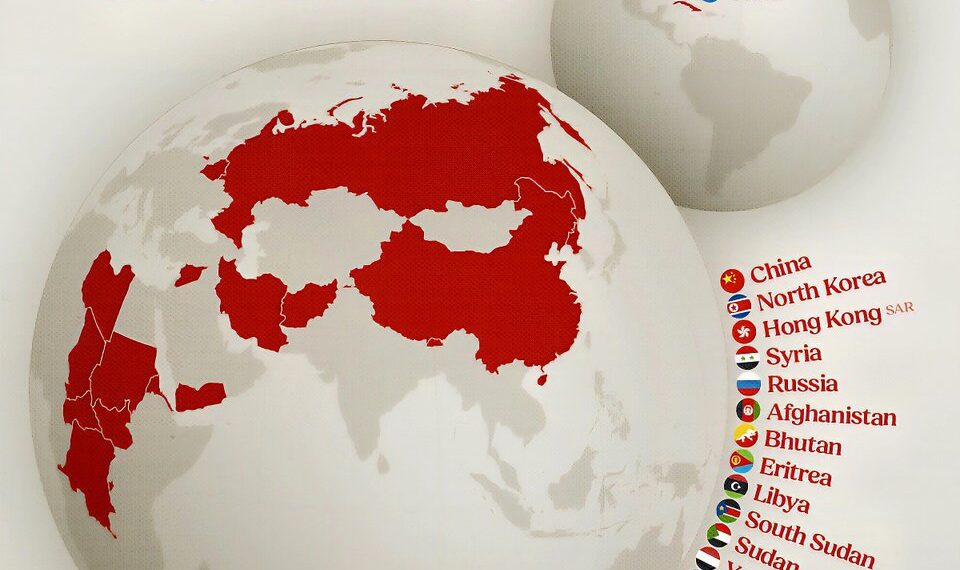
Countries and Regions Where ChatGPT Is Still Banned in 2025

As AI technology continues to evolve, different countries maintain varying policies regarding its use. While some nations embrace ChatGPT and similar AI tools for their potential benefits, several others have imposed restrictions or outright bans. Here is a comprehensive list of regions and countries where ChatGPT remains prohibited as of 2025.
1. China: A Stringent Regulatory Environment
China remains one of the most prominent countries with strict controls over AI technology. The government enforces rigorous standards and requires foreign AI companies to partner with local firms, often leading to bans on unapproved tools. Despite efforts to develop indigenous AI, ChatGPT’s accessible version is currently blocked, citing concerns over data security, misinformation, and censorship. The Chinese government emphasizes the need for AI that aligns with its social ideology, which directly influences restrictions on platforms like ChatGPT.
2. North Korea: Highly Restricted Internet and AI Usage
North Korea continues to maintain one of the world’s most restricted online environments. All internet access is heavily monitored, limited to a government intranet called Kwangmyong, and ordinary citizens are barred from accessing international sites, including ChatGPT. The country’s internal policies prevent AI tools that could disseminate outside information or promote independent thought, ensuring total control over digital content.
3. Iran: Limited Internet Freedom and AI Regulations
Iran’s government regulates online activity to maintain control over information and limit external influences. While the country invests in developing its own AI technologies, access to international AI platforms like ChatGPT remains blocked. Authorities cite concerns over security, misinformation, and the potential influence on political stability as primary reasons for maintaining this ban.
4. Cuba: Restricted Internet Access Stymies AI Adoption
In Cuba, internet restrictions and slow connectivity hinder widespread adoption of advanced AI tools. The government tightly controls online content and access to foreign platforms, including ChatGPT. The limited infrastructure and regulatory barriers mean that AI-based language models are effectively inaccessible to most of the population, emphasizing the country’s cautious approach toward unlimited digital information.
5. Syria: Security Concerns and Limited Connectivity
Syria’s ongoing conflict and political instability have resulted in restricted internet services and tight control over digital tools. Despite the global proliferation of AI, ChatGPT remains blocked within the country. Authorities cite security concerns, potential misuse, and the unstable infrastructure as reasons for limiting access to such language models, which could challenge state narratives or spread unintended content.
6. Turkmenistan: Tight State Control Over Technology
Turkmenistan is widely regarded as one of the most closed-off countries regarding internet freedom. The government maintains strict oversight of all online content, with access to international platforms like ChatGPT being either heavily filtered or outright banned. The country’s leadership perceives AI as a potential threat to their control and stability, opting for cautious regulation instead.
7. Saudi Arabia: Partial Bans Amidst Regulatory Uncertainty
While Saudi Arabia has shown interest in adopting AI for its Smart City projects and government services, access to ChatGPT is limited for the general public. The country’s regulatory framework is still evolving, and concerns over data privacy, content moderation, and national security have led to restrictions. Certain sectors like education and government may have limited access, but widespread public utilization remains hindered.
8. Russia: Focused on Domestic AI Development Before Foreign Platforms
Russia has prioritized developing its own AI technologies amidst geopolitical tensions, resulting in limited access to foreign models like ChatGPT. The government restricts or bans access to unapproved platforms, citing potential security risks and the desire for technological sovereignty. While some citizens employ VPNs or alternative methods to access blocked content, official restrictions remain in place.
9. Libya: Political Instability and Internet Limitations
Libya’s ongoing political unrest and limited internet infrastructure severely restrict access to many online services, including ChatGPT. The country’s digital environment remains unstable, and government censorship often targets foreign platforms. Consequently, AI tools like ChatGPT are largely inaccessible to the general population.
10. Vietnam: Tightened Regulations on Foreign Digital Platforms
Vietnam has recently ramped up regulations on foreign digital services, citing concerns over content and national security. While some local AI initiatives are underway, access to ChatGPT is officially restricted, with authorities blocking the platform due to content moderation challenges and data sovereignty issues.
Conclusion
The landscape of AI regulation continues to shift globally, with many nations opting for strict control to safeguard sovereignty, cultural norms, or national security. As technology advances, expect these bans to evolve—either relaxing or tightening based on local policies and geopolitics. For now, users in these regions must navigate restrictions or explore alternative local services compliant with their respective governments’ standards.
Note: The status of these bans may change rapidly due to geopolitical developments and technological advancements. Always check local regulations and updates from official sources.