Select Language:
The Most Consumed Type of Meat by Country in 2025
Beef Dominates in Argentina and the United States
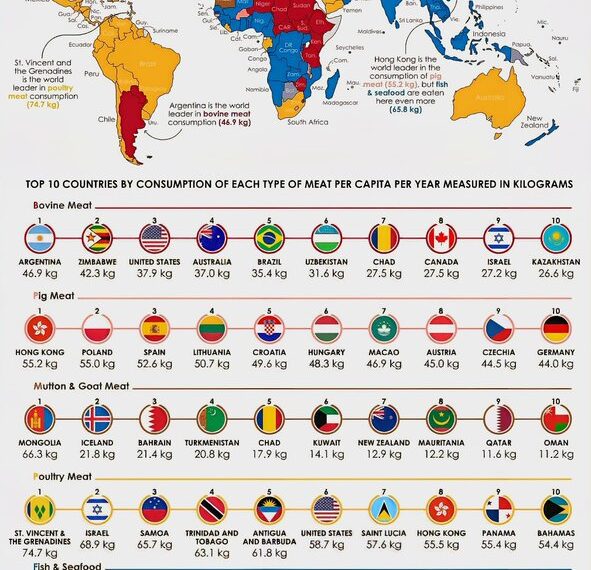
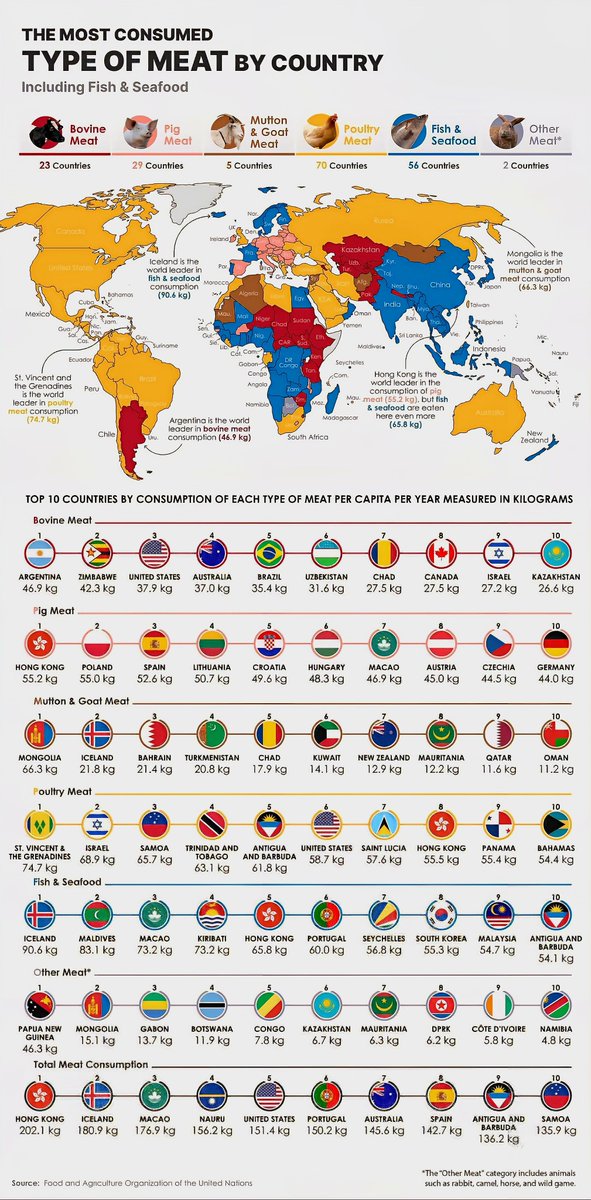
When it comes to meat consumption, beef remains the star in countries like Argentina and the United States. Argentinian cuisine is famous worldwide for its succulent grilled steaks and barbecue-style dishes, making beef the most popular meat. In the U.S., beef continues to lead due to its integral role in traditional dishes such as burgers, steaks, and roasts. The high demand influences local agriculture, with extensive cattle ranching dominating rural landscapes. Despite growing concerns about sustainability, beef consumption persists, driven by cultural preferences and culinary traditions.
Chicken Takes the Lead in Brazil and China
In Brazil, chicken surpasses other meats as the favorite choice, thanks to its affordability, versatility, and widespread availability. Dishes like “Frango Assado” (roast chicken) and “Galinha Caipira” (free-range chicken) are staples across Brazilian households. Meanwhile, China, the world’s most populous country, confirms chicken as its most-consumed meat. Its affordability, ease of cooking, and cultural significance in dishes like Kung Pao Chicken and Peking Duck bolster its popularity. China’s vast poultry industry ensures a steady supply to meet the high demand.
Pork Is the Favorite in Germany and the Philippines
Germany maintains a deep-rooted appreciation for pork, particularly sausages, schnitzels, and roasted pork dishes, making it the top choice in the country. Pork is not only a staple for traditional festivals but also features heavily in everyday cuisine. Similarly, the Philippines has a strong preference for pork, evidenced by popular dishes such as lechon, adobo, and sinigang. Its affordability and cultural significance contribute to its dominant role in Filipino diets.
Lamb and Mutton Flourish in Middle Eastern and Mediterranean Countries
Lamb and mutton hold prominent statuses in Middle Eastern countries like Lebanon, Jordan, and Iraq. Popular dishes such as kebabs, shawarma, and stews rely heavily on lamb, celebrated for its tender texture and rich flavor. Mediterranean nations like Greece and Turkey also rank lamb highly, used extensively in roasts and grilled specialties. These meats are not only part of everyday meals but also pivotal during religious celebrations and festivals.
Fish and Seafood Lead in Coastal Nations
For countries with extensive coastlines like Japan, Norway, and Spain, fish and seafood are central to their diets. Japan’s tradition of sushi, sashimi, and grilled fish underscores its reliance on fresh seafood. Norway’s reputation as a major fish exporter includes cod, salmon, and herring, consumed domestically in hearty stews and smoked preparations. Spain’s coastal cuisine features seafood tapas, paellas, and grilled fish, reflecting its maritime heritage.
Vegetarian and Plant-Based Alternatives on the Rise Globally
While meat remains dominant, 2025 marks a noticeable shift toward plant-based diets worldwide. Countries such as Sweden, Canada, and Australia report rising consumption of vegetarian and vegan options, driven by environmental concerns, health awareness, and animal welfare considerations. Innovative plant-based meats like burgers, sausages, and nuggets are increasingly found in supermarkets and restaurants, challenging traditional meat consumption patterns.
Adoption of Sustainable Meat-Eating Practices
Many countries are now adopting sustainable practices amid growing environmental concerns. Efforts include promoting organic farming, reducing meat consumption, and supporting local producers. The rise of lab-grown meats and alternative proteins signals a transformative shift in how nations approach their dietary habits, balancing tradition with responsibility toward the planet.
This year’s global meat consumption trends reflect a complex interplay of tradition, economics, cultural preferences, and evolving societal values. While beef, chicken, and pork retain their status as top choices in various regions, the increasing popularity of plant-based diets hints at a more sustainable and diversified future for global food consumption.