Select Language:

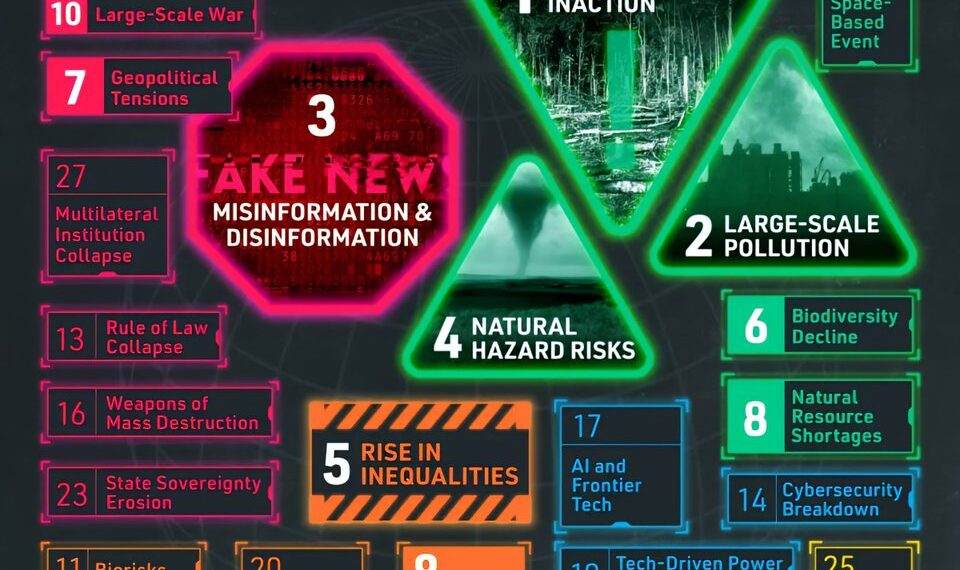
In an ever-evolving world, the threats that loom over our global community are becoming increasingly complex and interconnected. A recent survey conducted by the United Nations Global Risk Report 2024 reveals crucial insights from over 1,100 stakeholders across 136 countries, including representatives from government, industry, civil society, and academia. Here are the most pressing global risks identified in the report.
## Climate Change Inaction
Climate change continues to be one of the most significant threats to humanity. The failure of governments and corporations to take decisive action exacerbates this crisis, which affects everything from natural disasters to food security.
## Large-Scale Pollution
Pollution on a grand scale is not just an environmental concern; it poses serious health risks to global populations. Toxic waste, plastic pollution, and air quality issues contribute to widespread health problems and negatively impact ecosystems.
## Misinformation & Disinformation
The proliferation of false information, especially through social media, undermines trust in institutions and science. This misinformation can lead to polarized societies and affect global governance, making it hard to reach consensus on crucial issues.
## Natural Hazard Risks
Natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods pose significant risks to lives and infrastructure. Climate change is increasing the frequency and intensity of these events, leading to devastating humanitarian crises.
## Rise in Inequalities
Economic disparities are widening both within and between countries. This increase in inequality fuels social unrest and hinders sustainable development, as marginalized communities lack access to resources and opportunities.
## Biodiversity Decline
The rapid loss of biodiversity threatens food systems and ecological stability. As species become extinct at alarming rates, the interconnectedness of ecosystems is jeopardized, which could have catastrophic consequences.
## Geopolitical Tensions
Escalating tensions between nations can lead to conflict and instability. Issues such as territorial disputes, trade wars, and resource competition threaten international cooperation and peace.
## Natural Resource Shortages
Scarcity of essential resources like fresh water and arable land is a growing concern. These shortages can spark conflicts, migration, and heightened competition among nations.
## Mass Movement of People
Displacement due to conflict, climate change, and economic hardship is leading to unprecedented levels of migration. This movement of people creates challenges for both the displaced and the countries they move to.
## Large-Scale War
The potential for a large-scale war remains a constant threat. Geopolitical tensions, combined with weapons proliferation, could lead to devastating consequences for global security.
## Biorisks
Biological risks, including the misuse of biotechnology and synthetic biology, pose a grave threat to public health and security. Mishaps or intentional misuse could have far-reaching effects.
## New Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the vulnerability of global health systems. Preparedness for future pandemics is crucial to mitigate their impact on lives and economies.
## Rule of Law Collapse
The erosion of the rule of law can lead to increased crime, corruption, and instability. Societies that lack a strong legal framework are at risk of descending into chaos.
## Cybersecurity Breakdown
As our reliance on technology increases, so does the threat of cyberattacks. A significant cybersecurity breach could compromise critical infrastructure and personal data, with disastrous implications.
## Global Financial Crisis
Economic stability is fragile, and the potential for a global financial crisis looms large. Factors such as rising debt levels and economic fragmentation can precipitate widespread financial turmoil.
## Weapons of Mass Destruction
The existence and potential use of nuclear, biological, and chemical weapons continue to be a significant risk to global security. Diplomatic efforts are vital to mitigate these threats.
## AI and Frontier Tech
Advancements in artificial intelligence and other emerging technologies raise ethical and security concerns. The unchecked proliferation of these technologies could lead to unintended consequences.
## Proliferation of Non-State Actors
The rise of non-state actors, including terrorist organizations and organized crime, complicates governance and can destabilize regions, challenging traditional forms of security.
## Tech-Driven Power Concentration
The concentration of power in tech giants poses a threat to democracy and social equity. The influence of a few corporations can overshadow democratic processes and citizen rights.
## Social Cohesion Collapse
Deteriorating social cohesion threatens community stability. Factors such as discrimination, inequality, and political polarization contribute to social fragmentation.
## Widespread Debt Crisis
High levels of public and private debt can lead to economic instability. Countries struggling with debt may face harsh austerity measures, affecting vulnerable populations the most.
## Economic Fragmentation
Shifts towards isolationism and protectionism can fracture the global economy, leading to trade wars and reduced collaboration among countries.
## State Sovereignty Erosion
Globalization pressures are leading to a decline in state sovereignty. International agreements and organizations can challenge national policies and governance structures.
## Global Economic Stagnation
Persistent economic stagnation can lead to job losses, reduced public services, and increased social unrest. Maintaining economic growth is crucial for global stability.
## Supply Chain Collapse
The interconnectedness of global supply chains makes them vulnerable to disruptions. Natural disasters, pandemics, and geopolitical tensions can lead to catastrophic failures.
## Geoengineering Disasters
Attempts to manipulate the climate through geoengineering pose unknown risks. Unintended consequences could exacerbate existing environmental problems.
## Multilateral Institution Collapse
The failure of international organizations to address global issues undermines collective action. A breakdown in multilateralism could lead to a less cooperative global community.
## Space-Based Event
As space activities increase, so does the risk of catastrophic events, such as collisions or space debris. Established protocols and regulations are critical to mitigate these risks.
As these risks interconnect, proactive measures are essential to safeguard our future. The survey results highlight the urgency for global cooperation and action to mitigate these complex challenges.