Select Language:
Understanding Worldwide Income Disparities in 2025

1. The Wealthiest Countries Dominating Top Ranks
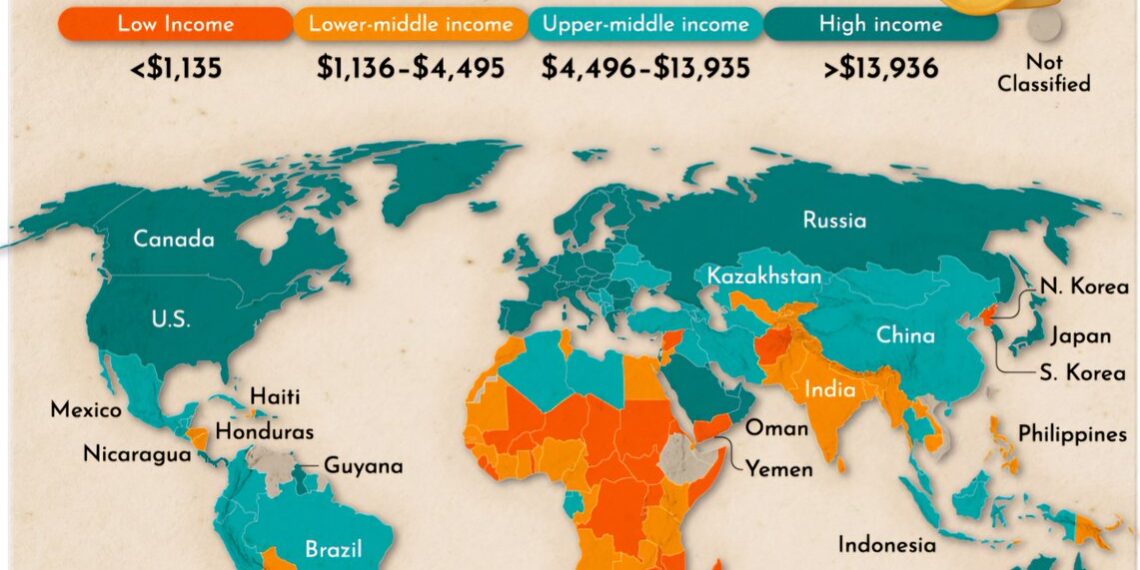
In 2025, the United States continues to lead the world with the highest average income per capita, maintaining its position as a global economic powerhouse. Countries like Luxembourg, Switzerland, and Singapore also rank high, showcasing impressive wealth distribution within their borders. These nations benefit from advanced financial systems, innovation hubs, and robust industries ranging from tech to finance, which contribute significantly to their high income levels.
2. Emerging Economies Closing the Gap
Climbing steadily in income rankings are emerging economies such as China, India, and Brazil. Over recent years, they have experienced rapid economic growth, lifting millions out of poverty. China’s urban centers now boast median incomes comparable to some Western countries, driven by technological advancements and infrastructure development. India’s expanding middle class is reflected in rising incomes, although disparities still persist. Brazil’s economy benefits from natural resources and manufacturing sectors, boosting income levels for middle-class families.
3. Income Disparities within Countries
Despite national averages, income inequality remains a pressing issue globally. In many nations, wealth is concentrated among a small percentage of high-income earners, leaving large segments of populations with limited economic security. The United States, for instance, exhibits notable income disparity, with affluent regions like the West Coast significantly outpacing rural areas. Similarly, countries like South Africa and Mexico face stark contrasts between the wealthy and the impoverished, emphasizing the need for equitable economic policies.
4. The Impact of Digital Transformation on Income
Digital technology continues to reshape economic landscapes worldwide. Countries with high digital adoption, such as South Korea, Israel, and Estonia, are seeing an increase in average incomes due to tech-driven industries and online commerce. Conversely, nations with limited access to digital infrastructure, like some African and Southeast Asian countries, lag in income growth. Bridging this digital divide is essential for ensuring widespread economic development in 2025.
5. The Role of Education and Innovation
Higher education levels and innovation ecosystems remain critical factors in elevating national income levels. Countries investing heavily in educational infrastructure, research, and development tend to see their citizens earning higher wages. Canada, Australia, and several Scandinavian countries exemplify this trend, combining a skilled workforce with technological innovation. This alignment fuels productivity and sustains high income levels across various sectors.
6. International Income Inequality Challenges
Income disparities between countries have broader implications for global stability and development. While some nations experience rising prosperity, others struggle with stagnation or recession. International organizations emphasize the importance of policies promoting fair trade, climate resilience, and poverty alleviation to address these imbalances. The ongoing efforts aim to foster economic growth that is inclusive and sustainable for all nations.
7. Future Outlook: The Race Toward Wealth Equality
As we look toward the future, global efforts to reduce income inequality hinge on technological access, educational opportunities, and inclusive economic policies. Countries investing in these areas will likely see further increases in income levels, narrowing the existing gaps. Meanwhile, economic shocks, geopolitical tensions, or environmental crises could influence these trajectories, making cooperation essential for sustained global prosperity.
In summary, 2025 presents a complex yet promising landscape of global income levels, marked by high achievers, rising economies, and persistent disparities. Addressing inequality remains paramount to ensuring that economic growth benefits the broadest possible population, fostering a more equitable world economy for future generations.