Select Language:
Exploring the Driving Forces Behind Cultural Origins

1. Historical Events Shape National Identity
One of the most significant factors that shape a culture is its historical past. Major events such as wars, revolutions, or colonial eras leave a profound impact on the collective consciousness of a nation. For example, countries that experienced liberation movements often emphasize freedom and independence in their cultural narratives. This history influences everything from national holidays to the stories passed down through generations, creating a collective identity rooted in resilience and sovereignty.
2. Geographic Location Influences Cultural Practices
Your country’s geography plays a vital role in setting the tone for its culture. Coastal nations tend to develop maritime traditions with a focus on fishing and seafaring, while landlocked countries may prioritize agriculture or land-based commerce. Climate conditions also impact cultural elements like clothing, cuisine, and social activities. For instance, colder regions might emphasize indoors activities and hearty foods, shaping social norms and cultural expressions over time.
3. Religion and Spiritual Beliefs Guide Cultural Norms
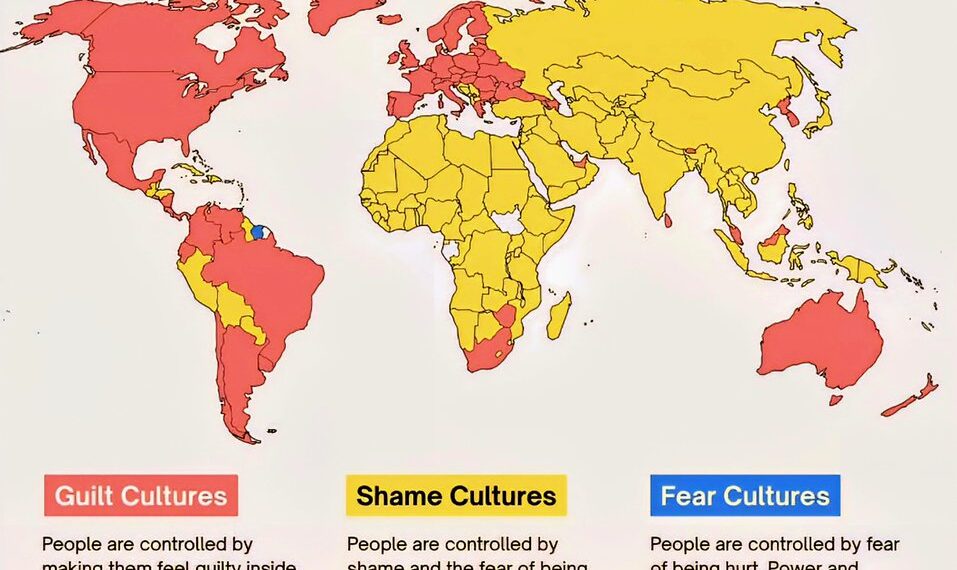
Religion remains a central pillar in many cultures worldwide, influencing festivals, moral codes, and daily routines. In 2025, the diverse tapestry of religious beliefs continues to shape societal values and laws. From Christian celebrations in the United States to Buddhist festivals in Southeast Asia, spiritual beliefs inform cultural practices profoundly. These traditions often foster community cohesion and serve as a foundation for shared identities.
4. Language and Communication Styles Drive Cultural Expression
Language is more than just a means of communication; it embodies tradition, humor, and social etiquette. Different cultures develop unique communication styles, whether it’s the indirect politeness of East Asian societies or the straightforwardness common in Western cultures. These communication preferences influence social interactions, business practices, and even negotiations, shaping how societies function and evolve.
5. Economic Factors Promote Cultural Innovation
Economic stability and development significantly influence cultural evolution. Wealthier nations tend to invest more in arts, education, and cultural preservation, promoting innovation and diversity. Conversely, regions facing economic hardships might see their cultural expressions centered around survival, resilience, and community bonding. In 2025, the digital economy further accelerates cultural exchange, allowing countries to share arts and traditions globally at unprecedented speeds.
6. Social Structures Define Cultural Hierarchies
The traditional organization of societies—such as class systems, gender roles, and family units—determine many cultural norms. For example, some cultures emphasize collective familial ties and respect for elders, while others promote individualism and personal achievement. These social structures influence laws, education, and everyday interactions, molding the cultural fabric of nations and communities.
7. Artistic and Literary Heritage Spark Cultural Pride
Arts, music, dance, and literature serve as mirrors reflecting a country’s history and values. Celebrating artistic heritage cultivates pride and reinforces cultural continuity. Countries invest in preserving historical monuments, supporting traditional crafts, and promoting contemporary arts that speak to their unique identity. In recent years, digital media has also expanded access to cultural expressions, creating new avenues for cultural preservation and innovation.
8. Global Connections and Cultural Exchange
In 2025, increased globalization continues to influence and reshape cultural landscapes. Countries participate in cultural exchanges through technology, travel, and international collaborations, blending traditions and creating hybrid cultures. This interconnectedness fosters understanding but also challenges traditional cultural boundaries, prompting communities to adapt and redefine their identities in a global context.
Understanding what motivates cultures helps us appreciate the diversity and richness of human societies. Each nation’s unique combination of history, geography, religion, language, economy, social norms, arts, and global interactions crafts a vibrant tapestry that reflects its collective journey through time.