Select Language:
Top Countries Holding the Most Nuclear Weapons in 2025
The global landscape of nuclear armament remains a critical aspect of international security. As of 2025, certain nations hold significant arsenals, shaping geopolitical strategies and diplomatic relations. The following list highlights the countries with the largest nuclear stockpiles, their current capabilities, and the implications for global stability.
1. United States: The Largest Nuclear Arsenal
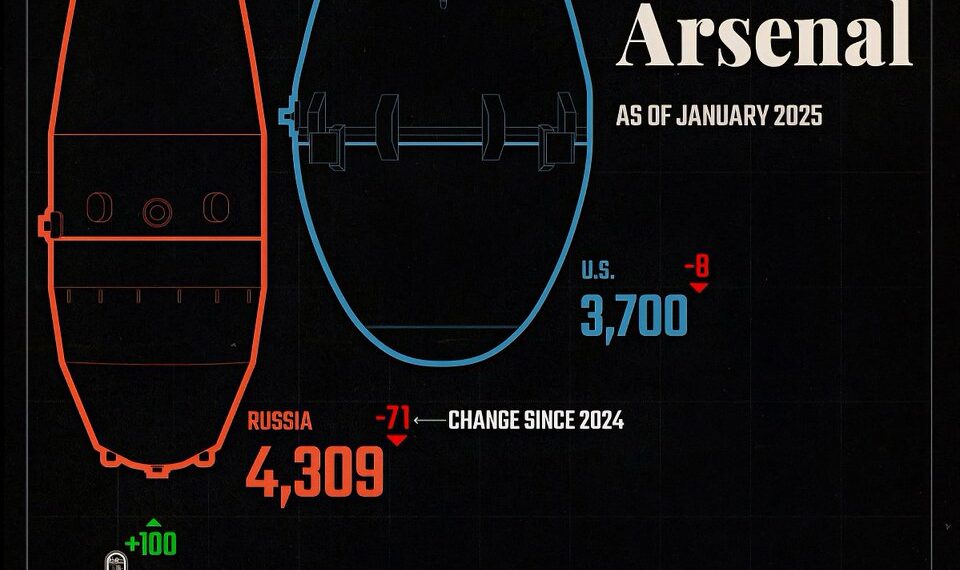
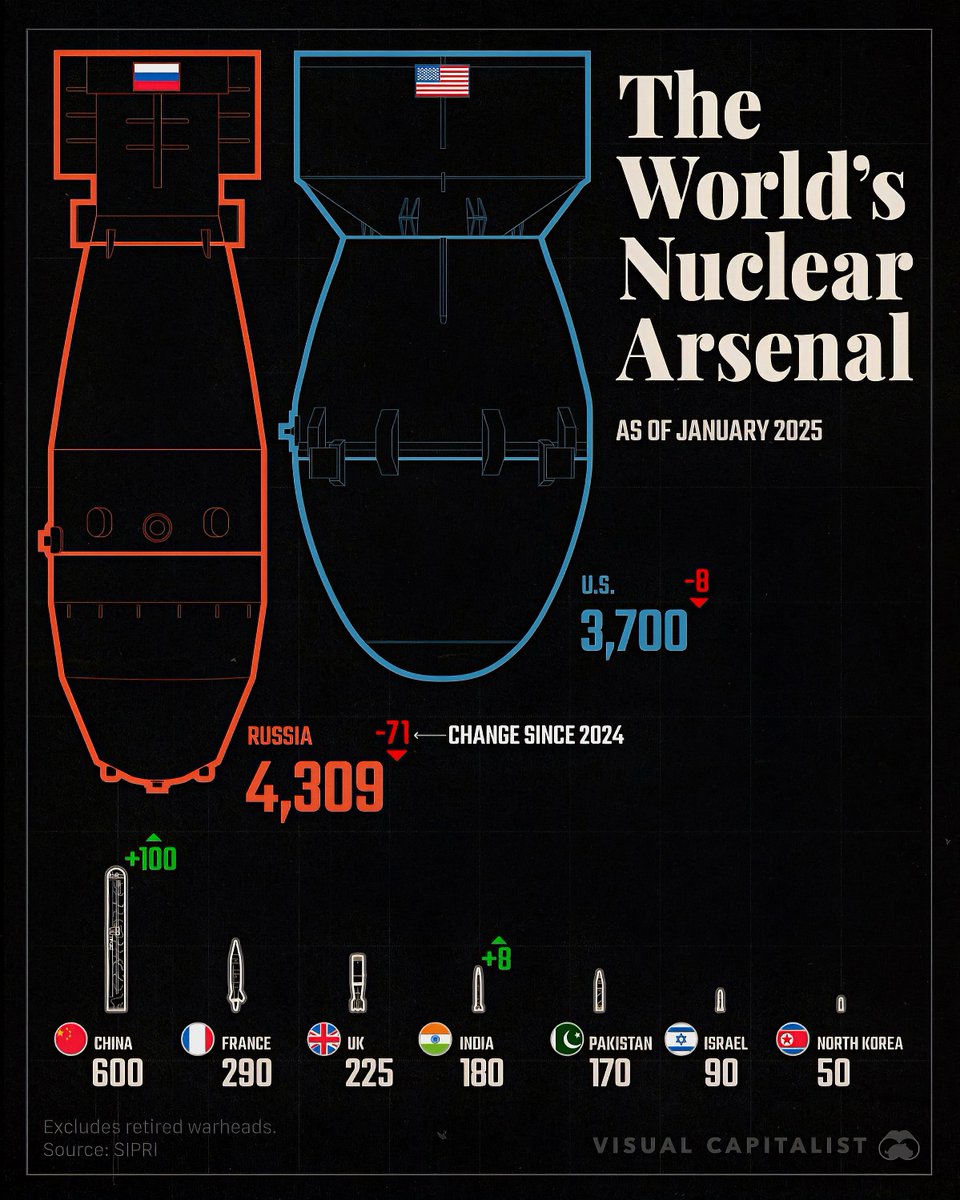
The United States continues to lead the world in nuclear weapon stockpiles, maintaining approximately 5,500 active and inactive warheads. The nation’s strategic deterrent remains a cornerstone of its defense policy, with a focus on modernization programs that aim to upgrade existing warheads and delivery systems. The U.S. also maintains a diversified triad—including land-based ICBMs, submarine-launched ballistic missiles, and strategic bombers—that ensures a second-strike capability.
2. Russia: Maintaining Its Nuclear Supremacy
Russia holds the second-largest arsenal globally, with around 4,500 nuclear warheads. Despite arms reduction treaties, Moscow has modernized its nuclear forces, emphasizing new delivery systems such as advanced nuclear submarines and missile systems. The country views its nuclear capabilities as a vital element of its national defense and regional influence, especially amid ongoing international tensions.
3. China: Rapid Expansion of Its Nuclear Capabilities
China has rapidly expanded its nuclear stockpile over the past decade, now possessing approximately 350 warheads. Its modernization and expansion efforts include deploying new missile systems and developing submarine-launched ballistic missiles. Beijing’s strategic goal appears to be achieving a credible and survivable deterrent that can challenge its rivals and safeguard its growing global interests.
4. India: Strengthening Its Strategic Deterrent
India’s nuclear arsenal has grown steadily, with an estimated 70 warheads in its inventory. The country emphasizes nuclear deterrence primarily against Pakistan and China. India has developed a triad of delivery systems—ballistic missiles, submarine-launched missiles, and aircraft—to ensure stability and security in its region, especially amid persistent border disputes.
5. Pakistan: Focused on Regional Security
Pakistan holds roughly 50 nuclear warheads, mainly aimed at countering India’s superior conventional and nuclear forces. Its nuclear program prioritizes strategic stability and deterrence in a volatile region. The country continues to develop delivery systems such as ballistic missiles and is believed to be working on tactical nuclear weapons to address evolving threats.
6. North Korea: A Nuclear Force at the Brink
North Korea’s nuclear program remains a significant concern for regional and global security. Its estimated stockpile includes around 20-40 warheads, with ongoing advancements in missile technology. Pyongyang’s focus is on developing a credible deterrent capable of threatening the United States and its allies, leading to ongoing diplomatic challenges and limited negotiations.
7. France and the United Kingdom: Maintaining Modern Nuclear Forces
Both France and the United Kingdom possess approximately 300 nuclear warheads each. While their arsenals are smaller compared to the U.S. and Russia, they continue to maintain and modernize their nuclear forces, emphasizing technological advancements in delivery systems and safety measures. Their nuclear policies focus on maintaining a credible deterrent within NATO and European defense frameworks.
8. Other Notable Nations and Future Trends
While only a handful of countries possess declared nuclear arsenals, ongoing covert programs and technological advancements could alter the global balance. Countries like Israel, which maintains a policy of ambiguity, are believed to have a significant nuclear stockpile. Further, nations such as Iran are under international scrutiny for potential nuclear capabilities, although their arsenals remain unconfirmed.
Conclusion: A Delicate Balance
The nuclear landscape in 2025 underscores the importance of international treaties and diplomatic efforts aimed at stability and disarmament. While major powers continue modernization efforts, the risk of proliferation and regional conflicts persists. Continued dialogue and verification are essential to ensure that nuclear weapons serve as deterrents rather than catalysts for conflict.
Note: The figures mentioned are estimates based on the latest available data and may evolve with ongoing international security developments.