Select Language:
India’s Population Surpasses 1.5 Billion, Solidifying Its Global Dominance
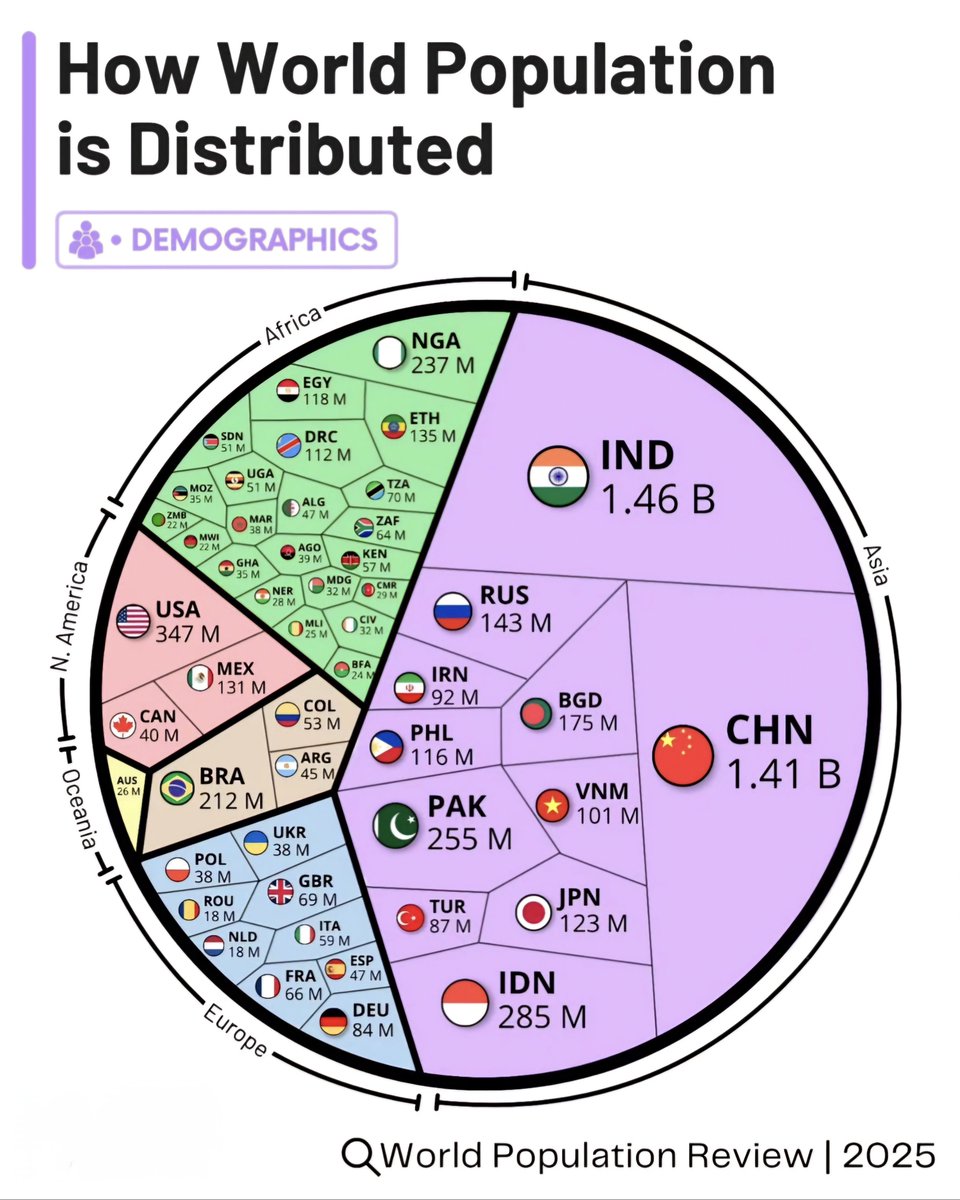
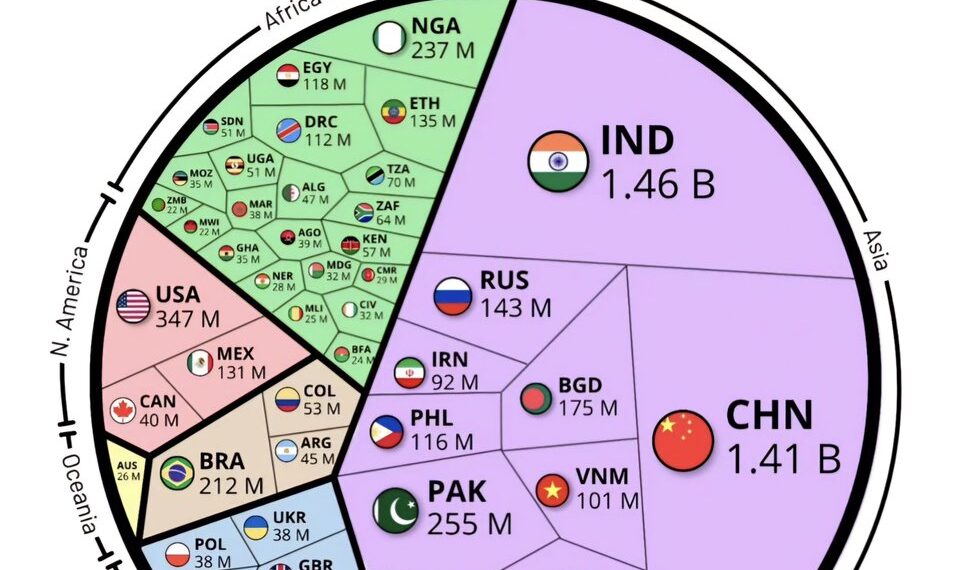
India continues its rapid demographic expansion, and in 2025, it officially exceeds 1.5 billion residents, making it the most populous country in the world. This milestone has major implications for global economics, environmental sustainability, and geopolitical influence. Let’s explore the key highlights of the world’s population dynamics in 2025.
1. India Becomes the Most Populous Nation
India’s population growth has accelerated over the past decade, fueled by higher birth rates and decreasing mortality rates. Official estimates from the United Nations indicate that India has now crossed the 1.5 billion mark, overtaking China, which has experienced a significant decline in its population growth due to demographic aging and lower fertility rates. The rapid expansion underscores India’s youthful demographic profile, with a median age of approximately 28 years, compared to China’s median age of 39.
2. China’s Population Continues to Shrink
China’s population has been in decline since 2021, and current statistics suggest a reduction of about 4 million people in 2025. The country’s aging population and the lingering effects of its one-child policy have contributed to this shrinkage. This demographic change presents challenges for China’s economic growth, pension system sustainability, and workforce availability. Urban centers are experiencing an aging boom, prompting policymakers to focus on immigration liberalization and family support policies to stabilize numbers.
3. Nigeria Becomes Africa’s Most Populous Country
Nigeria has experienced rapid population growth and is projected to reach approximately 280 million residents by 2025, cementing its status as Africa’s most populous nation. Its high fertility rate, around 5.4 children per woman, contributes to this growth spurt. Nigeria’s burgeoning youth population signals both immense economic potential and the need for substantial investments in education, healthcare, and infrastructure to manage urbanization and employment demands.
4. The United States Maintains Its Global Leadership in Population
The United States remains the third most populous country, with an estimated population of about 340 million. While growth has slowed compared to previous decades, continued immigration and relatively higher birth rates sustain its demographic momentum. The U.S. remains a melting pot of cultures, with diversity serving as a key economic and social strength.
5. India’s Urbanization Accelerates
With its growing population, India is also witnessing rapid urban development. Cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bangalore are experiencing unprecedented growth, leading to expanded urban infrastructure, greater economic opportunities, and increased environmental pressure. Experts warn that sustainable urban planning remains critical as India balances population growth with ecological conservation.
6. Effect of Population Shifts on Global Resources
As populations surge in countries like India and Nigeria, the strain on global resources intensifies. Increased demand for water, energy, and food is already causing environmental concerns, including deforestation and climate change. The global community faces urgent challenges to develop sustainable solutions to support expanding populations without degrading the planet.
7. Demographic Trends Indicate Future Challenges
A continuing trend across nations is aging populations in developed countries and youthful demographics in developing nations. Countries like Japan and Germany are experiencing stagnating or declining populations, impacting their economies and social welfare systems. Conversely, rapid population growth in emerging economies emphasizes the need for robust education, healthcare, and employment programs to ensure stability.
8. Population Policies Adapted to New Realities
Governments worldwide are revising policies based on current demographic data. For instance, India has implemented initiatives to promote family planning, while Nigeria is investing heavily in health and education services to manage population growth. Such efforts aim to balance population expansion with sustainable development goals. China’s recent relaxation of its birth restrictions exemplifies adaptive policymaking to counteract its declining population.
9. The Role of Migration in Population Growth
Migration remains a significant factor influencing population numbers, especially in countries with aging populations. The United States continues to attract migrants due to its economic opportunities and political stability. Meanwhile, regional migration within Africa and Asia contributes to demographic shifts, often leading to urban overcrowding but also boosting labor markets.
10. Future Outlook: Navigating the Demographic Wave
Projections suggest global population will reach approximately 8.1 billion by 2030. The demographic shifts observed in 2025 will impact world economies, environmental sustainability, and social systems for decades to come. Policymakers, scientists, and international organizations must collaborate to address challenges posed by these trends — from resource management to healthcare provision — to ensure a balanced and sustainable future.
As nations adapt to their evolving demographics, the year 2025 marks a pivotal point in global population history. The surge in countries like India and Nigeria signals both opportunities and responsibilities for the international community to foster sustainable growth and development.