Select Language:
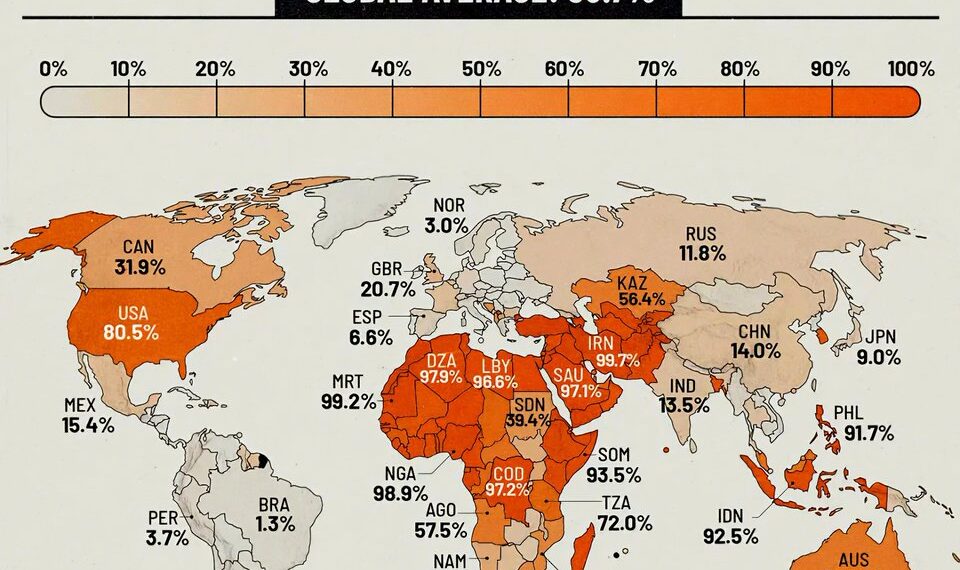
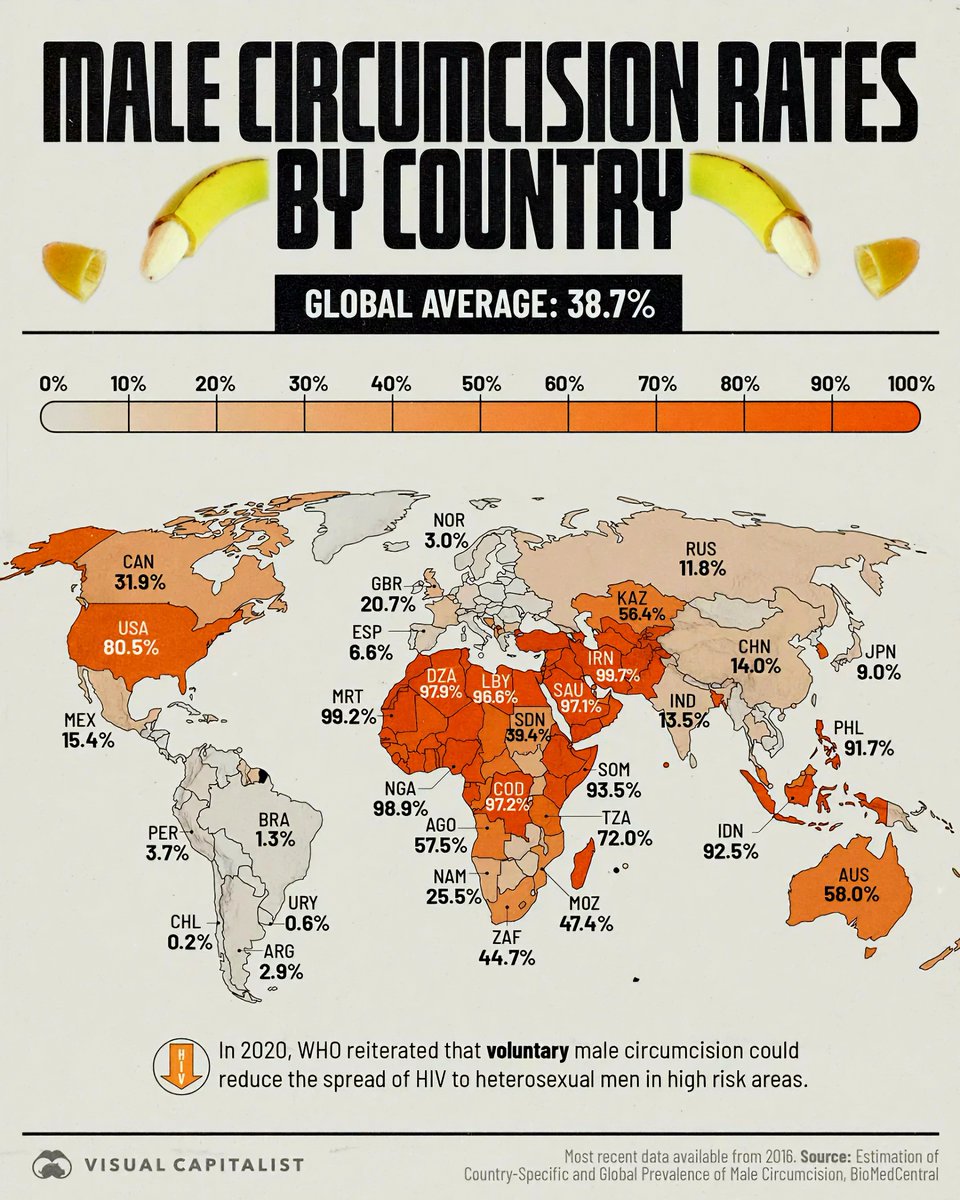
Understanding Global Male Circumcision Rates in 2025
1. United States: Steady Adoption Amid Cultural Diversity
The United States continues to lead in male circumcision rates, with approximately 70-80% of male infants undergoing the procedure. This high prevalence is largely driven by cultural, religious, and medical considerations. While some states show slightly lower percentages, overall, circumcision remains a common practice across diverse communities. Medical guidelines often cite potential health benefits, such as a lower risk of urinary tract infections and certain sexually transmitted infections, as reasons for continuing the practice.
2. Middle Eastern Countries: A Cultural and Religious staple
In countries like Egypt, Saudi Arabia, and Iran, circumcision rates hover above 95%. For many, it is an integral part of religious rites, especially within Islamic communities. The custom is often performed shortly after birth, with strong societal norms reinforcing its prevalence. These countries also have widespread community acceptance, making circumcision almost universal among young males.
3. Sub-Saharan Africa: Variations Influenced by Region and Tradition
Male circumcision rates in Sub-Saharan Africa are heterogeneous, influenced by religious, cultural, and health initiatives. Countries such as South Africa and Kenya show rates around 70-80%, while others like Nigeria and Ethiopia have rates jumping to over 90%. Efforts by health organizations aim to promote circumcision as a means of reducing HIV transmission, leading to increased uptake, especially in areas most affected by the epidemic.
4. European Countries: A Decline in Western Nations
Most Western European nations exhibit lower circumcision rates, often below 20%. Countries like the United Kingdom, France, and Germany have experienced a decline over recent decades due to changing social attitudes, medical debates, and concerns around consent and bodily autonomy. Although the practice is less common, it persists within specific religious groups, such as Jewish and Muslim communities, maintaining a presence in the cultural landscape.
5. Australia and Canada: Moderate Practice and Cultural Diversity
In Australia and Canada, circumcision rates are estimated to be between 30-50%. These countries have diverse populations, including significant Jewish and Muslim communities for whom circumcision is customary. Medical guidelines differ, with some practitioners recommending it for health reasons while others advocate for parental choice based on individual beliefs and cultural identity.
6. Asian Countries: Cultural and Medical Divergence
In nations like South Korea, Japan, and China, circumcision rates are generally low, often below 20%. In South Korea, circumcision gained popularity during the 20th century, reaching rates of about 80%, but recent health discussions have prompted a decline. In China and Japan, the practice is less culturally embedded, and most circumcisions are performed for medical or cosmetic reasons rather than religious or traditional ones.
7. Latin America: Marginal Practice with Cultural Roots
Most Latin American countries display low circumcision rates, typically under 10%. The practice is rare, often associated with religious minorities such as Jewish and Muslim communities. The dominant cultural attitude considers circumcision unnecessary unless for medical reasons, reflecting a broader trend toward bodily autonomy and changing medical opinions.
8. Emerging Trends and Future Outlook
In 2025, efforts to promote male circumcision as part of public health initiatives continue to grow, especially in regions heavily impacted by HIV/AIDS. New studies suggest additional health benefits, leading to increased acceptance in some areas. Conversely, ongoing debates around consent and ethics challenge widespread adoption in countries where the procedure is less culturally ingrained. As healthcare policies evolve, regional differences in circumcision rates are poised to shift further in the coming years.
Note: Circumcision prevalence varies significantly across the globe, shaped by an intricate blend of religious beliefs, cultural traditions, health considerations, and personal choice. The figures presented are estimates based on recent surveys, health data, and governmental reports as of 2025.