Select Language:
Top Nations with the World’s Largest Public Debt in 2025
1. Japan: The Global Debt Champion
Japan continues to hold the record for the highest national debt, surpassing $13 trillion in 2025. The country’s relentless economic stagnation, combined with an aging population requiring extensive social services, has compelled the government to borrow heavily. Despite this, Japan maintains a relatively low debt-to-GDP ratio compared to some Western nations, thanks to its sizeable economy and domestic savings. However, the sheer scale of its debt remains a concern for long-term fiscal stability.
2. United States: Battling Huge Borrowing Levels
The United States trails closely, with federal debt reaching nearly $35 trillion in 2025. The nation’s ongoing budget deficits, exacerbated by increased defense spending, social programs, and economic stimulus measures, have driven its debt skyward. The U.S. government’s reliance on debt to fund infrastructure, healthcare, and climate initiatives has sparked debates over debt sustainability, particularly with inflationary pressures on the rise.
3. China: Rapid Growth’s Hidden Cost
China’s public debt has ballooned to over $8 trillion, reflecting its aggressive infrastructure investments and social spending. While China’s debt-to-GDP remains below that of many Western nations, concerns linger over the quality of borrowing and the risk of financial instability. The country’s government continues to support ambitious economic reforms, even as local government debt and corporate liabilities pose challenges.
4. Italy: The European Debt Dilemma
Italy’s government debt stands at approximately $3.5 trillion, constituting one of the highest ratios in Europe. Persistent economic stagnation, high youth unemployment, and political instability have hindered growth and fueled borrowing. The Italian government faces pressure to implement reforms while managing a fragile banking sector heavily exposed to sovereign debt.
5. United Kingdom: Post-Brexit Fiscal Pressures
The UK’s public debt has risen to nearly $3.2 trillion, a direct consequence of post-pandemic recovery efforts and the economic uncertainties following Brexit. Increased social spending and infrastructure projects have contributed to the debt accumulation, raising concerns about long-term fiscal health amidst economic shifts.
6. France: Balancing Growth and Debt
France’s national debt has reached around $2.8 trillion. The country’s challenge lies in balancing social welfare commitments with economic growth. Strained public finances are a constant headache for policymakers, especially as France seeks to sustain its extensive social programs without further enlarging its debt burden.
7. India: Rapid Expansion Yet Still Managing Debt
India’s public debt has ticked above $2.5 trillion. Despite a strong economic growth trajectory, government borrowing has increased to support infrastructure, health, and social schemes. India’s focus remains on maintaining growth while managing debt prudently to avoid future debt crises.
8. Brazil: Emerging Market Debt Concerns
Brazil’s government debt has surged beyond $1.1 trillion, driven by economic instability and political turmoil. The country continues to grapple with inflation and currency volatility, making debt management more critical but challenging amidst domestic and global uncertainties.
9. Canada: Growing Debt Amid Economic Shifts
Canada’s debt levels now sit around $1 trillion. The country has increased borrowing to finance social programs and infrastructure upgrades, particularly in response to climate change and pandemic recovery efforts. The rising debt raises questions about future fiscal flexibility.
10. Germany: The Largest Economy’s Debt Load
Germany, Europe’s largest economy, holds a public debt of approximately $2.2 trillion. While known for its fiscal discipline, recent spending on energy, defense, and social programs has pushed its debt higher. Policymakers aim to balance fiscal stability with economic competitiveness.
Visual Representation of Global Debt
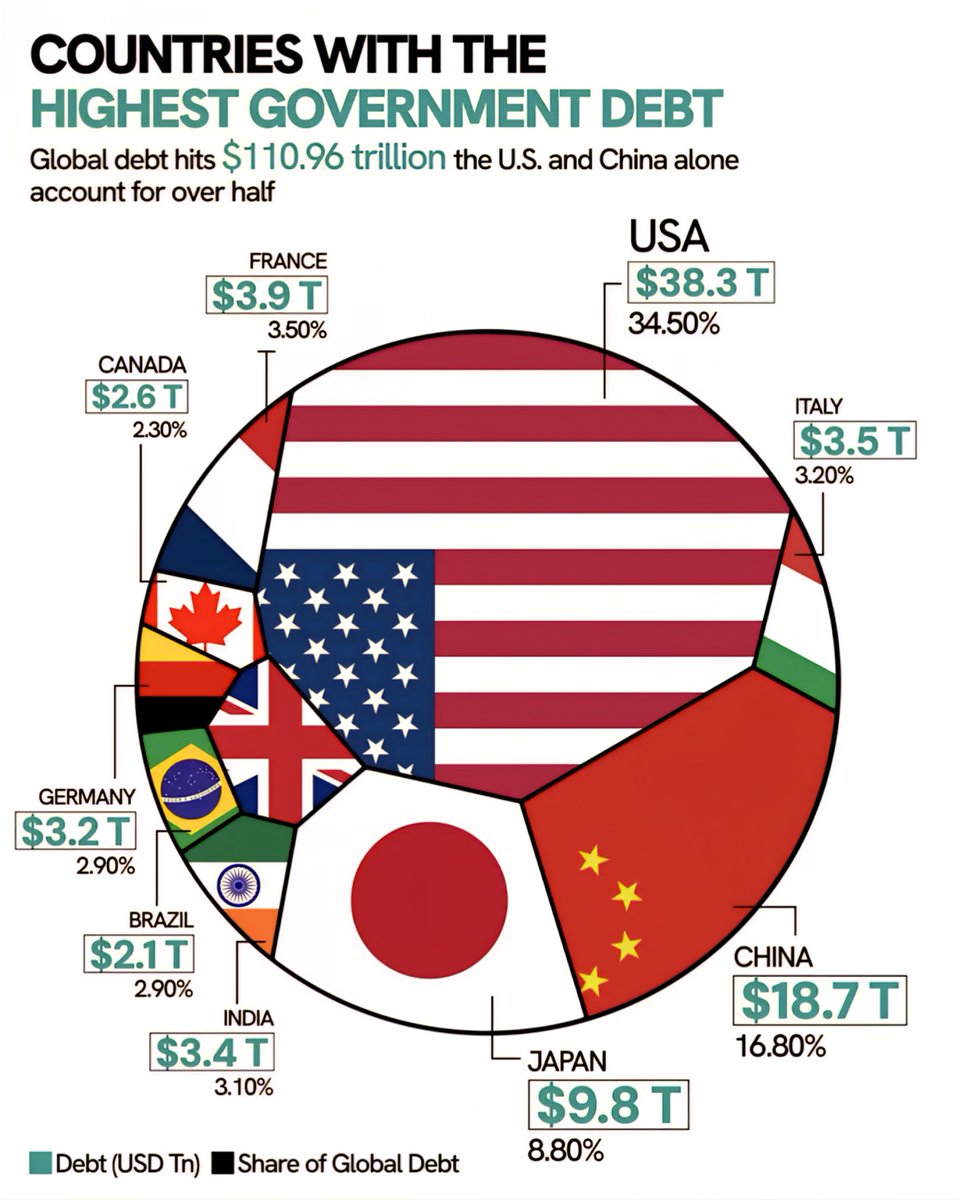
As global economies navigate 2025, the mounting debts highlight varied fiscal strategies, economic resilience, and ongoing challenges faced by nations worldwide. Managing these debt levels will be crucial for ensuring sustainable growth and stability in the years ahead.