Select Language:
Unlocking the Global Language Gap: Insights from the 2025 English Proficiency Map
1. The United States Leads in English Fluency
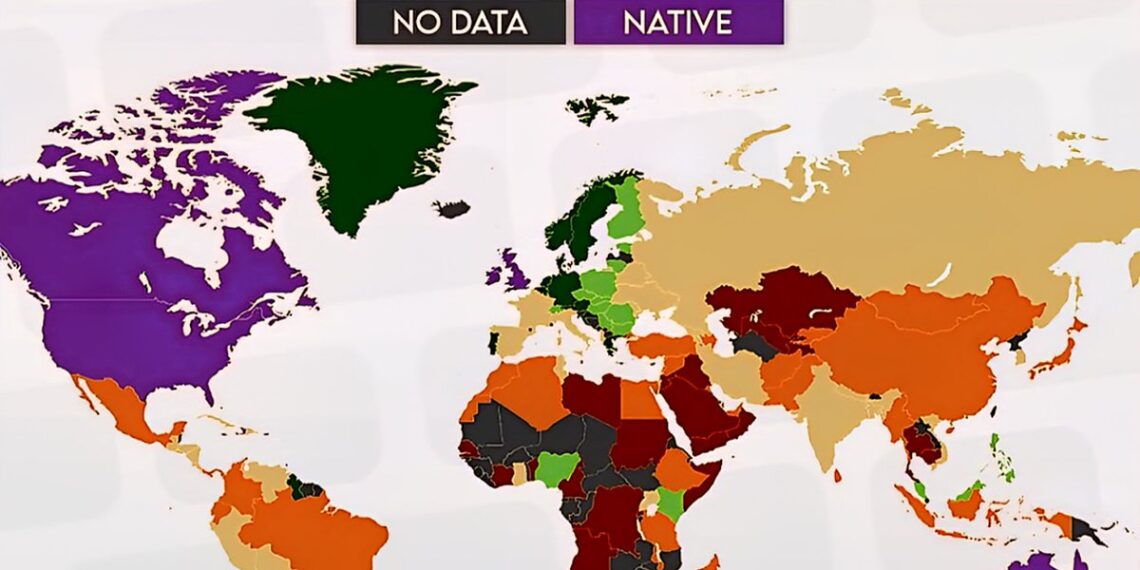
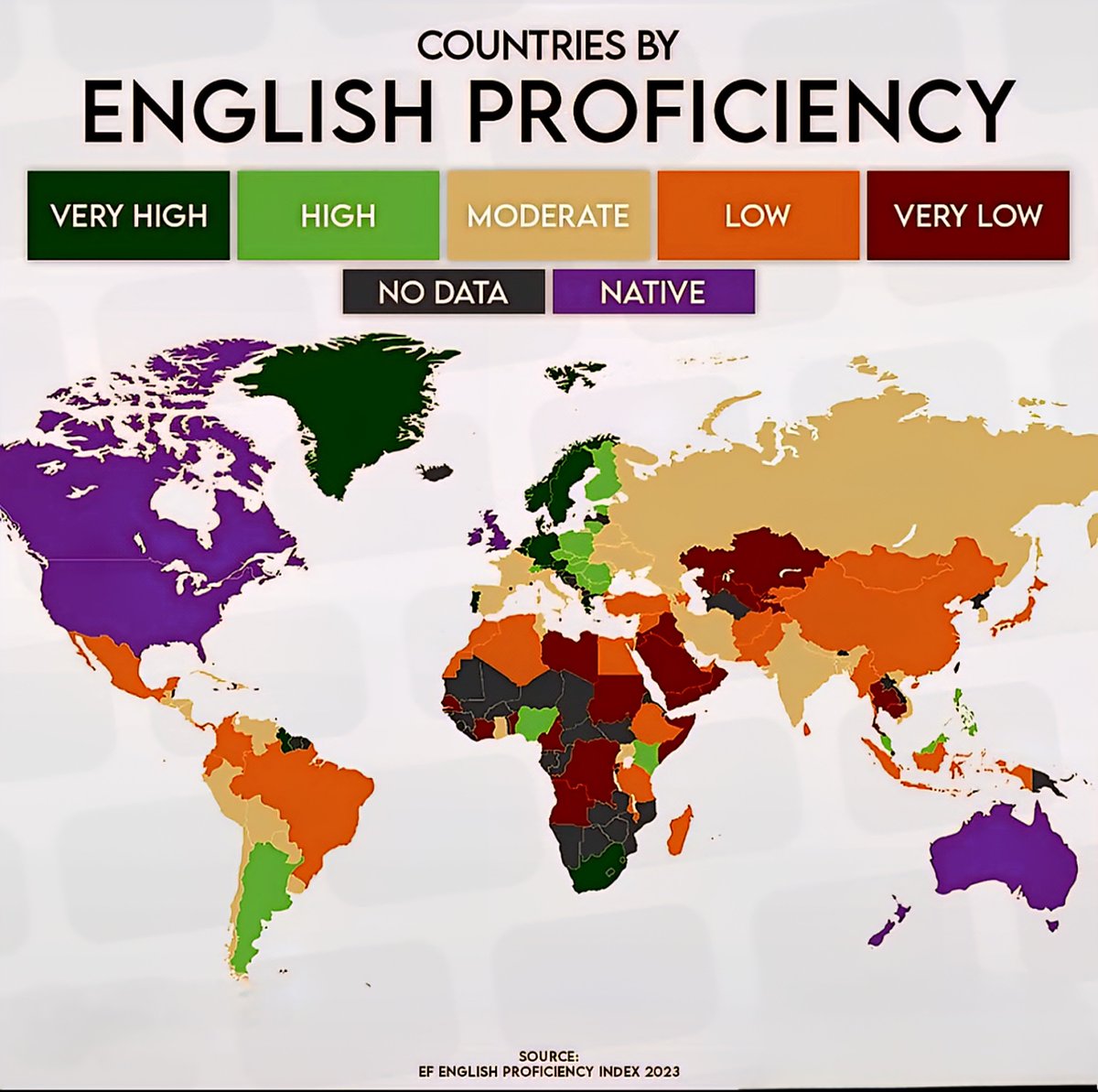
The United States remains at the forefront in English proficiency, with nearly 97% of its population demonstrating strong command over the language. This dominance is fueled by the country’s international influence, education systems, and the widespread use of English in business and media. Despite regional dialects and accents, the overall fluency contributes significantly to the nation’s global communication power. The high proficiency levels further facilitate international business, diplomacy, and cultural exchange.
2. European Countries Show Varied Levels of English Skill
Across Europe, proficiency varies considerably. Scandinavian nations like Sweden and Norway top the charts, boasting over 90% of their populations fluent in English. Conversely, countries such as France and Italy show more moderate proficiency, around 60-70%. The European Union’s language policies, education, and cultural exposure influence these differences substantially. Young Europeans increasingly adopt English, especially in business and technology sectors, narrowing the gap further.
3. Asian Countries Exhibit Rapid Growth in English Proficiency
Asia continues to see a surge in English language skills, with nations like Singapore, the Philippines, and India leading this charge. Singapore maintains an impressive 96% fluency rate thanks to its bilingual education system. The Philippines’ high proficiency—around 85%—is driven by its widespread use of English in daily life and the booming call center industry. India is a rising star, with roughly 70% of urban professionals proficient in English, fueling its tech and outsourcing industries.
4. Africa’s Diverse English Landscape
Africa presents a complex picture of English proficiency. Countries like Nigeria and Kenya display high levels of English fluency, at approximately 80% and 73% respectively, primarily due to colonial histories and English-centered education systems. South Africa also boasts notable proficiency, though disparities exist between urban and rural areas. English serves as an official language and a lingua franca in many African nations, fostering development, education, and enterprise across diverse communities.
5. Australia and New Zealand Maintain High Standards
Down under, Australia and New Zealand uphold strong English proficiency rates, exceeding 95%. English is the official language, supported by robust educational and immigration policies that attract speakers globally. This linguistic consistency bolsters their tourism, international education, and business sectors, contributing to their economies and cultural exchanges.
6. Latin America’s Increasing Engagement with English
Latin American nations are progressively improving their English skills, propelled by regional economic shifts and tourism. Countries like Costa Rica, Chile, and Argentina exhibit proficiency levels hovering between 55-70%. International schools, online learning platforms, and economic integration with the United States and Canada accelerate this trend. This improved English competence supports local industries, foreign investment, and educational exchange programs.
7. Middle East’s Growing Focus on English Education
The Middle East shows heightened emphasis on English education amid economic diversification efforts. The United Arab Emirates and Qatar, for instance, report proficiency levels around 80%, mainly in urban centers and among youth. English has become integral in academia, business, and diplomacy, supporting the region’s aspirations to be global hubs for trade and innovation.
8. Challenges Faced by Low-Proficiency Regions
Despite global advancements, some regions remain behind in English proficiency. Parts of Central Asia, rural parts of Southeast Asia, and certain island nations lag due to limited educational resources, political instability, and language barriers. These deficits can hinder international collaboration, economic development, and access to global markets, emphasizing the need for targeted language training initiatives.
9. Impact of Technology on Language Learning
The proliferation of online education platforms and language apps has democratized access to English learning globally. In 2025, innovative tools employing AI and immersive virtual reality are helping learners overcome traditional barriers. This technological penetration is particularly impactful in developing regions, where it accelerates skills acquisition and increases global connectivity.
10. Future Trends in Global English Proficiency
As the world becomes more interconnected, the demand for English remains strong. Predictions suggest continued growth in proficiency across Asia, Africa, and Latin America, aided by global digitalization and international trade. Moreover, as multilingualism becomes valued, more non-native speakers are expected to attain conversational fluency, fostering cross-cultural collaborations efficiently.
In an increasingly interconnected world, understanding the nuances of where and how English is spoken enriches global communication and development strategies. Countries that prioritize language education and leverage technological advances will position themselves advantageously on the world stage in 2025 and beyond.