Select Language:
Surprising Insights into 2025 Global Inflation Trends
1. United States Faces Moderate Inflation Despite Economic Growth
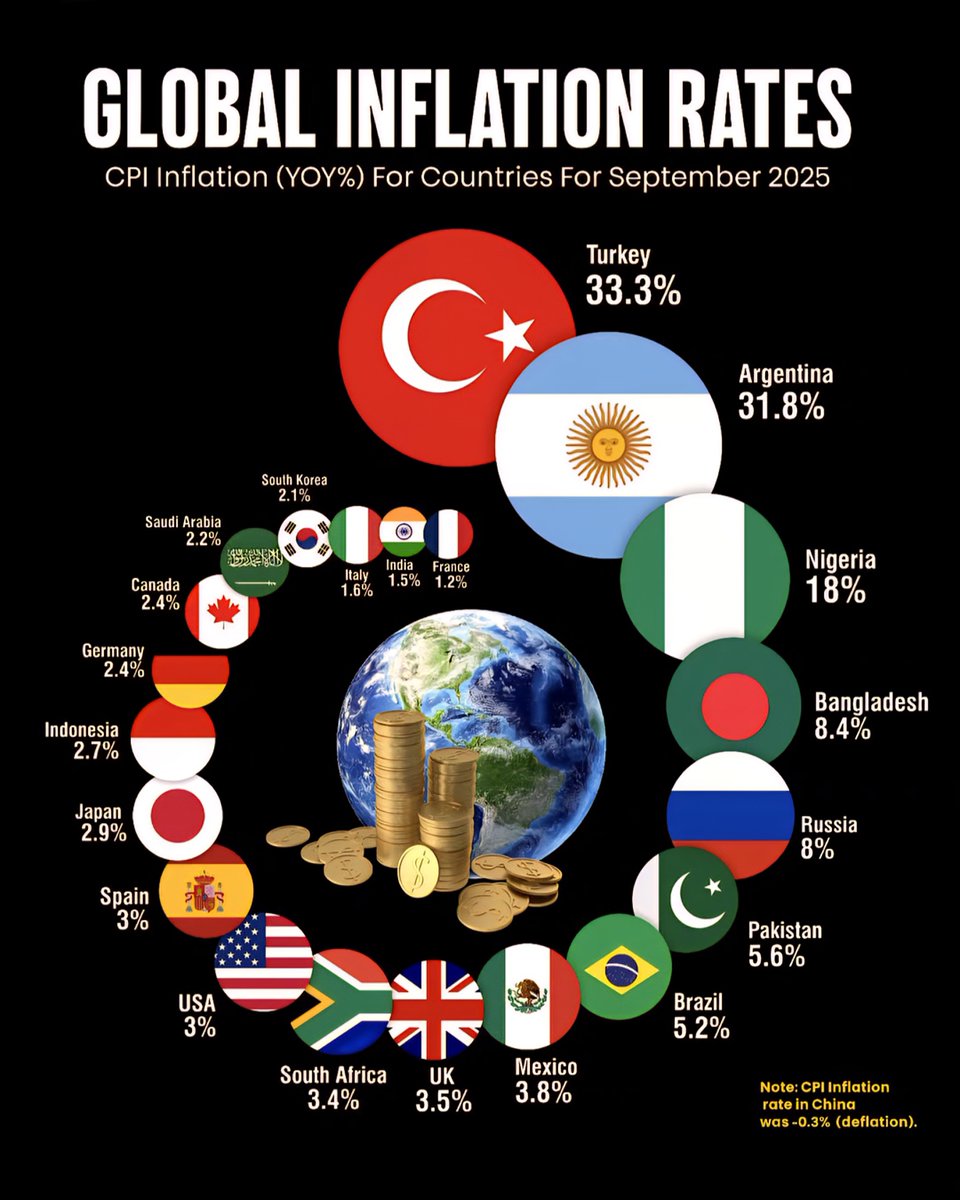
In 2025, the United States has experienced a relatively moderate inflation rate of approximately 3.2%. This stability is partly due to strategic monetary policies aimed at balancing economic growth with inflation control. Despite a resilient job market and consumer spending, inflation remains in check thanks to measures by the Federal Reserve, which has kept interest rates steady. Analysts believe this will help foster continued economic stability, making it more predictable for both consumers and investors.
2. European Union Experiences Minimal Inflation Rates
Across the Atlantic, the European Union boasts an inflation rate of around 1.8%, the lowest in recent years. Countries like Germany, France, and Italy have benefitted from energy subsidies and renewable energy investments, helping keep consumer prices stable. However, energy prices still present some fluctuations, mainly due to geopolitical tensions affecting supplies. The EU’s focus on green energy initiatives appears to be a major factor in tempering inflationary pressures.
3. Rising Inflation in Emerging Markets
Emerging economies such as India, Brazil, and South Africa are grappling with inflation rates approaching 6-8%. Factors include fluctuating commodity prices, currency devaluations, and strained supply chains impacted by global disruptions. India, specifically, has seen inflation hovering around 6.5%, driven largely by food and fuel costs. Governments are implementing fiscal policies and subsidies to curb the impact on ordinary citizens, but inflation remains a concern for policymakers.
4. China Maintains Low Inflation Amid Growth Challenges
China has managed to keep its inflation rate around 2%, despite facing economic slowdowns and trade tensions. The government’s focus on stabilizing domestic markets and controlling housing prices has played a role in keeping inflation in check. However, some economists warn that persistent low inflation could hamper wage growth and consumer spending, potentially impacting long-term economic expansion.
5. Latin America Experiences High Inflation in Some Countries
Countries like Argentina and Venezuela continue to experience hyperinflation, with rates exceeding 50% in some cases. Economic instability, currency devaluations, and political upheaval have driven drastic price increases. Efforts to stabilize these economies involve currency reforms and international aid, but inflation remains a persistent challenge, affecting everyday life and economic prospects for millions.
6. Middle East and North Africa See Varied Inflation Rates
Regions such as the Gulf Cooperation Council countries have generally maintained low inflation levels, around 1-2%, thanks to oil revenues and prudent fiscal policies. Conversely, nations like Egypt and Turkey face inflation rates upwards of 9-10%, driven by currency devaluations and domestic economic policies. These contrasting trends highlight regional disparities based on resource dependence and economic strategies.
7. Africa’s Inflation with Mixed Trends
While nations like Nigeria and Kenya are managing inflation rates around 4-5%, others such as Zimbabwe continue to experience hyperinflation, with rates exceeding 500%. The divergence stems from differing economic structures, levels of foreign investment, and monetary policies. Many African countries are working to stabilize their currencies and control inflation through reforms and international cooperation.
8. Impact of Global Inflation Trends on Consumers and Businesses
As inflation rates vary widely across the globe, consumers face differing challenges—rising food prices, increased fuel costs, and higher housing expenses are common themes. Businesses, on the other hand, are navigating supply chain disruptions, fluctuating costs, and changing consumer demand. Governments are adopting diverse strategies to manage inflation’s impact, including tightening monetary policies, providing subsidies, and promoting economic diversification.
9. The Role of Geopolitical Factors in Inflation Fluctuations
Global geopolitical tensions, such as conflicts over energy routes and trade disputes, continue to influence inflation trends worldwide. Energy prices, in particular, have a significant effect—countries heavily dependent on energy imports experience more volatile inflation. Ongoing diplomatic efforts and efforts to diversify supply sources aim to mitigate these effects in the coming years.
10. Inflation Predictions for 2025 and Beyond
Economists predict that inflation rates will stabilize in many developed nations over the next few years, thanks to proactive monetary policies. Emerging markets may face continued inflationary pressures, but reforms and global cooperation are expected to help moderate these trends. The focus remains on balancing growth, controlling inflation, and ensuring economic stability amid ongoing geopolitical and technological shifts.
Keeping an eye on these inflation trends gives valuable insight into the varying economic realities across the globe in 2025. Whether it’s the steady progress in the U.S. or the economic turbulence in parts of Latin America, understanding inflation’s intricacies helps policymakers, businesses, and consumers navigate the future with confidence.