Select Language:
Countries with Overseas Military Bases: A Global Overview
In today’s interconnected world, military bases stationed abroad represent more than just a presence; they symbolize a country’s strategic intentions and capabilities. Establishing overseas military bases allows nations to project power, conduct operations, and influence global events. Here, we delve into the countries that maintain military bases outside their borders, highlighting the strategic implications of these installations.
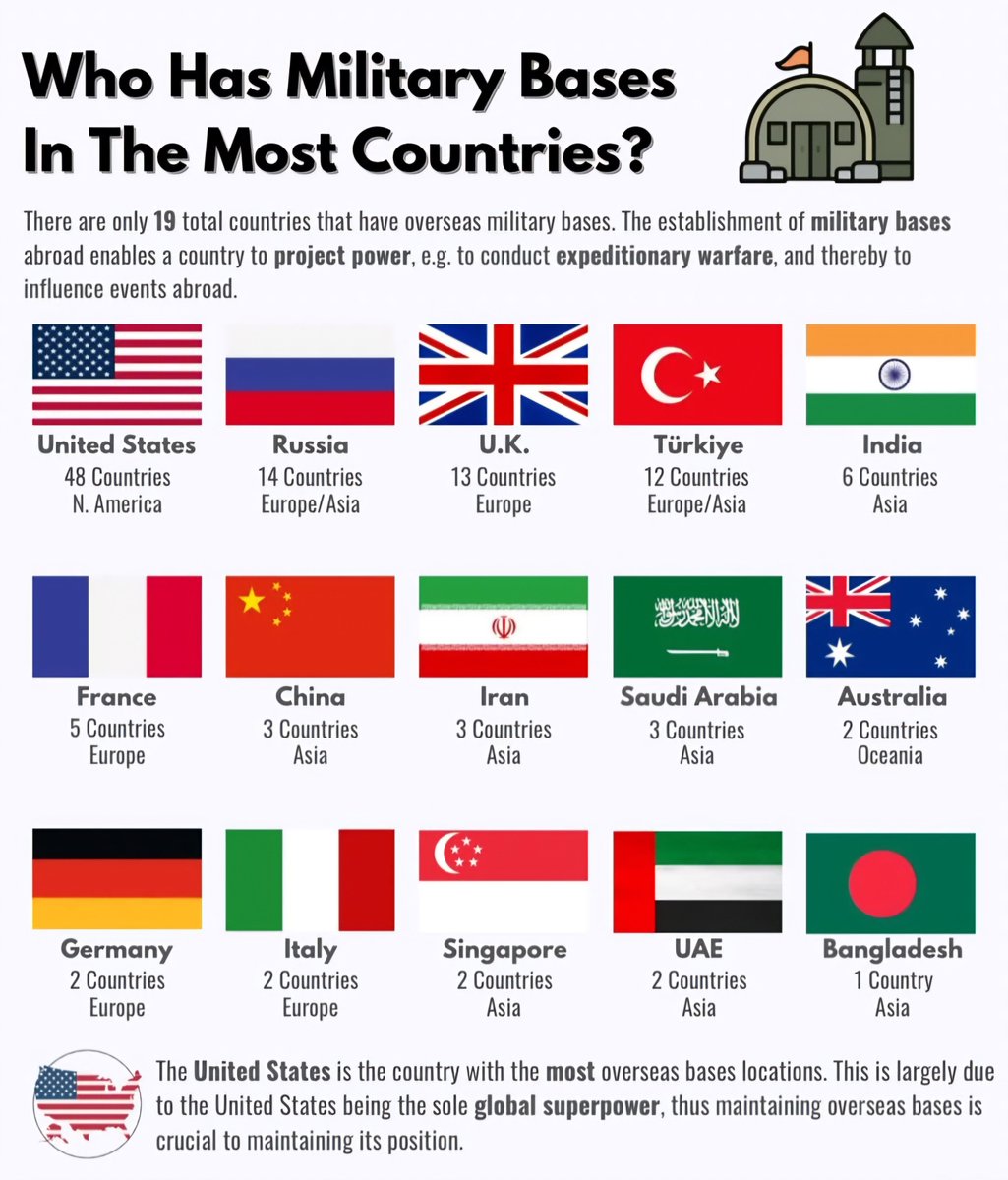
United States – 48 Countries
The United States leads the world with a staggering 48 military bases positioned across the globe. As the foremost global superpower, the U.S. leverages these bases for power projection and strategic military operations. Locations range from Europe to Asia and the Middle East, enabling quick responses to international crises and fostering alliances with partner nations. This extensive network not only enhances U.S. security but also allows for flexible military engagement.
Russia – 14 Countries
In second place is Russia, with 14 overseas bases. These installations serve various purposes, including support for naval operations and strategic positioning in Eastern Europe and beyond. Russia’s military bases are deepening its presence in strategic locations, especially in regions like the Middle East and parts of Africa, enhancing its security and influence.
United Kingdom – 13 Countries
The United Kingdom maintains 13 military bases worldwide. These bases play a crucial role in facilitating operations in regions of interest, including Africa and the Middle East. The UK focuses on maintaining a global military presence as part of its commitment to international security and defense partnerships, often working alongside NATO allies in joint operations.
Türkiye – 12 Countries
Türkiye (Turkey) has established 12 overseas military bases, reflecting its geopolitical interests, especially in the Middle East. These bases allow Türkiye to exert influence and conduct operations in surrounding regions while also supporting NATO missions and other international endeavors.
India – 6 Countries
Emerging as a significant player on the global stage, India operates 6 military bases beyond its borders. This expansion highlights India’s strategic interest in securing trade routes and boosting its presence in the Indian Ocean. With growing partnerships, especially with nations like the U.S. and Japan, India’s base network is poised for further development.
France – 5 Countries
France maintains 5 military bases overseas, rooted in its historical colonial connections and current international commitments. These bases are strategically located to facilitate operations in Africa and the Middle East, allowing France to project power and maintain its influence in former colonies while supporting global security missions.
China – 3 Countries
With a focus on expanding its global influence, China has established 3 military bases outside its borders. For China, these bases are essential for safeguarding trade routes and asserting its presence in strategic maritime areas. The construction of military outposts in locations such as Djibouti symbolizes China’s increasing assertiveness on the global stage.
Iran – 3 Countries
Iran has 3 overseas military bases, primarily focused on the Middle East. These installations enhance Iran’s ability to project power and maintain its influence in regional conflicts, often acting as a counterbalance to U.S. military presence in the area.
Saudi Arabia – 3 Countries
Saudi Arabia also operates 3 military bases abroad, primarily in the context of regional security and alliances. These bases support operations for counter-terrorism and other military partnerships, reinforcing Saudi Arabia’s strategic security objectives in a volatile region.
Australia – 2 Countries
Australia maintains 2 military bases outside its borders, facilitating joint operations with allies, notably in the Asia-Pacific region. These bases play a critical role in enhancing Australia’s strategic partnerships, particularly with the United States.
Germany – 2 Countries
As a key member of NATO, Germany has 2 overseas bases, contributing to collective security efforts. These bases support international missions and foster military cooperation among allied nations.
Italy – 2 Countries
Italy operates 2 military bases abroad, supporting NATO missions and facilitating security operations in the Mediterranean region. These bases represent Italy’s commitment to international security and defense collaboration.
Singapore – 2 Countries
Singapore maintains 2 overseas military bases, which contribute to its strategic objectives in Southeast Asia and enhance its role as a regional security partner.
UAE – 2 Countries
The United Arab Emirates has established 2 military bases abroad, reflecting its ambitions in global security and regional stability, particularly in the Middle East.
Bangladesh – 1 Country
Lastly, Bangladesh has a singular overseas military base, showcasing its developing approach to international military engagement and contribution to regional stability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the establishment of overseas military bases is a crucial component of modern military strategy for nations worldwide. With only 19 countries possessing such installations, the implications of these bases are profound. Power projection, strategic defense operations, and international collaboration all hinge on the ability of nations to maintain influence far beyond their borders. As global dynamics continue to evolve, the nature, number, and purpose of military bases will likely transform, shaping the future of international relations and security.






