Select Language:
Major Global Economy Concentration: How a Tiny Land Area Holds Half of World’s GDP

1. The Astonishing Concentration of Wealth
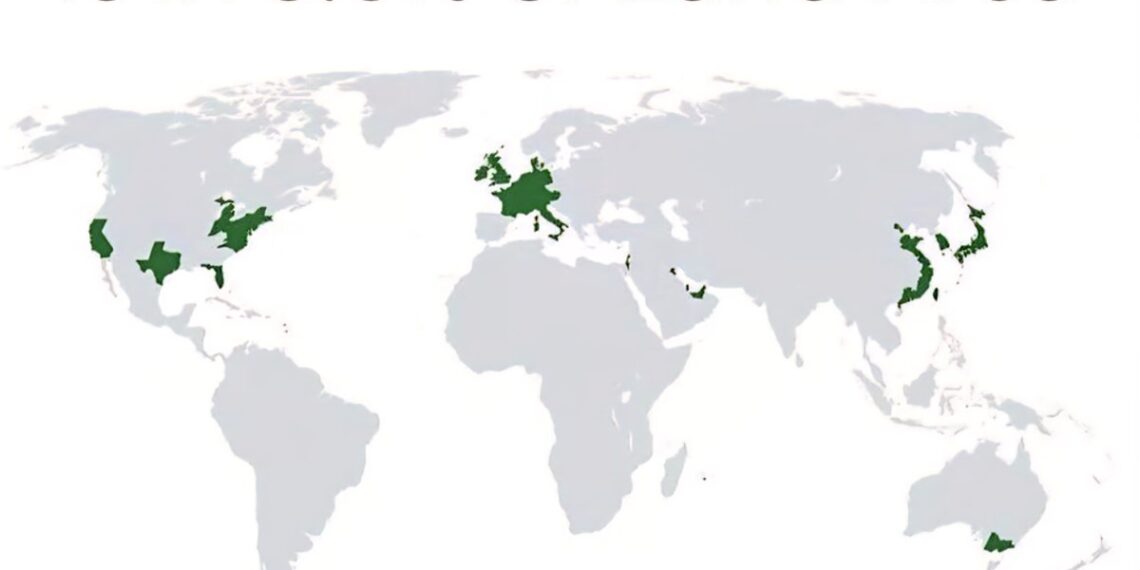
In 2025, a startling discovery highlights that just 3.6% of the world’s land area accounts for nearly 50% of the global gross domestic product (GDP). This means a tiny fraction of the Earth’s surface is home to the bulk of our economic activity, emphasizing how economic power is tightly clustered.
2. The Power Hubs: Countries Leading the Pack
Most of this land area is concentrated within highly developed nations, including parts of the United States, Western Europe, wealthy Asian countries, and a handful of thriving city-states. For example, regions like the U.S. Northeast Corridor, Western Europe’s urban centers, and the economic clusters around Tokyo and Shanghai make up these land-rich power hubs.
3. Urbanization and Economic Density
Urban centers within these regions contribute significantly to their economic dominance. The dense concentration of businesses, financial institutions, skilled labor, and infrastructure spurs high productivity, allowing them to generate massive GDP figures relative to their land size. These urban giants exemplify how density and infrastructure foster financial dominance.
4. The Environmental and Social Impact
This uneven distribution of economic activity impacts both the environment and societies. Overcrowded urban areas face challenges such as pollution, housing shortages, and transportation congestion. Meanwhile, rural regions and less developed countries often struggle to attract investments, perpetuating global inequalities.
5. Economic Disparities and Development
The stark concentration raises questions about economic disparities across regions. While these land areas generate the lion’s share of wealth, vast swaths of the world still grapple with poverty and underdevelopment. Bridging this gap is crucial for fostering sustainable global growth.
6. Real Estate and Infrastructure Premiums
In these land-dense areas, real estate prices and infrastructure investments soar, reflecting their importance as economic hubs. High property values attract even more investment, fueling a cycle that further consolidates economic power within these neighborhoods.
7. The Role of Technology and Innovation
Technological advancements play a vital role in maintaining this economic concentration. Innovation hubs, like Silicon Valley and similar zones around the world, thrive within these regions, reinforcing their dominance. These areas lead global trends in AI, finance, and biotech, contributing disproportionally to worldwide economic growth.
8. Future Trends: Will It Persist?
While the current trend underscores the concentration of wealth in tiny land areas, new factors could shift this landscape. Remote work technology, decentralization, and emerging economies may gradually distribute economic activity more evenly. However, as of 2025, the trend remains largely intact, emphasizing the importance of urban centers in the global economy.
9. Policy Implications: Building More Equitable Economies
Policymakers face the challenge of balancing development and equity. Investing in infrastructure and education in less developed regions can foster growth, potentially easing the tight concentration of wealth. International cooperation is essential to ensure sustainable and inclusive economic progress.
10. Understanding the Future of Global Economy
This data offers a sobering perspective—global economic stability hinges on a small percentage of land yet produces half of the wealth. Recognizing these patterns helps shape policies for more balanced growth, emphasizing innovation, infrastructure, and equitable development strategies worldwide.