Select Language:
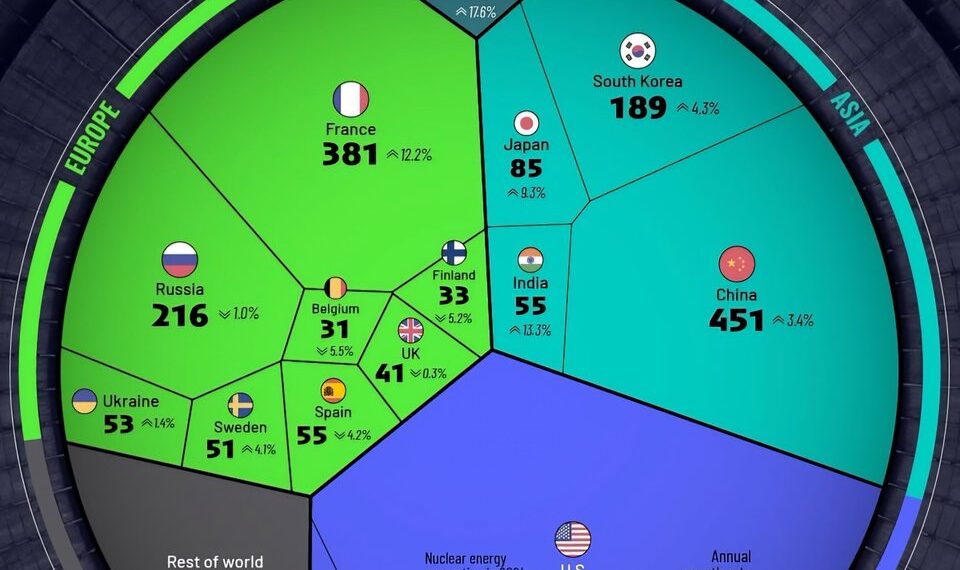
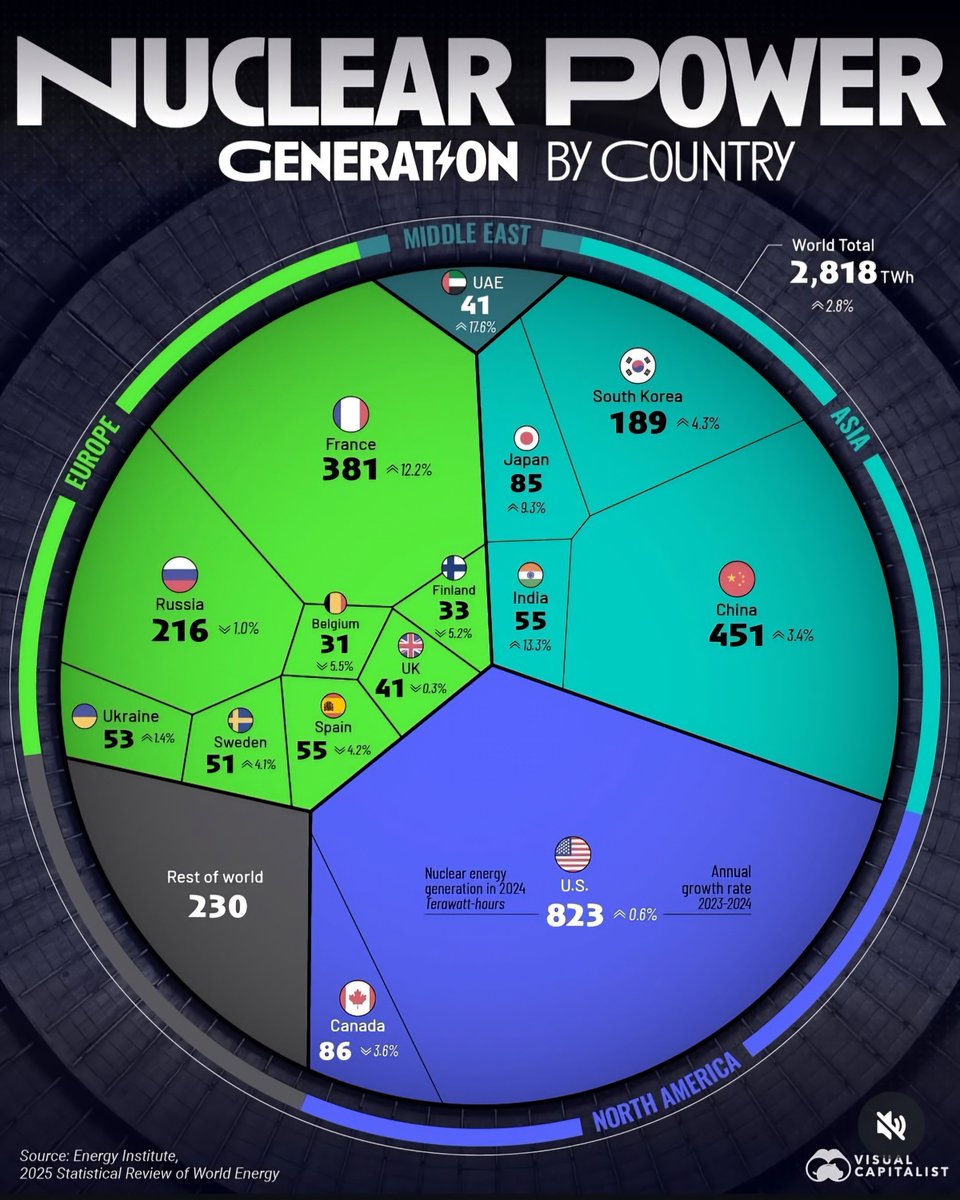
The Leading Countries in Nuclear Power Generation in 2025
1. United States Holds the Top Spot in Nuclear Power Capacity
Despite global fluctuations, the United States remains the dominant force in nuclear energy, accounting for approximately 20% of the world’s nuclear power production. As of 2025, the U.S. boasts a fleet of over 90 operational reactors spread across more than 50 facilities. The reliance on nuclear energy in the nation continues to be driven by the need for a stable, low-carbon energy source to support its vast energy consumption demands.
The US government has invested heavily in modernizing existing reactors and exploring next-generation nuclear technologies such as small modular reactors (SMRs). These advancements aim to enhance safety, reduce waste, and increase efficiency, potentially transforming the country’s nuclear landscape in the years ahead.
2. France’s Heavy Dependence on Nuclear Power
France remains a nuclear energy headline in 2025, generating approximately 70% of its electricity from nuclear sources. The country operates 56 reactors, making it one of the most nuclear-dependent nations in the world. This reliance has historically helped France achieve relatively low carbon emissions compared to neighboring countries.
Recent investments are focusing on extending the lifespan of aging reactors and expanding renewable energy integration to diversify its energy mix. Nonetheless, nuclear power continues to be central to France’s strategy for meeting climate commitments and ensuring energy security.
3. China Rapidly Expanding Its Nuclear Capacity
In 2025, China has firmly established itself as the world’s fastest-growing nuclear power player. With over 50 reactors now operational and more under construction, China aims to significantly boost its nuclear capacity by 2030. The country has prioritized nuclear energy as a critical component of its “dual carbon” goal—achieving carbon neutrality by 2060.
Chinese firms are pioneering innovative reactor designs, including the development of fast breeder reactors and indigenous SMRs. These projects aim to address energy demand while reducing dependence on coal, which has historically made up a large segment of China’s energy mix.
4. Russia’s Strategic Investment in Nuclear Technology
Russia continues to wield influence in the global nuclear arena through its extensive nuclear infrastructure and technology exports. With nuclear power generating about 20% of Russia’s electricity, the country operates 38 reactors domestically and has signed numerous international agreements to build reactors abroad, notably in Asia, Africa, and Europe.
Russia’s state-owned entity, Rosatom, is aggressively investing in next-generation reactors and floating nuclear power plants, which expand its capacity to deliver reliable power to remote regions and developing nations.
5. Japan’s Road to Nuclear Recovery
Japan is gradually rebuilding its nuclear sector following the Fukushima disaster in 2011. In 2025, the country operates approximately 10 reactors that have undergone rigorous safety upgrades. Despite public skepticism, Japan recognizes nuclear power as a critical element in its climate strategy, particularly as it strives to reduce dependency on fossil fuels.
Government policies now emphasize safety, technological innovation, and public transparency. New reactors are being designed with advanced safety features, and restart procedures have become more streamlined, paving the way for a cautious revival of nuclear energy.
6. South Korea’s Focus on Nuclear Innovation
South Korea, often praised for its nuclear expertise, continues to develop advanced nuclear technology in 2025. The country operates around 24 reactors, providing about 30-35% of its electricity. Recent efforts have concentrated on exporting nuclear technology to other countries and developing its own small modular reactors.
South Korea sees nuclear power as essential for achieving a low-carbon future and maintaining energy security amid global supply chain uncertainties. The government supports innovation in reactor safety, waste management, and overall efficiency to maintain its competitive edge.
7. India’s Ambitious Nuclear Expansion
India’s nuclear energy program is rapidly expanding, with over 23 reactors currently in operation and several more under construction. The country is aiming for a significant boost to its nuclear capacity to support its growing economy and address energy shortages.
India’s strategic focus includes harnessing thorium, abundant in the region, and advancing fast breeder reactor technology. These efforts are part of its vision to achieve energy independence while transitioning to cleaner sources.
8. Canada’s Safe and Sustainable Nuclear Approach
Canada maintains a steady position in the nuclear power arena, with about 19 reactors mainly located in Ontario. The country prioritizes safety, waste management, and technological innovation. Recent developments include the potential deployment of small modular reactors to address remote and off-grid communities.
Canada is committed to keeping nuclear power as a vital part of its clean energy portfolio, contributing to its climate goals and energy stability.
9. Other Notable Players and Emerging Markets
Countries such as the United Arab Emirates, Argentina, and South Africa have made strategic investments in nuclear technology. The UAE has successfully operated its first reactors, aiming to become a regional nuclear hub.
Emerging markets in Southeast Asia and the Middle East show increasing interest in nuclear power as a means to diversify their energy sources and accelerate economic development.
As the global energy landscape shifts towards sustainability, nuclear power’s role continues to evolve. Countries are investing in newer, safer, and more efficient reactor technologies, emphasizing the importance of nuclear energy in achieving climate goals and ensuring energy security.