Select Language:
Projected Population Decline by 2100: Key Insights for 2025

1. Global Population Set to Shrink Dramatically
Recent projections indicate a significant decline in the world’s population by the year 2100. Experts estimate that the global population could decrease by as much as 10% to 15%, primarily driven by declining birth rates and aging populations in several parts of the world. This shift marks a departure from the rapid growth seen in the 20th century and presents unique challenges for economies, healthcare systems, and environmental sustainability.
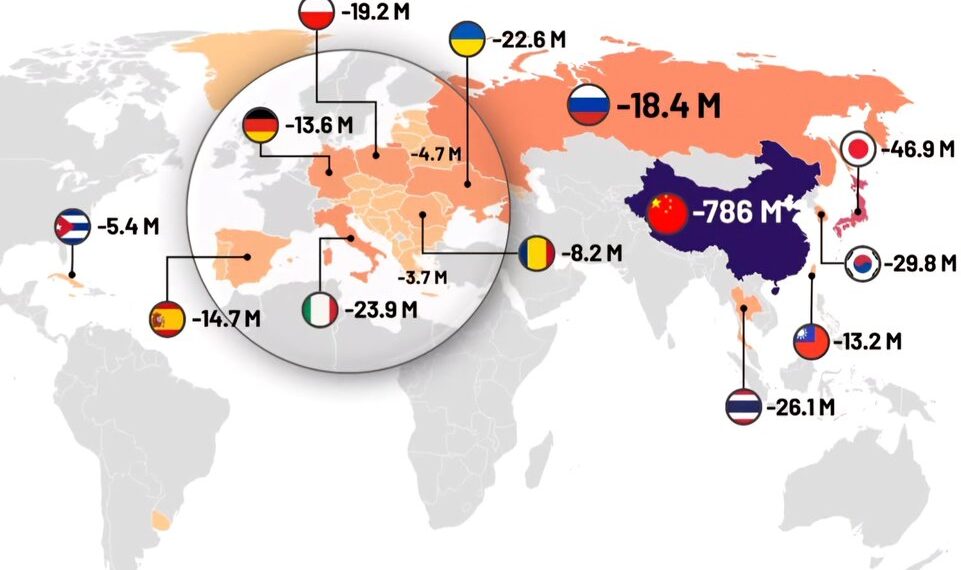
2. Asia’s Population Faces Steep Decline
One of the most notable trends is the projected decline in Asia, especially in countries like China and Japan. With birth rates dropping below the replacement level, China could see its population shrink by approximately 30% over the next 75 years. Japan’s population is expected to decline by nearly 40%, leading to a shrinking workforce and increasing eldercare demands. These demographic changes could reshape the region’s economic landscape and pose logistical challenges for social services.
3. Europe’s Population Outlook: Aging but Not Growing
Europe is already experiencing a relatively high proportion of older adults, and projections suggest that the population will continue to decline, falling by around 10-15%. Countries such as Italy, Germany, and Spain are expected to see their populations decrease significantly, exacerbating labor shortages and putting pressure on pension systems. However, some nations may attempt to counteract decline through policies promoting immigration and higher birth rates.
4. Africa and the Middle East: A Different Trajectory
While much of the world faces population declines, Africa and parts of the Middle East may chart a different course. Some projections indicate that Africa’s population could continue to grow, potentially doubling by 2100, reaching over 3 billion. The Middle East’s population growth is expected to stabilize or slow somewhat but remain relatively robust compared to other regions, driven by higher fertility rates.
5. Impact on the Global Economy and Workforce
A declining global population could have profound effects on the economy. Shrinking workforces might lead to decreased productivity, higher labor costs, and slower economic growth. Countries heavily reliant on a young demographic may face the challenge of adapting to a graying population, with increased demand for healthcare, elder services, and pension support. Conversely, regions experiencing growth, such as Africa, could benefit from a youthful workforce if sustainable development is achieved.
6. Environmental Benefits and Concerns
Some environmental experts argue that population decline might benefit efforts to combat climate change by reducing human pressure on natural resources. However, a shrinking population could also lead to abandoned infrastructure, urban decay, and reduced innovation, which might hinder future technological advancements and sustainable development. Balancing demographic shifts with environmental goals will be a critical issue in the coming decades.
7. Urbanization and Rural Decline
Population decline is expected to accelerate urbanization in some regions while causing rural areas to become increasingly depopulated. This could result in economic disparities, with thriving megacities continuing to expand, while rural communities face decline, loss of services, and infrastructure deterioration. Governments will need to develop strategies to manage these demographic shifts to maintain regional stability and economic health.
8. Policy Responses and Future Planning
Policymakers worldwide are already contemplating strategies to address potential population decline. These include promoting family-friendly policies, improving access to childcare, and incentivizing higher birth rates. Others are considering resettlement programs and adapting social services to cater to aging populations. The success of these initiatives will largely determine how societies adapt to the demographic realities of 2100.
9. Technological Innovations Could Shape Demographic Outcomes
Advancements in healthcare, fertility treatments, and automation may influence future population trends. For example, breakthroughs in reproductive technology could help sustain birth rates in declining regions. Similarly, automation and AI could mitigate workforce shortages, but ethical considerations and social acceptance remain uncertain. The interplay of technology and policy will crucially shape demographic shifts.
10. The Need for Global Collaboration
Ultimately, addressing the implications of population decline requires coordinated international efforts. From economic planning to healthcare innovation and climate action, collaborative strategies are vital to ensuring sustainable development amid changing demographic landscapes. The next decades will be pivotal in shaping a resilient global society capable of adapting to these profound changes.
As we move further into 2025, staying informed about these demographic shifts and their implications is essential for individuals, businesses, and governments alike.