Select Language:
Unveiling the Leading Importers of 2025: A Deep Dive Into Global Trade
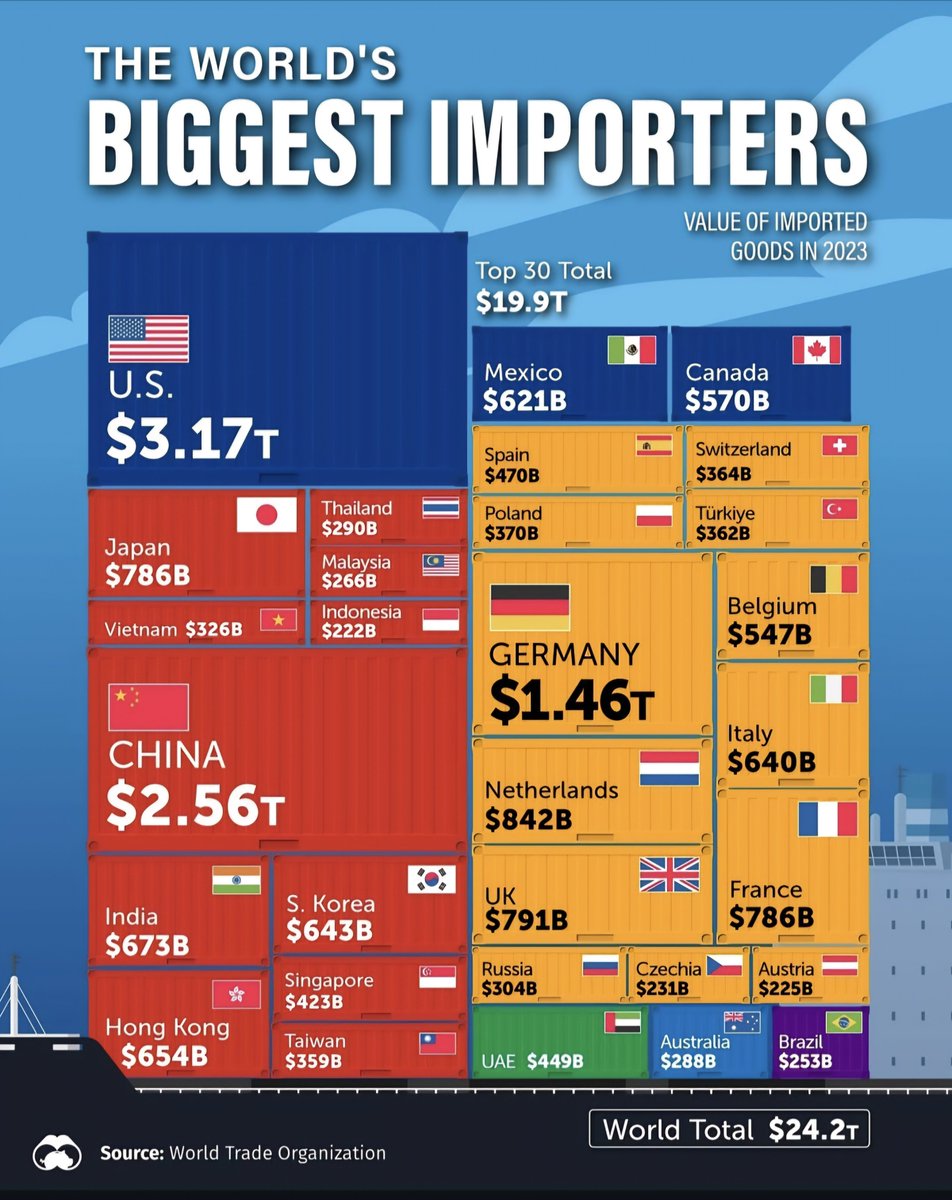
1. United States Leads the Pack
The United States maintains its position as the world’s largest importer in 2025, driven by a resilient economy, high consumer demand, and a strong retail sector. The country imports everything from electronics and automobiles to clothing and raw materials, fueling its expansive consumer market and global supply chains.
2. China’s Continued Dominance in Importing
China remains a critical global importer, primarily importing raw materials, semiconductors, and luxury goods to support its manufacturing sector. Despite its export prowess, China’s surging domestic consumption has bolstered its import figures, reflecting its shift toward a more balanced trade approach.
3. European Union’s Steady Growth
Eurozone countries collectively form one of the largest importing blocs. Germany leads the EU with significant imports of machinery and vehicles, emphasizing its role as an industrial hub. France, Italy, and the Netherlands also contribute substantially, importing luxury goods, energy products, and technology components.
4. Japan’s Strategic Imports
Japan continues to import a large volume of energy resources, raw materials, and electronics to sustain its technologically advanced economy. Its reliance on energy imports remains high due to limited domestic natural resources.
5. India’s Rapid Expansion
India’s rapid economic growth has resulted in a surge in imports, including crude oil, gold, electronic goods, and machinery. The nation’s expanding middle class and urbanization are significant drivers for increased import demands.
6. South Korea’s Tech and Machinery Imports
South Korea imports substantial amounts of semiconductors, petroleum products, and machinery. The country’s tech industry’s growth continues to rely heavily on imports of raw materials and advanced components from abroad.
7. Canada’s Resource-Driven Imports
Canada primarily imports machinery, vehicles, and energy products. Its close economic ties with the United States facilitate substantial trade exchanges, especially in oil, natural gas, and high-tech equipment.
8. Hong Kong’s Re-Export Hub Status
Though technically a part of China, Hong Kong functions as a critical re-export center. Its strategic port and free trade policies make it a vital gateway for goods entering and leaving Asian markets.
9. Mexico’s Manufacturing-Driven Imports
Mexico’s integration into North American supply chains is evident in its high import levels of machinery, electronics, and parts used in automobile manufacturing and other industrial sectors.
10. Singapore’s Role as a Trade Nexus
Singapore continues to serve as a global trading hub, importing electronics, energy products, and consumer goods. Its port remains one of the busiest worldwide, facilitating regional and global trade.
11. Saudi Arabia’s Energy Imports
Despite being a top oil exporter, Saudi Arabia imports high-tech goods, machinery, and certain food products, reflecting its modernizing economy and increasing domestic consumption.
12. United Arab Emirates’ Diversification
UAE’s imports comprise electronics, luxury goods, and machinery, supporting its diversification strategy away from oil dependency and fostering a thriving services sector.
13. Australia’s Resource and Technology Imports
Australia’s import list emphasizes machinery, vehicles, and electronics, mainly to support its mining, agriculture, and urban development sectors.
14. Brazil’s Growing Consumer Market
Brazil’s imports include automobiles, electronics, and pharmaceuticals, driven by an expanding middle class and increased consumer spending.
15. Germany’s Industrial Supply Chain
Germany remains a logistics hub for Europe and boasts high imports of machinery, vehicles, and electronic components to sustain its manufacturing excellence.
16. France’s Luxury and Tech Imports
France’s top imports include high-end fashion, cosmetics, and electronics, aligning with its global luxury and technology industries.
17. Italy’s Fashion and Manufacturing Imports
Italy continues to import raw materials for fashion production, alongside machinery and electronics, supporting its renowned manufacturing sector.
18. Netherlands’ Logistics and Trading Power
The Dutch import significant quantities of energy, machinery, and chemical products, leveraging its strategic port and trade infrastructure.
19. South Africa’s Resource and Consumer Goods
South Africa mostly imports machinery, electronics, and fuel, supporting its mining, infrastructure, and industrial sectors.
20. Indonesia’s Consumer Goods and Energy
As an emerging market, Indonesia’s imports list includes energy resources, electronics, and vehicles, reflecting growing urbanization and economic development.
21. Russia’s Energy and Industrial Imports
Russia focuses on importing machinery, electronics, and goods that complement its energy exports, supporting domestic industries and modernization efforts.
22. Belgium’s Trade Hub Status
Belgium imports machinery, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals, benefiting from its strategic location within Europe’s logistics network.
23. Poland’s Industrial Growth
Poland’s increasing industrial base drives imports of machinery, electronics, and energy products, fueling its economic expansion.
24. Singapore’s Continued Trade Centrality
Singapore’s role as a major transshipment hub persists, importing advanced electronics, energy, and consumer goods from around the world.
25. Vietnam’s Manufacturing Boom
Vietnam’s surging manufacturing sector imports raw materials, electronics, and machinery necessary for its export-oriented economy.
26. Thailand’s Consumer Market Expansion
Thailand’s import list grows with electronics, vehicles, and fuel, supported by strong domestic demand and regional trade agreements.
27. Malaysia’s Tech and Resource Imports
Malaysia imports semiconductors, machinery, and energy products to sustain its electronics industry and manufacturing sector.
28. Argentina’s Agricultural and Industrial Imports
Argentina’s imports include machinery, petroleum, and vehicles to support its agricultural exports and growing industries.
29. Nigeria’s Rising Consumer and Energy Imports
Nigeria’s economy imports fuel, electronics, and vehicles, reflecting its expanding middle class and increased urbanization.
30. Turkey’s Strategic Imports
Turkey’s imports comprise machinery, electronics, and energy sources, supporting its manufacturing and energy sectors amid geopolitical shifts.
As global economies evolve in 2025, the constant flux of international trade highlights the interconnectedness of nations. Countries continue to adapt their import strategies, balancing domestic production with global supply chain needs, shaping the future of international commerce.





