Select Language:
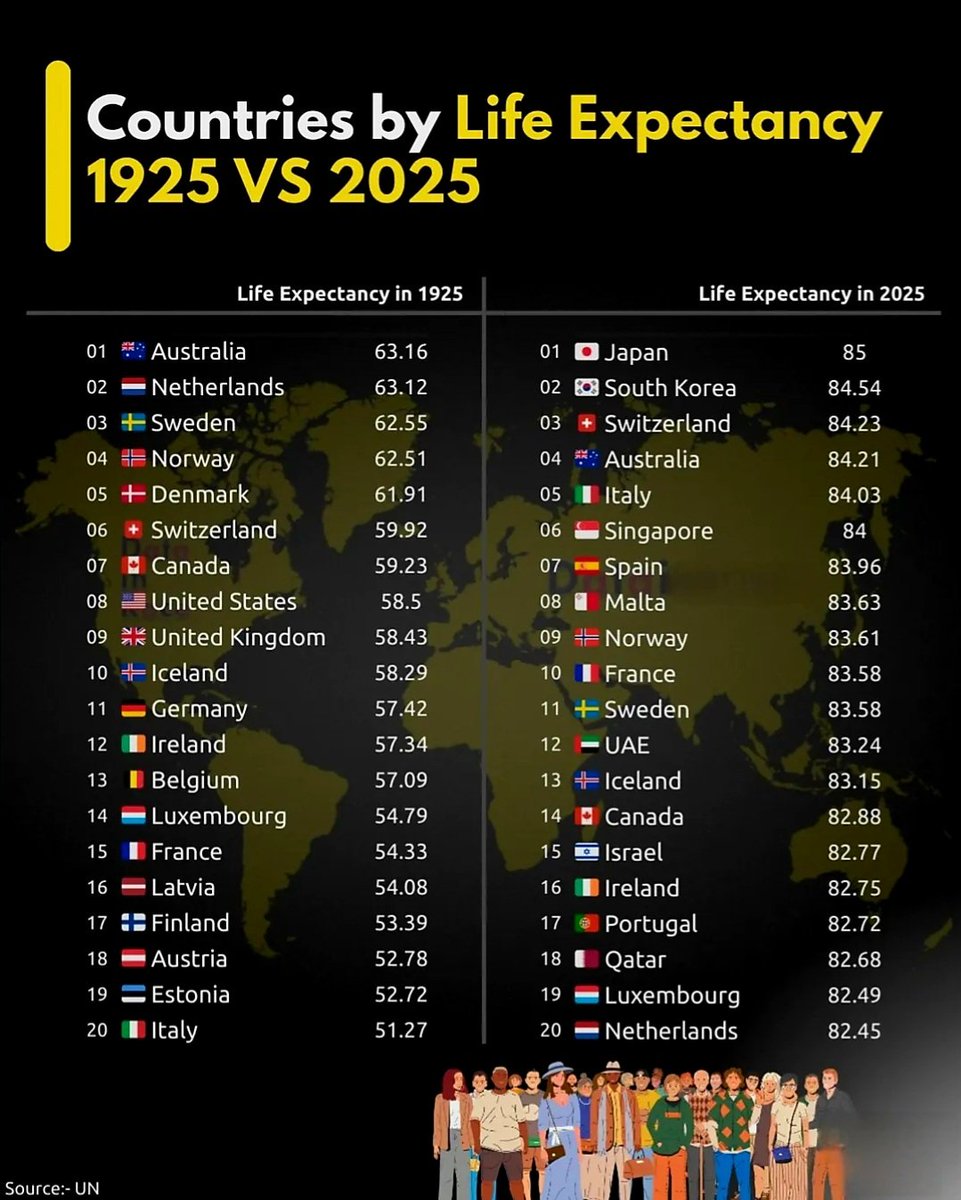
Significant Changes in Global Life Expectancy from 1925 to 2025
1. Japan’s Rise to Top of the List
In 1925, Japan’s life expectancy was considerably lower compared to today. Fast forward to 2025, Japan has emerged as the country with the highest life expectancy globally, reaching an impressive 85 years. This remarkable transformation can be attributed to advancements in healthcare, healthy diets, and widespread social welfare programs.
2. Switzerland Continues As a Leading European Nation
Switzerland’s commitment to high-quality healthcare and socio-economic stability has kept it near the top of the list. Its average lifespan has grown from about 55 years in 1925 to approximately 84 years today, reflecting steady progress in medical technology and public health initiatives.
3. The United States’ Gains and Challenges
The U.S. saw significant improvements in lifespan, increasing from roughly 55 years in 1925 to over 80 years in 2025. However, disparities remain, especially among different socioeconomic groups, underscoring ongoing challenges within the healthcare system.
4. African Countries Making Strides
Contrasting 1925’s very low life expectancy in many African nations, today countries like Algeria and Morocco enjoy an average lifespan of around 75 years. Continued focus on disease prevention and healthcare access has driven these gains.
5. The Impact of Healthcare Systems in Scandinavia
Denmark, Norway, and Sweden have consistently ranked high in life expectancy. Their robust healthcare services, combined with environmental quality and education, have helped extend the average lifespan well into the 80s.
6. China’s Rapid Progress
In 1925, China’s average life expectancy was approximately 30 years. By 2025, that number has surged beyond 77 years, largely driven by economic development, improved sanitation, and healthcare reforms.
7. India’s Emerging Role in Longevity Trends
India has experienced a substantial increase from a life expectancy of around 24 years in 1925 to approximately 74 in 2025. Addressing infectious diseases and improving maternal health are key factors fueling this improvement.
8. Latin America’s Steady Growth
Countries such as Chile and Costa Rica have seen their life expectancies climb into the 80-year range, thanks to universal healthcare coverage and better economic stability.
9. Southeast Asia’s Advances in Healthcare
Vietnam, Thailand, and Malaysia have all significantly increased longevity over the past century, benefiting from government initiatives targeting healthcare access and disease prevention.
10. Australia’s Consistent High Life Expectancy
With an average lifespan of around 83 years in 2025, Australia remains among the world’s leaders due to its strong healthcare system, emphasis on outdoor activities, and high standard of living.
11. The Nordics’ Health and Environmental Policies
The Nordic countries lead globally in life expectancy, thanks to policies focused on environmental sustainability, public health, and social equality. This holistic approach keeps their citizens living longer lives.
12. Brazil’s Remarkable Progress
Brazil has seen its life expectancy grow from 33 years in 1925 to close to 76 years today. Investments in health infrastructure and vaccination campaigns have played vital roles.
13. Middle Eastern Countries Improving Rapidly
Countries like Qatar and the United Arab Emirates now boast life expectancies nearing 80 years, driven by modernization, economic diversification, and healthcare investments.
14. Challenges in Developing Nations
Despite progress, many developing countries still face hurdles like infectious disease burdens and limited healthcare access, keeping their average lifespans below 65. Continued international aid and policies are crucial for future improvements.
15. The Role of Technology in Longevity
Innovations in medical technology, personalized medicine, and telehealth have significantly contributed to increasing life expectancy worldwide, especially in developed nations.
16. Political Stability and Healthcare Access
A stable political environment correlates strongly with higher life expectancy. Countries with ongoing conflicts or political unrest continue to lag behind in health outcomes.
17. The Age of the Population and Healthcare Demands
The global increase in life expectancy is contributing to aging populations, which pose new challenges for healthcare systems, pension schemes, and social services worldwide.
18. The Future Outlook
If current trends persist, by 2035, more nations are likely to surpass the 80-year milestone, with many more entering the 90s—highlighting ongoing progress and remaining disparities.
19. The Importance of Preventative Care
Prevention strategies such as vaccination, health education, and early disease detection are vital in further extending lifespan, emphasizing the need for continued investment in public health.
20. Efforts to Address Global Disparities
International organizations and governments are working towards equitable healthcare access, aiming to lift countries with low life expectancy to match global averages, thereby making longer, healthier lives accessible to all.