Select Language:
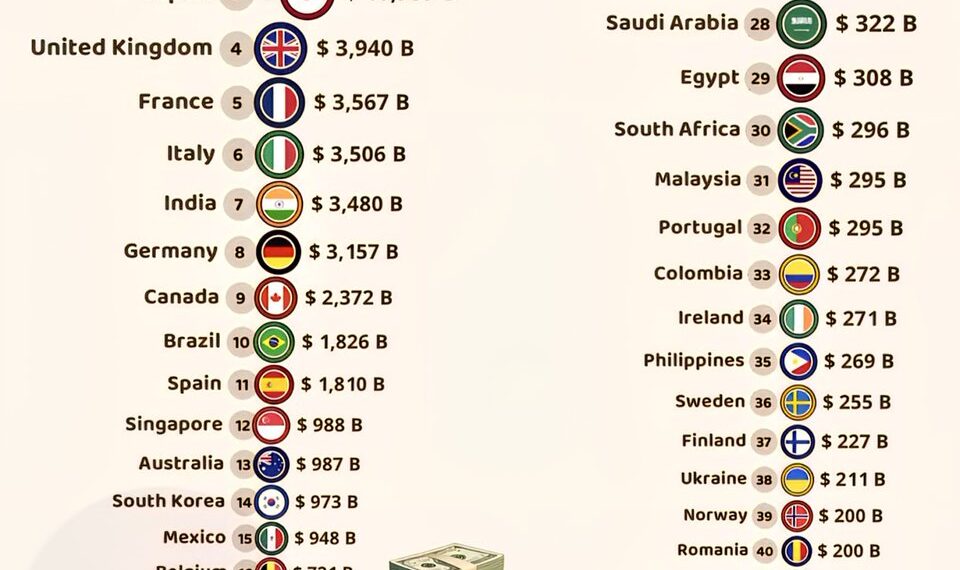
Top Countries with the Largest Government Debts in 2025

1. Japan: The National Debt Leader
Japan continues to hold the distinction of having the highest government debt in the world as of 2025. Its national debt surpasses 250% of the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Despite a shrinking population and economic stagnation, Japan’s government maintains high levels of spending, largely driven by an aging population and rising social welfare costs. This debt burden has prompted discussions about fiscal sustainability and the need for comprehensive reforms. Nonetheless, Japan’s government bonds remain heavily favored by global investors due to its stable economy and high liquidity.
2. United States: The $33 Trillion Debt
The United States stands as the most heavily indebted in absolute terms, with its total federal debt reaching approximately $33 trillion in 2025. The surge in borrowing is largely attributed to ongoing defense expenditures, infrastructure investments, and social security commitments. Despite the high debt level, the U.S. benefits from the dollar’s status as the world’s primary reserve currency, allowing it to borrow at relatively low-interest rates. However, concerns about debt sustainability are growing among economists and policymakers, especially given the recent increases in interest rates.
3. China: Rising Debt, Growing Risks
China’s government debt has hit a new high amid rapid economic development over the past decade. Official figures show China’s debt ratio has climbed past 60% of its GDP. Major investments in infrastructure and state-owned enterprises have spurred the country’s growth but have also increased fiscal vulnerabilities. As China seeks to manage its transition from an exporting economy to one driven by domestic consumption, the government faces the challenge of balancing growth with debt control.
4. Italy: Europe’s Heaviest Debt
Italy maintains one of the highest debt-to-GDP ratios among European nations, exceeding 150%. Persistent political uncertainties, sluggish economic growth, and high public spending have hampered efforts to reduce debt levels. Rising borrowing costs and EU fiscal regulations create additional hurdles for Italy’s government to stabilize its finances. The country’s debt situation remains a critical concern for the broader Eurozone economy.
5. France: Battling Rising Debt Levels
France’s national debt continues to climb, reaching over 100% of its GDP in 2025. Public spending on healthcare, social services, and pension schemes has driven debt accumulation. Economic reforms aimed at reducing deficits face political resistance. The government is under pressure to implement austerity measures and stimulate economic growth to prevent further increases in debt ratios, which could threaten fiscal stability.
6. India: Rapid Debt Accumulation Amid Growth
India’s government debt has surged to about 85% of its GDP as the country invests heavily in infrastructure, healthcare, and social programs to support its growing population. While these investments are crucial for long-term development, the rising debt level raises concerns over fiscal discipline and the sustainability of growth. Efforts are underway to increase revenue collection and improve fiscal management, but challenges remain.
7. Brazil: Latin America’s Largest Debt
Brazil’s government debt is estimated to be over 80% of its GDP. Political instability, economic downturns, and the need for extensive social programs have contributed to this high level. The country is working to implement reforms in pensions and taxation, aiming to stabilize its finances and reduce its debt burden. However, uncertainties in global markets and internal political issues continue to influence Brazil’s fiscal outlook.
8. United Kingdom: The Post-Pandemic Debt Surge
Despite a recent dip in economic growth, the UK’s government debt remains significant, exceeding 100% of GDP in 2025. The country’s economic recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic was hampered by inflation and Brexit-related disruptions, leading to increased borrowing costs and higher debt levels. The government is focusing on fiscal consolidation and growth strategies to bring debt under control without stifling economic recovery.
9. Canada: Keeping Pace with Developments
Canada’s debt has grown to approximately 90% of its GDP, driven by increased government spending on health and economic stimulus measures. While its economy remains resilient, concerns about rising interest rates and inflation pose challenges for debt management. The government continues to prioritize sustainable fiscal policies to ensure long-term stability.
10. Germany: Sustained Debt Challenges
Germany, Europe’s largest economy, has a government debt ratio approaching 70%. Efforts to balance fiscal responsibility with investment needs, such as infrastructure modernization and green energy initiatives, influence debt levels. Political debates continue over the appropriate level of public spending and fiscal discipline to maintain Germany’s economic strength.
As of 2025, the global landscape reveals a complex picture of government debt, with some nations facing significant challenges in maintaining fiscal sustainability. While economic growth and favorable interest rates have temporarily eased concerns, the rising debt levels underscore the importance of prudent fiscal policies to ensure long-term stability.