Select Language:
The Obesity Debate: Exploring Rates in High-Income Countries (2025)
In recent years, the conversation around obesity has intensified, especially in high-income nations. This 2025 analysis ranks countries based on adult obesity rates, revealing a sharp contrast between the most and least obese populations globally. The data gathered from the Global Obesity Observatory provides insights into this growing health crisis.
Most Obese Countries
-
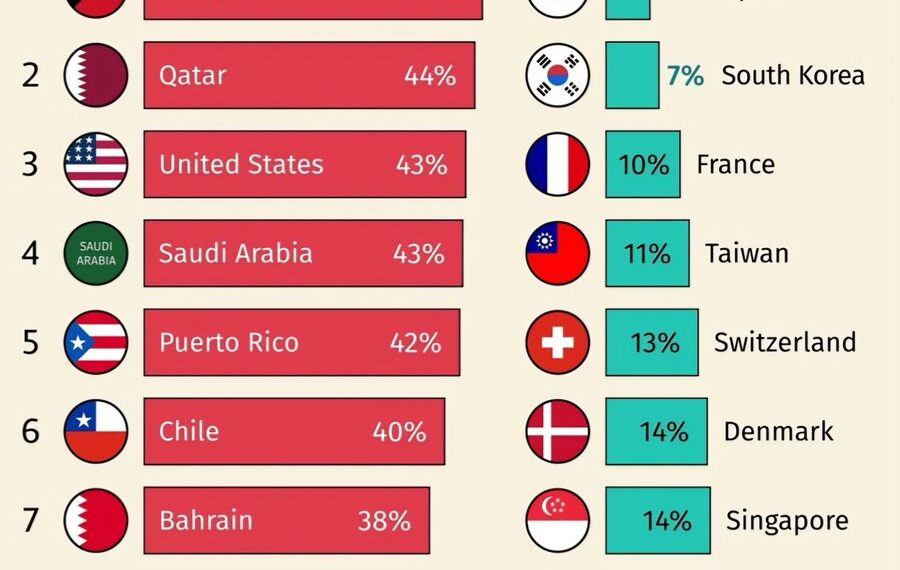
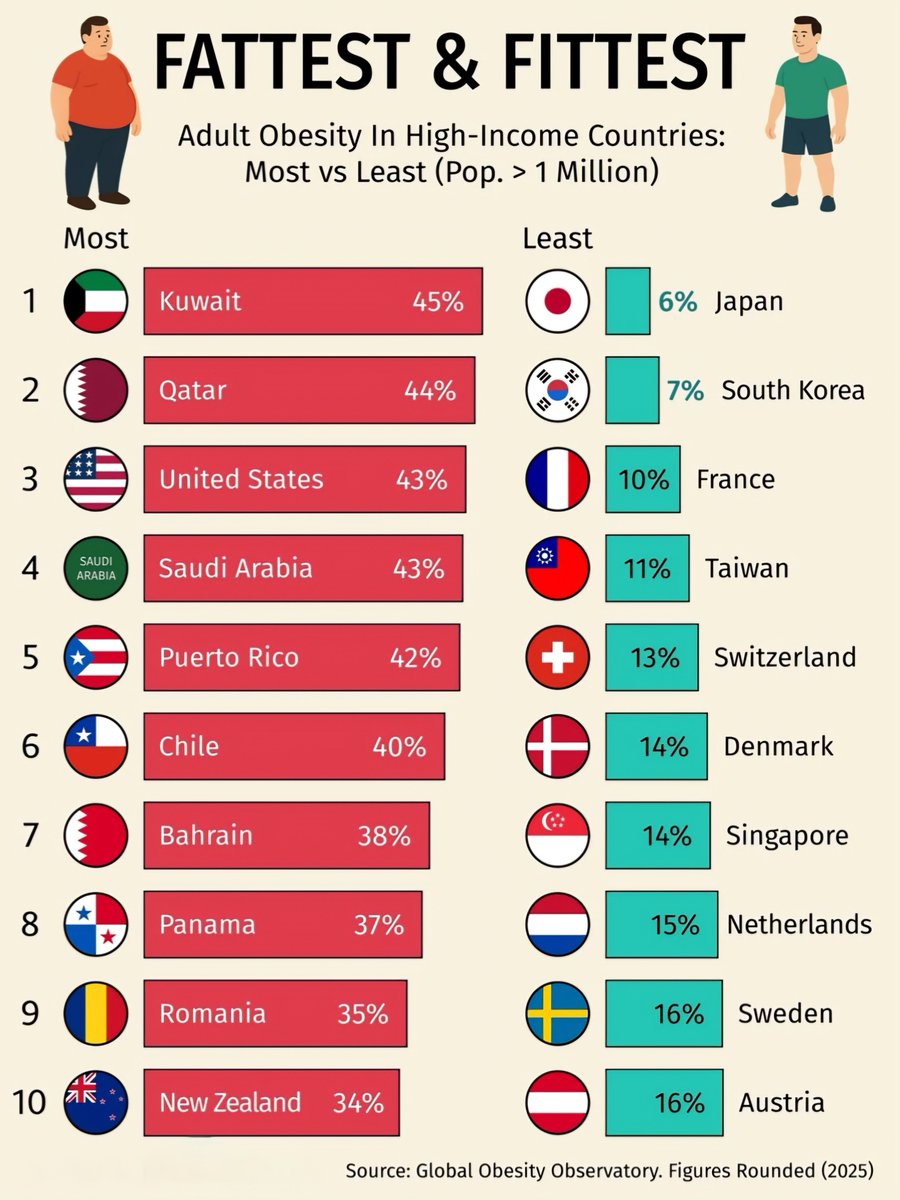
Kuwait – 45%
Kuwait tops the list with the highest obesity rate among high-income countries. This alarming statistic highlights a pressing public health challenge, as sedentary lifestyles and high-calorie diets become prevalent. -
Qatar – 44%
Just behind Kuwait, Qatar faces similar challenges, with nearly half of its adult population classified as obese. Rapid urbanization and diet shifts have contributed to this surge. -
United States – 43%
The U.S. has long struggled with obesity, maintaining a position among the highest rates globally. Factors such as fast food consumption, lack of exercise, and socio-economic disparities exacerbate the issue. -
Saudi Arabia – 43%
Saudi Arabia mirrors the U.S. with its 43% obesity rate. The country’s growing reliance on processed foods and sedentary work environments has led to a significant health crisis. -
Puerto Rico – 42%
Puerto Rico’s bikini beaches might be attractive, but its obesity rate tells a different story, ranking high among the most affected regions. -
Chile – 40%
Chile continues to grapple with rising obesity rates, emphasizing the need for government policies that encourage healthier eating habits and active lifestyles. -
Bahrain – 38%
Bahrain’s increasing obesity levels reflect broader regional health trends, where traditional diets are being replaced by more calorically dense options. -
Panama – 37%
As Panama develops economically, its obesity rate also climbs, raising questions about nutritional education and health awareness. -
Romania – 35%
Romania’s growing obesity rate has raised alarms among health officials, especially as the nation tries to bolster its healthcare system. - New Zealand – 34%
Down south, New Zealand’s obesity challenges may surprise some, but they echo what many developed nations face: a need for better food options and active lifestyle promotion.
Least Obese Countries
-
Japan – 6%
In stark contrast, Japan boasts the lowest obesity rate among high-income countries. Cultural dietary practices emphasize fresh, minimally processed foods contributing to a healthier population. -
South Korea – 7%
South Korea continues to maintain its position as one of the healthiest nations, with lower calorie intakes and higher physical activity levels contributing to this success. -
France – 10%
France’s unique approach to food, which celebrates moderation and quality over quantity, has resulted in lower obesity rates despite a perception of indulgent eating. -
Taiwan – 11%
Taiwan’s emphasis on fresh ingredients and traditional cooking contributes significantly to its low obesity rates, showing the value of cultural dietary practices. -
Switzerland – 13%
Switzerland’s combination of a healthy diet, high quality of life, and active lifestyle plays a significant role in maintaining their lower obesity statistics. -
Denmark – 14%
Denmark’s commitment to public health initiatives and high standards for food quality contribute to its impressive obesity rate. -
Singapore – 14%
Singapore continues to innovate in public health outreach, emphasizing physical activity and balanced diets, significantly lowering obesity rates. -
Netherlands – 15%
The Dutch focus on biking and physical exercise, along with dietary awareness, has kept obesity rates relatively low. -
Sweden – 16%
Sweden’s strong emphasis on health education and community programs promotes active living and healthy eating. - Austria – 16%
Austria’s ranking ties with Sweden’s, showcasing a commitment to wellness and balance in dietary consumption.
Conclusion
The juxtaposition between the most and least obese countries reveals essential insights into global health trends. While some nations battle higher obesity rates, others serve as models of healthy living. Strategies focusing on nutritional education, accessible recreation, and public health initiatives can help address obesity concerns in high-income countries. As nations evaluate their health policies, the goal remains clear: achieving a world where health, wellness, and fitness are prioritized for all citizens.
With the stark differences highlighted by these statistics, it’s imperative to keep the conversation going and propose actionable solutions to combat obesity issues globally.