Select Language:
A Closer Look at Global Wealth Disparities in 2025
1. The Stark Divide Between the Wealthiest and the Rest
A recent graphic encapsulates the stark economic divide worldwide, highlighting that the top 1% of the global population controls nearly half of the world’s wealth, while the bottom 80% share just a fraction. This striking visualization drives home the ongoing inequality that persists even in an era marked by technological advancements and economic growth.
2. Visualizing the Wealth Gap: An Eye-Opening Map
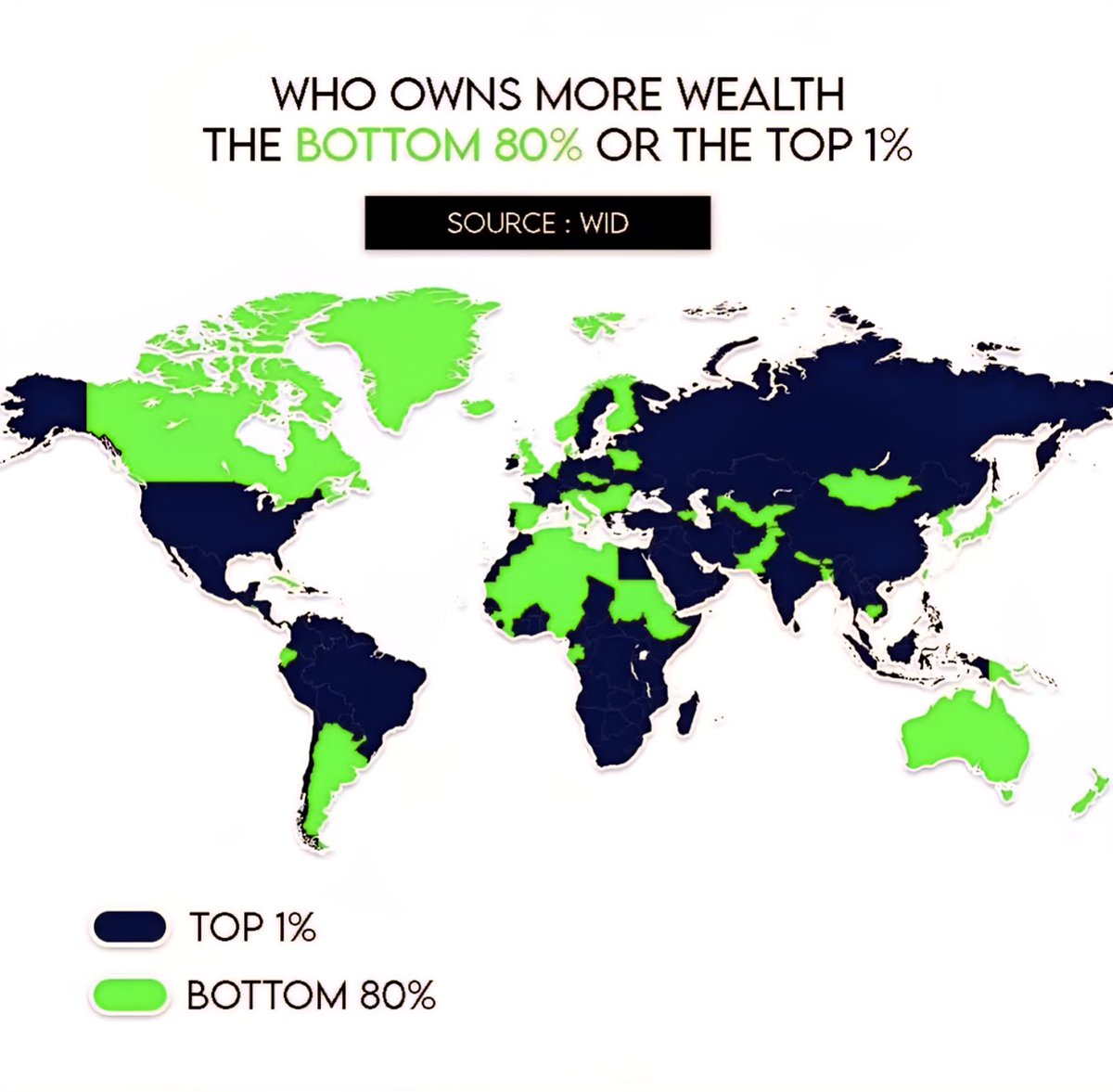
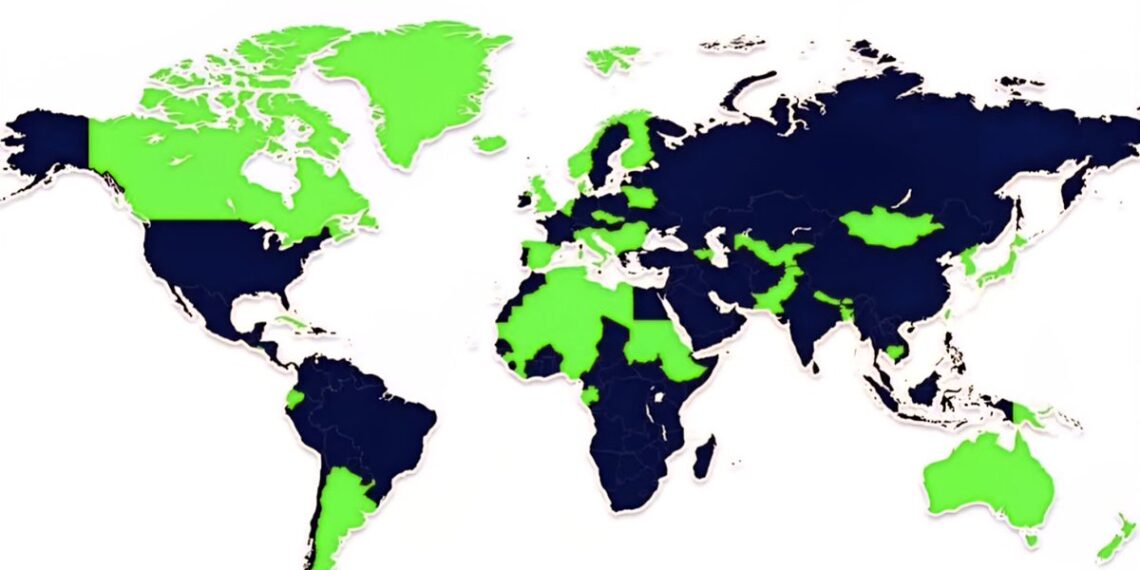
The world wealth map vividly illustrates the disparity, with countries like the United States, China, and numerous Gulf nations having a significant portion of the globe’s assets concentrated among their wealthiest individuals. Conversely, regions in Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, and parts of Southeast Asia showcase vast populations with minimal wealth accumulation, further emphasizing the inequality challenge.
3. How Wealth Is Distributed Across Continents
Throughout North America and parts of Europe, the top 1% holds a disproportionate amount of wealth—sometimes exceeding 50% of national riches. In stark contrast, African and South Asian countries often have a large fraction of their populations in the bottom 80%, living in conditions far removed from the wealth concentrations seen in the West and parts of Asia.
4. The Role of Economic Policies and Globalization
Economic policies, tax laws, and globalization continue to influence this wealth distribution. Many argue that tax loopholes and favorable policies for the ultra-wealthy exacerbate the gap, enabling the billionaires at the top to amass even more wealth compared to the middle and lower classes.
5. Impact on Societal Stability and Development
Excessive wealth concentration at the top raises concerns about social stability. When a small percentage controls such a large share of resources, issues like income inequality, access to quality healthcare, education disparities, and political influence become magnified, potentially destabilizing societies and hindering inclusive development.
6. Emerging Trends in Wealth Redistribution Efforts
In recent years, initiatives such as wealth taxes, social welfare programs, and increased transparency in financial transactions aim to address this imbalance. Several countries are experimenting with policies designed to curb wealth concentration, although results are mixed and often met with resistance from affected elites.
7. The Future Outlook: Will the Gap Narrow?
Predictions suggest that unless substantial policy changes are adopted worldwide, the wealth disparity depicted in the map will persist or even worsen by 2030. Efforts to promote equitable economic growth, increase access to education, and implement fair taxation are critical to reversing this trend.
8. The Necessity of Global Cooperation
Addressing wealth inequality requires coordinated international action. Multilateral organizations, governments, and civil society must collaborate to develop strategies that ensure wealth is more evenly distributed, fostering economic resilience and social justice.
9. The Human Factor: Economic Inequality and Well-Being
Behind the numbers are real lives affected by economic disparities. From access to clean water and healthcare to educational opportunities and safe living conditions, wealth gaps influence every aspect of human well-being. Recognizing this human element is key to understanding the urgency of tackling this issue comprehensively.
10. Taking Action: What Can Be Done?
Individuals, policymakers, and corporations all have roles to play in narrowing the wealth divide. Advocacy for fair tax systems, corporate responsibility, social investments, and supporting poverty alleviation programs are vital steps toward building more equitable societies.
Image credit: World Wealth Map 2025
As the global economy evolves, understanding and addressing these disparities remain crucial for fostering sustainable growth and social cohesion worldwide.