Select Language:
The Evolution of Remote Work: Insights and Trends
The landscape of work has undergone a dramatic transformation over the last few years, primarily driven by the Covid-19 pandemic. As organizations faced unprecedented challenges, they swiftly adapted to the new reality—one where remote work became not just a necessity but a viable option for the future.
The Rise of Remote Work
In the wake of the pandemic, what started as a temporary shift evolved into a long-term strategy for many companies worldwide. Workers gained increased flexibility, reduced commuting time, and an improved work-life balance. As the world gradually returned to a semblance of normality, remote work didn’t simply fade away; it endured and diversified.
The Statistics Behind the Shift
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), more than 20% of workers, equating to nearly 35 million Americans, engaged in remote work at least occasionally by April 2025. This significant number indicates how deeply entrenched the remote work culture has become across various industries.
Industry Variations in Remote Work
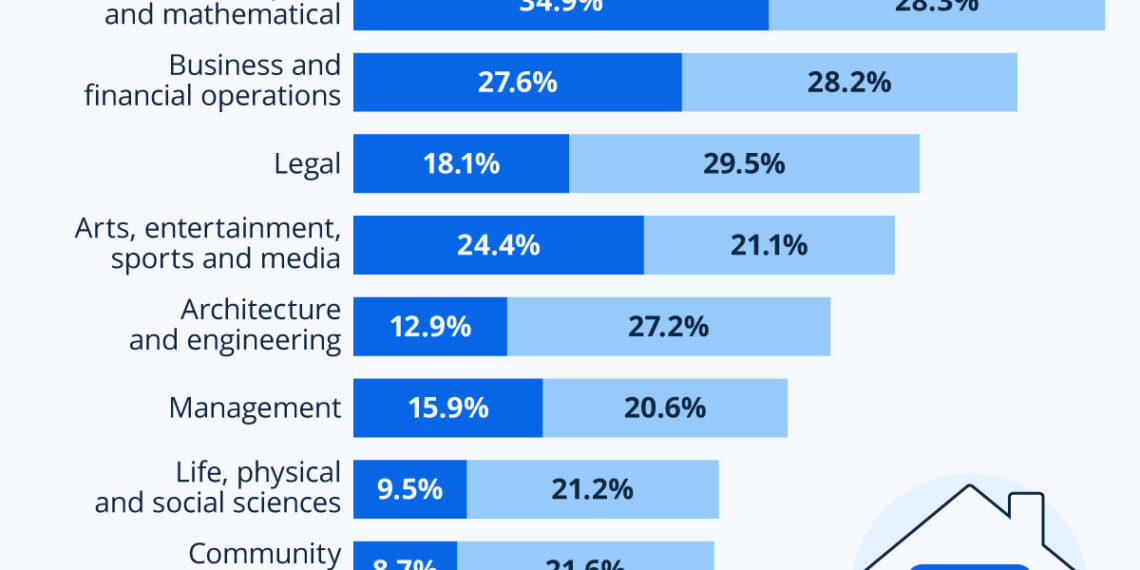
Notably, the prevalence of remote work varies widely among different sectors. While many service or production occupations can hardly accommodate working from home—where rates remain in the low single digits—white-collar jobs demonstrate a stark contrast.
-
Technology Sector: A remarkable 60% of workers in computer and mathematical occupations worked remotely at least part of the time. Moreover, over one-third of these workers operated entirely outside the traditional office environment.
-
Business and Financial Services: These fields also reported high telework rates, reflecting the digital nature of their tasks.
- Legal Professions: Legal workers experienced similar trends, benefiting from the flexibility that remote work affords.
A Closer Look at Occupations
The divide in remote work prevalence highlights the considerable differences in workplace flexibility across various occupations.
Professional and Management Roles
Approximately 36% of workers in management roles, as well as those in professional and related positions, engaged in remote work at least occasionally by April 2025. The ability to manage teams and processes online has reshaped perceptions of effective leadership.
Sales and Office Jobs
Workers in sales and office occupations experienced a telework rate of around 23%. This statistic underscores the adaptability of these roles to digital communication and collaboration tools, enabling employees to maintain productivity outside of traditional office environments.
Service and Production Industries
In stark contrast, service-related roles had a mere 5.5% of workers telecommuting, showcasing the challenges these sectors face. Similarly, construction and maintenance occupations noted a telework rate of just 3.5%, while production and transportation occupations lagged even further at 2.8%. The hands-on nature of these professions often necessitates physical presence.
Changing Workplace Dynamics
The shift towards remote work has fundamentally altered workplace culture and employee expectations. Flexibility has become a critical consideration for job seekers, influencing recruitment techniques and employee retention strategies.
As businesses continue to navigate this new landscape, the importance of ensuring a balanced approach to remote and in-office work becomes more evident. Embracing hybrid models, which allow for both remote and in-person interactions, is becoming a popular solution for many organizations.
Future Outlook
As remote work solidifies its place in the corporate world, ongoing discussions around its implications for productivity, collaboration, and employee satisfaction remain essential. Companies must explore ways to harness the benefits of remote work while addressing the unique challenges that accompany this new paradigm.
The conversation surrounding remote work is far from over. As industries evolve and adapt to these changes, the dynamics of the workplace will continue to shift, paving the way for innovative practices that redefine how we think about work.