Select Language:
Key Takeaways from the 2019 North Korean Election Results
1. Near-Universal Voter Turnout Signals a State-Controlled Election System
The 2019 North Korean elections once again showcased an almost 100% voter turnout, with reported figures exceeding 99%. Such overwhelming participation underscores the tightly controlled political landscape in North Korea, where voting is less about choice and more about obligatory participation. The government encourages and orchestrates this near-total involvement, reinforcing the regime’s image of unwavering support among its citizens. Despite international scrutiny, these figures illustrate the regime’s ability to mobilize voters across its highly centralized electoral framework.
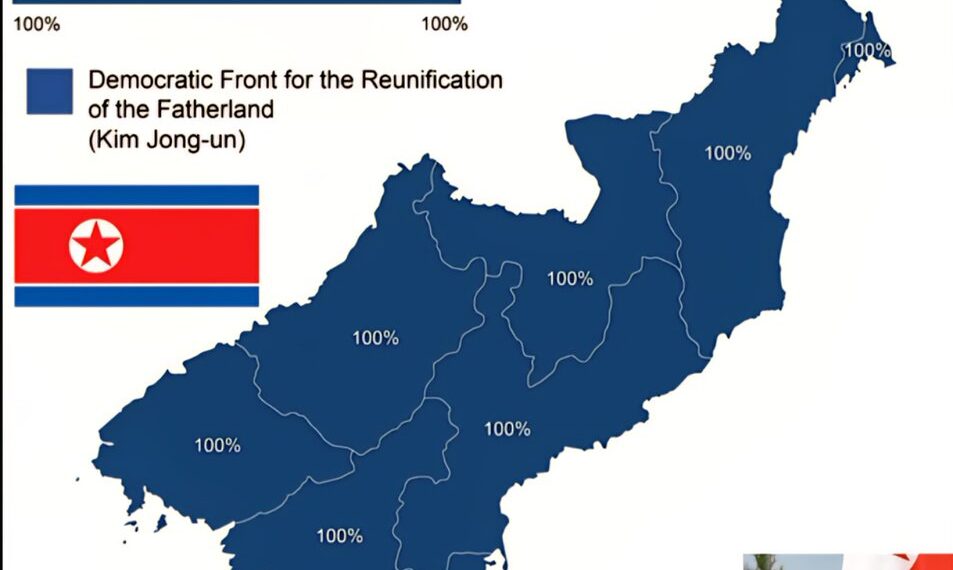
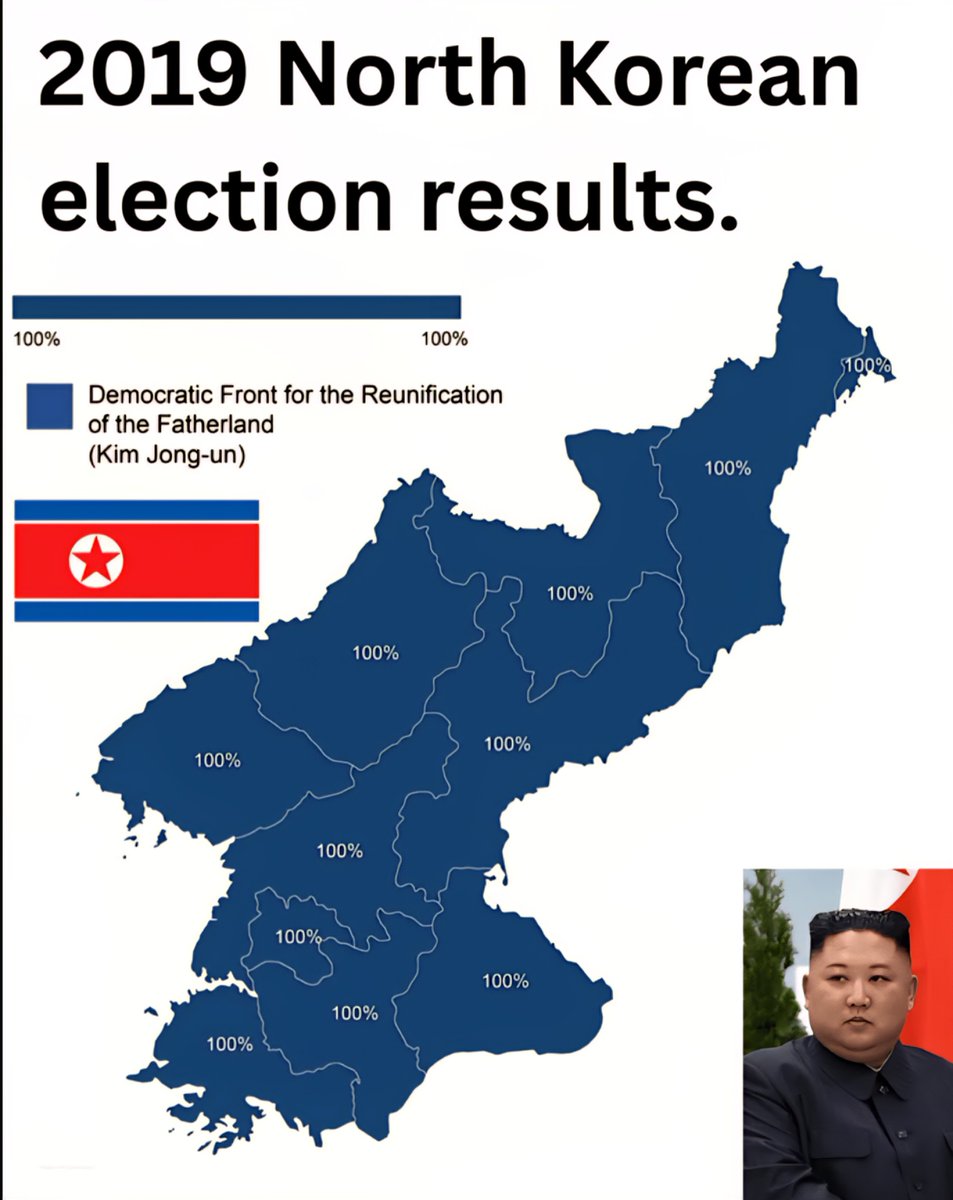
2. Official Results Show Near-Uniform Support for the Ruling Party
According to official sources, the Workers’ Party of Korea (WPK) and allied candidates garnered 100% of the vote across all districts. Campaigns are typically a formality, with candidates pre-selected and approved by the ruling authority. Such results—claiming every vote for the ruling party—are symbolic displays of unity designed to project stability and absolute loyalty to Prime Minister Kim Jong-un’s regime. Independent candidates or opposition are virtually non-existent, ensuring the electoral narrative remains tightly controlled.
3. The Election Serves as a Political Affirmation Rather Than Democratic Choice
Unlike competitive democracies, North Korean elections do not serve as platforms for political debate or policy change. Instead, they function as reaffirmations of the existing power structure. Ballot casts are often seen as pledges of loyalty rather than votes for choice; voting is considered a duty, and refusing to participate can lead to suspicion or punishment. The focus remains on maintaining regime stability through these staged electoral events rather than fostering genuine democratic representation.
4. Infrastructure and Voting Locations Demonstrate Authoritarian Control
Photos and reports from the 2019 election reveal meticulously organized voting stations, often situated within government facilities and community centers. Citizens line up mostly in orderly fashion, under the eye of state officials. The government exercises tight control over public spaces, and foreign observers are generally denied access. Such measures prevent any expression of dissent and reinforce the narrative that election results are accepted universally, bolstering the regime’s authoritative image.
5. The Role of Propaganda and State Media in Shaping Election Narratives
North Korean state media played a significant role in portraying the 2019 elections as a manifestation of the people’s unwavering support for their leader. News reports emphasized the high turnout and “enthusiastic participation,” framing the election as a patriotic duty. Propaganda materials highlighted images of jubilant voters and massive turnout celebrations. These narratives serve to cultivate a sense of national unity and loyalty, even as outside observers view the elections as largely symbolic exercises in consolidating power.
6. International Community’s Perspective on North Korean Elections
Global observers and countries generally regard North Korean elections as symbolic and lacking democratic legitimacy. The international community criticizes them as exercises manufactured to reinforce the regime’s authority rather than genuine democratic processes. Human rights organizations highlight the absence of political pluralism, freedom of speech, and the lack of fair competition. Despite these criticisms, the North Korean government maintains that these elections are vital for national sovereignty and stability.
7. Implications for North Korea’s Political Future
With the 2019 elections signaling continued unwavering support for Kim Jong-un’s regime, North Korea remains firmly under its centralized control. No significant political reforms are anticipated in the immediate future, as the governance model relies heavily on authoritarian control and propaganda. The elections serve more as ritual reaffirmations of loyalty than actual opportunities for political change, indicating the regime’s commitment to maintaining the current power structure.
Note: The details in this article provide a comprehensive overview of the 2019 North Korean elections, reflecting the regime’s political tactics and societal control mechanisms. As of 2025, these practices continue to shape North Korea’s political landscape, ensuring the stability of its leadership while posing ongoing challenges for international diplomacy and human rights efforts.