Select Language:
The Changing Landscape of Job Switching: An Analysis
The Great Resignation Phenomenon
In 2022, millions of Americans made headlines as they opted to quit their jobs, giving rise to what is now known as the "Great Resignation." A staggering 50 million workers left their positions, driven largely by a substantial demand for labor. This shift allowed employees to leverage their skills in a competitive job market, often securing more lucrative offers from new employers.
Higher Wages for Job Switchers
The Initial Surge
Data from ADP Pay Insights highlighted a remarkable trend: job switchers enjoyed median pay increases exceeding 15% throughout much of 2022. This contrasted starkly with the experiences of those who remained in their current positions, where average pay hikes hovered around 7-8%. The opportunity for immediate financial growth was a significant motivator for many as they sought better compensation packages.
The Impact of Labor Shortages
The labor shortage during this period enabled workers to negotiate effectively. As companies struggled to fill open positions, they raised wages to attract new talent. The market dynamics favored job changers, making it an ideal moment to seek new opportunities.
The Shift in the Job Market
Cooling Down of Labor Demand
As we moved into 2023 and beyond, the labor market began to stabilize. Job openings, which had once reached peak levels, started to decline, and the number of unfilled positions across various sectors decreased. This shift indicated a balancing act between labor supply and demand.
Wage Growth Trends
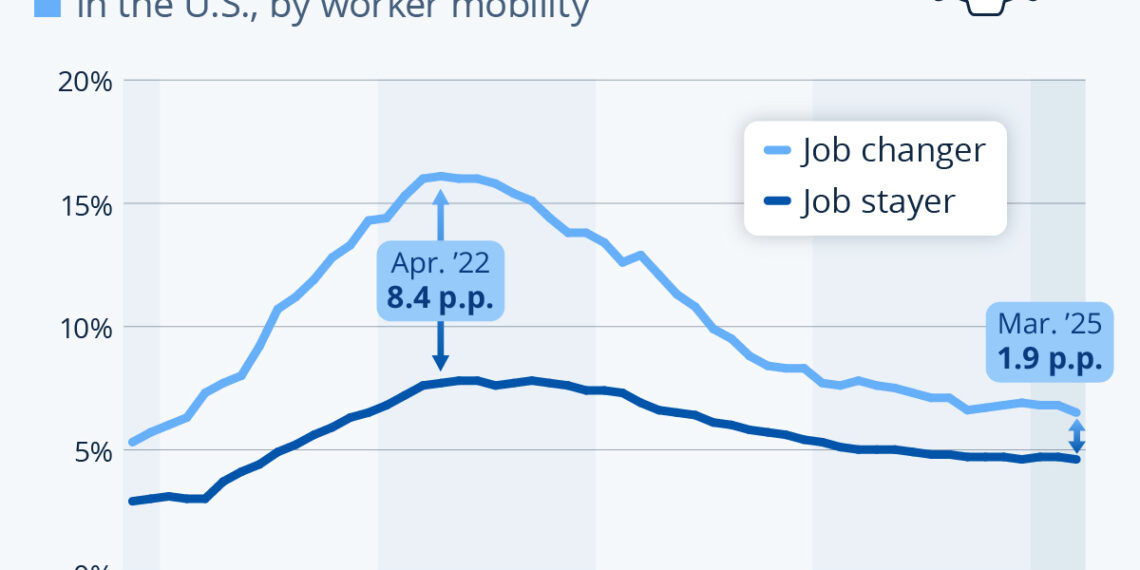
Correspondingly, wage growth slowed. ADP data indicated that the gap between the pay increases for job switchers and job stayers decreased dramatically. What was once an 8.4 percentage point advantage in April 2022 narrowed down to just 1.9 percentage points by March 2025. This shift reflects a more balanced labor market where the competitive edge gained by switching jobs is diminishing.
The Decline of Job Quitting Rates
Ending the Great Resignation
With the easing of the labor crunch, it’s noteworthy that fewer individuals are quitting their jobs. The initial wave of resignations, fueled by the allure of better compensation, has dwindled as job security and consistent pay rises within existing roles become more common.
Long-Term Implications for Workers
This trend signifies a potential cultural shift in workplace dynamics. Loyalty to employers may increase as job stability returns and workers become more conservative in their career moves. This changing sentiment could reshape how companies approach talent retention and employee satisfaction.
Employers’ Response to the Shift
Adjusting Compensation Strategies
In response to these changes, many employers are recalibrating their compensation strategies. To retain talent, businesses are focusing on improved benefit offerings, workplace culture, and growth opportunities.
Emphasis on Talent Retention
With the current labor market trends, companies are recognizing the importance of fostering long-term relationships with their employees. This has led to increased investment in employee training and development, as organizations aim to enhance workforce capabilities without the need for constant turnover.
Conclusion
The evolving job market highlights a transition from a worker’s advantage to a more balanced approach where both job seekers and employers must adapt to new realities.