Select Language:
Understanding Global Variations in Autism Diagnosis Rates
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) diagnosis rates exhibit significant disparities across different countries, influenced by various factors including healthcare access, awareness, and diagnostic practices. The variations shed light on the complexities of understanding autism on a global scale.
Autism Diagnosis Rates by Country
Recent data from the World Population Review highlights stark contrasts in autism diagnosis rates among countries.
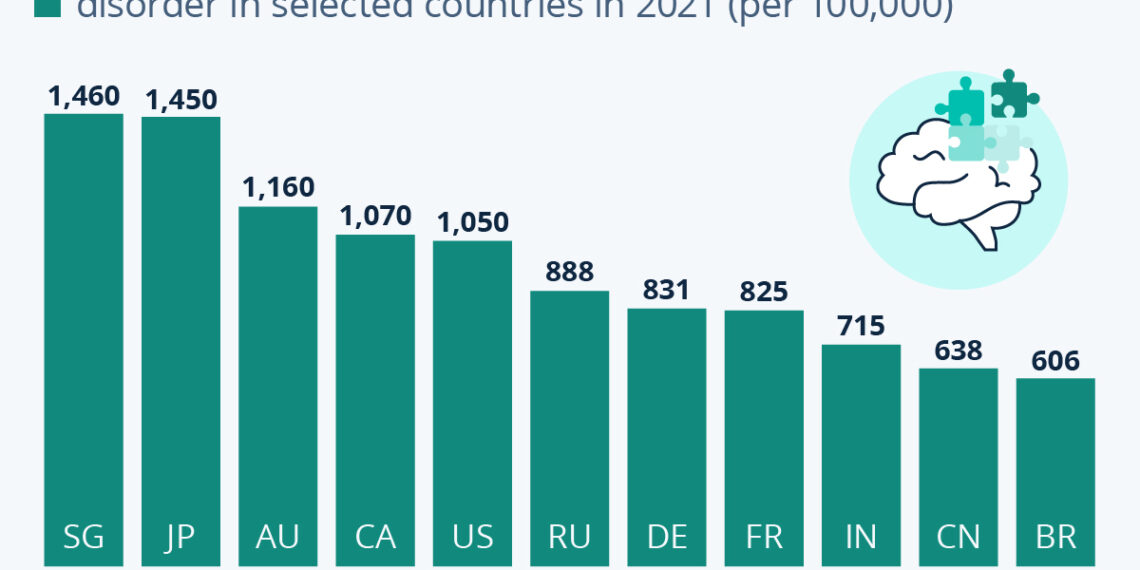
Countries with High Diagnosis Rates
- Singapore: 1,460 per 100,000 children
- Japan: 1,450 per 100,000 children
- Australia: 1,160 per 100,000 children
These countries are characterized by robust healthcare systems and high levels of public awareness regarding autism. The infrastructure in these nations may contribute to earlier and more frequent diagnoses.
Countries with Low Diagnosis Rates
- China: 638 per 100,000 children
- Brazil: 606 per 100,000 children
In contrast, countries like China and Brazil report significantly lower diagnosis rates. These figures may indicate under-diagnosis rather than a lower prevalence of ASD. Factors such as limited access to healthcare services and a lack of awareness about autism play pivotal roles in these statistics.
Factors Affecting Diagnosis Rates
The variations in autism diagnosis rates between countries are influenced by several key factors:
Access to Health Services
The presence of advanced healthcare systems allows for better identification and management of ASD. Countries with more resources are likely to have specialist centers, trained professionals, and screening programs that facilitate earlier and more accurate diagnoses.
Diagnostic Methodologies
Different regions may employ varied diagnostic criteria and methodologies when assessing autism. Some nations adhere to stringent guidelines, while others may have less standardized approaches, leading to inconsistencies in diagnoses.
Public Awareness and Education
A high level of public awareness regarding autism often correlates with increased diagnosis rates. Countries that emphasize education about ASD through campaigns and training programs tend to set a foundation for better detection of the disorder.
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Definition and Impact
ASD is defined as a developmental condition affecting how individuals perceive and interact with the world around them. It can lead to challenges in social interaction, communication, and the emergence of restrictive and repetitive behaviors. The term "spectrum" reflects the diverse range of symptoms and severity that can manifest in affected individuals.
Observations from Global Data
The higher prevalence of autism diagnoses in certain regions does not equate to a greater number of individuals with autism. Instead, it may signify more effective health systems capable of identifying and diagnosing the disorder. Conversely, regions with fewer medical resources may struggle with under-reporting, impacting the overall understanding of autism’s prevalence.
Worldwide Awareness Initiatives
April 2nd is recognized as World Autism Awareness Day, a global event aimed at raising awareness about ASD and promoting acceptance. This day serves as a platform for advocating for improved services and support for individuals on the autism spectrum and their families.
By studying the various factors influencing autism diagnosis rates globally, we can better understand the complexities surrounding this developmental disorder and work toward more equitable healthcare solutions.