Select Language:
Understanding Food Intolerances: A Global Perspective
Food intolerances have emerged as a significant health concern for many individuals worldwide, affecting their choices and lifestyles. Recent findings from a limited survey by Statista Consumer Insights reveal fascinating insights into the prevalence of food intolerances across different countries.
Prevalence of Food Intolerances
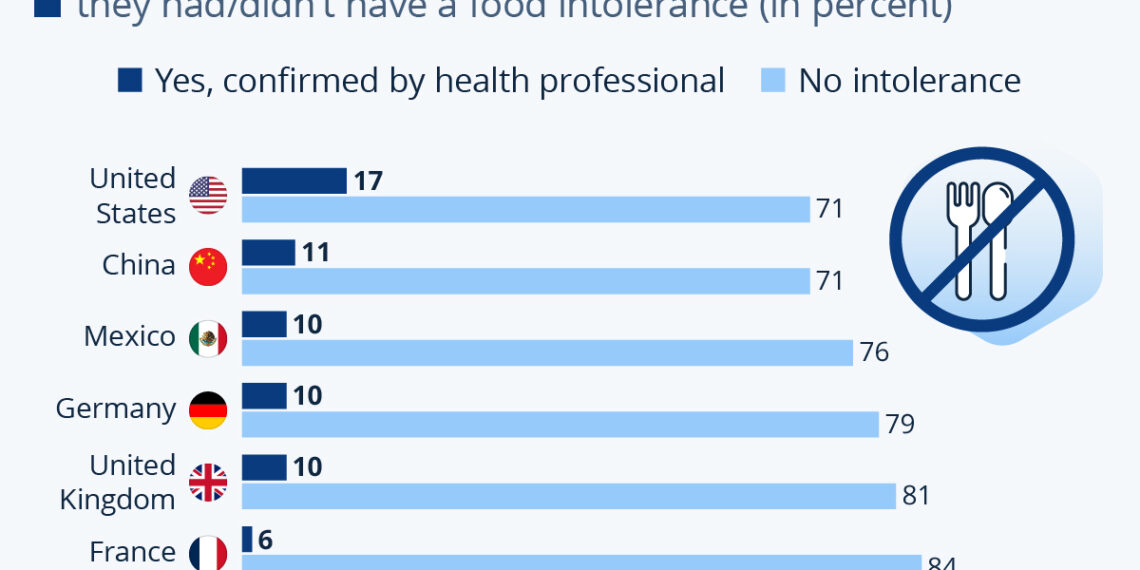
The survey indicates that between 6% and 17% of respondents reported having a food intolerance verified by a health professional. This figure varies significantly by location:
- United States: The highest percentage of confirmed food intolerances is found here, reflecting a growing awareness and health consciousness among its populace.
- France: Interestingly, this country reported the lowest incidence of confirmed food intolerances, suggesting cultural dietary factors or possibly differing diagnostic approaches.
- Other Countries: In the United Kingdom, Germany, Mexico, and China, the rates range between 10% and 11%, showing that food intolerances are a global issue and not limited to specific regions.
Common Food Intolerances
Food intolerances can manifest in various forms, often leading to discomfort and dietary restrictions. According to the NHS, several common intolerances include:
Lactose Intolerance
Lactose intolerance occurs when the body lacks the enzyme lactase, which is needed to digest lactose—a sugar found in milk and dairy products. Symptoms can include bloating, gas, and diarrhea after consuming dairy.
Gluten Intolerance
Gluten intolerance or non-celiac gluten sensitivity can cause gastrointestinal discomfort and other symptoms after the ingestion of gluten, even in individuals who do not have celiac disease.
Histamine Intolerance
Histamine intolerance arises when the body cannot effectively break down histamine, leading to symptoms such as headaches, skin irritation, and digestive issues when consuming histamine-rich foods.
Sulphite Sensitivity
Certain individuals may react to sulphites, commonly used as preservatives in foods and beverages. Reactions can range from mild headaches to severe allergic responses.
Other Intolerances
Individuals may also experience sensitivities to substances such as caffeine, alcohol, and salicylates, naturally occurring compounds found in many fruits and vegetables.
The Trend and Misconceptions
The rise in diagnoses of food intolerances has led to an increase in individuals eliminating specific foods from their diets. While some do so for valid health reasons, others may abandon foods based on trends or perceived health benefits. This phenomenon raises questions about the difference between health awareness and fad diets.
As more people become hyperconscious about what they eat, the line between legitimate dietary restrictions and trending health movements becomes increasingly blurred. As a result, the discourse surrounding food intolerances often oscillates between valid medical conditions and societal trends.
The Role of Awareness
The increasing prevalence of diagnosed food intolerances suggests a shift toward greater health awareness and proactive health management. Many individuals seek out health professionals for clarity on their dietary restrictions, leading to more accurate diagnoses and better support systems.
In different cultures, food intolerances can be viewed through varying lenses. In some countries, dietary restrictions may be met with skepticism, while in others, they are readily accepted and accommodated.
The landscape of food intolerances continues to evolve, with future developments expected as awareness grows and more research is conducted in this field. As people continue to explore their relationship with food, the implications for public health and nutrition remain critically important.