Select Language:
Significant Changes in Per Capita Electricity Consumption from 2000 to 2025
1. Dramatic Shift in Energy Consumption Patterns
Between 2000 and 2025, per capita electricity usage has undergone a notable transformation. In 2000, many countries exhibited lower average consumption, reflecting less reliance on electricity-intensive technologies. By 2025, a combination of rapid technological advancements, increased urbanization, and economic growth has propelled per capita electricity use to new heights. This shift indicates not only rising energy demands but also a broader adoption of digital devices, electric vehicles, and smart technologies in daily life.
2. The Surge of Renewable Energy Adoption and Its Impact
The increasing transition toward renewable energy sources has significantly influenced electricity generation and consumption. Countries investing heavily in solar, wind, and hydroelectric power have seen their per capita electricity consumption rise in tandem with renewable capacity. This evolution has led to more sustainable energy consumption patterns, reducing dependence on fossil fuels, and promoting cleaner energy use per individual.
3. Urbanization and Smart Infrastructure Driving Consumption
Major urban centers have expanded rapidly over the past two decades, resulting in higher electricity demands. Modern cities now incorporate smart infrastructure—like connected homes and automated systems—that optimize energy efficiency but also contribute to higher overall per capita consumption. The proliferation of smart grids and building management systems has enabled more detailed tracking and increased usage of electricity among urban dwellers.
4. The Rise of Electric Vehicles and Transportation Electrification
The transportation sector has seen a paradigm shift, with electric vehicles (EVs) becoming mainstream by 2025. The widespread adoption of EVs has added substantial load to residential and commercial electricity grids. This transition from traditional combustion engines to electric transportation means that individual transportation habits now significantly influence per capita electricity consumption.
5. Digital Transformation and Increased Device Usage
The explosive growth of smartphones, laptops, tablets, streaming services, and smart appliances has contributed to a substantial increase in household electricity use. By 2025, digital devices are more integrated into daily life than ever before, with many households controlling everything from lighting to security systems via internet-connected devices, consequently increasing per capita power consumption.
6. Energy Efficiency Improvements and Their Limitations
While technological improvements in energy efficiency have been adopted globally, they haven’t been enough to offset the surge in overall consumption driven by modern lifestyles. High-efficiency appliances and LED lighting have somewhat mitigated increases, but the net effect remains an uptrend in per person electricity use, especially in emerging economies experiencing rapid development.
7. Healthcare and Industrial Sector Expansion
Healthcare facilities, especially in developed nations, rely heavily on continuous electricity for advanced medical equipment, lighting, and climate control. Similarly, industrial productivity increases, powered by automation and digital manufacturing, demand more electricity per capita. Both sectors have contributed to the upward trend in consumption, showcasing how infrastructure and technological needs shape energy patterns.
8. The Environmental and Policy Drivers
Environmental concerns and climate policies have nudged many nations to rethink their energy consumption strategies. While some countries have succeeded in decoupling economic growth from energy use, others continue to see per capita electricity consumption grow due to infrastructural investments and modernization efforts. These policy shifts directly impact how much electricity individuals use and help shape future patterns.
9. The Continued Impact of Global Economic Growth
Economic advancement remains a primary driver of increased per capita electricity consumption. Countries experiencing sustained economic growth generally see a corresponding rise in energy use. This growth supports better living standards but also presents challenges for sustainable energy management.
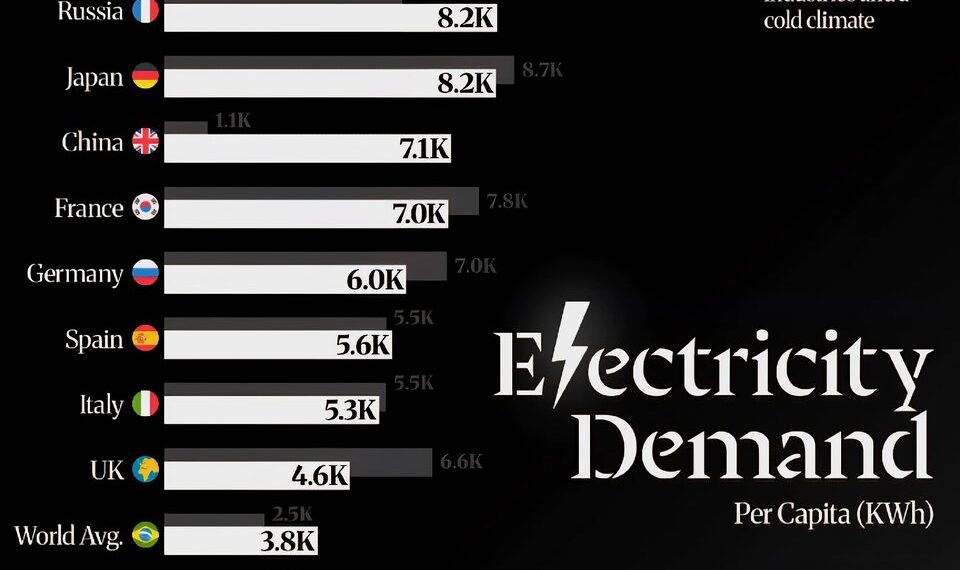
10. Visualizing the Change: A Comparative Perspective
Insert the image here
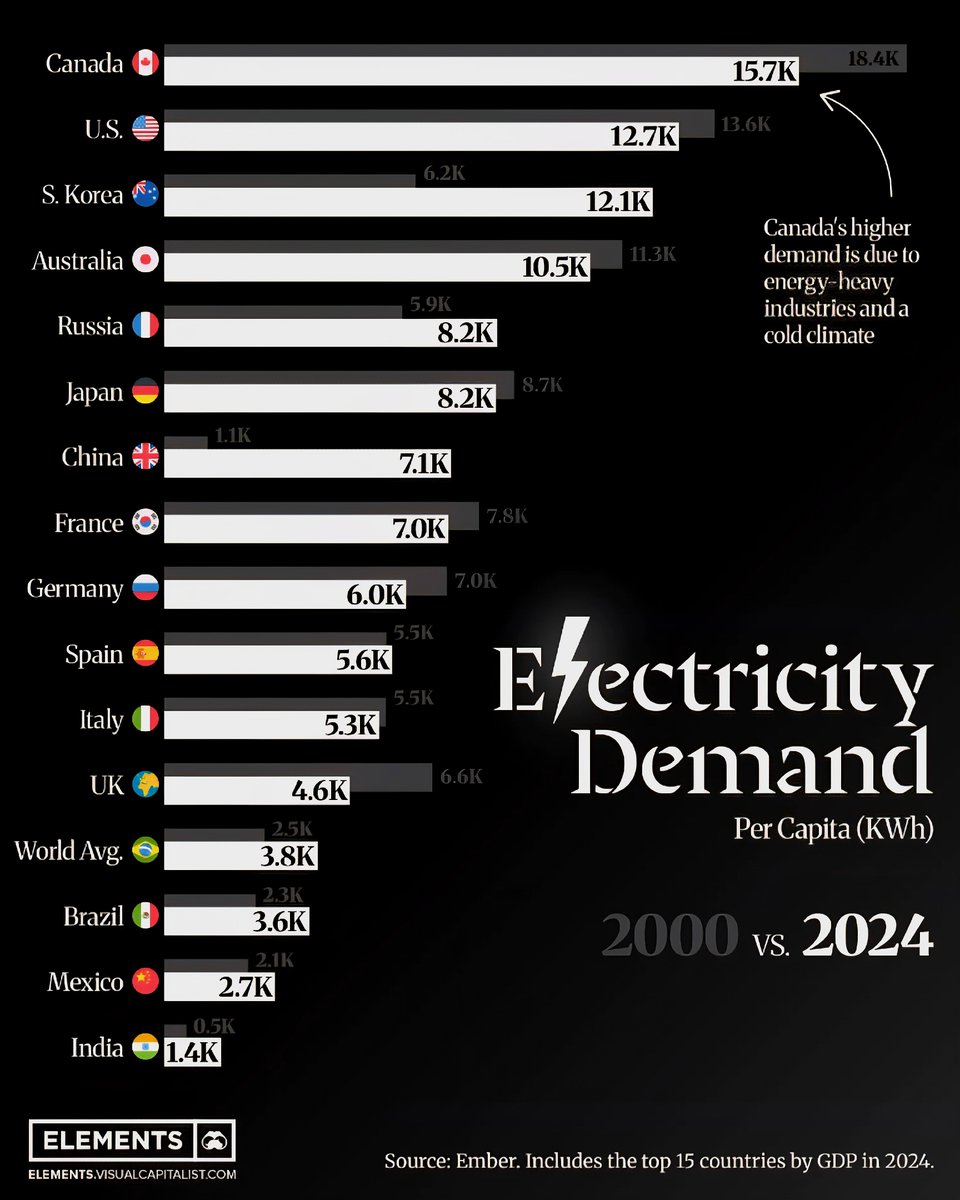
The visual comparison clearly illustrates how personal energy consumption has escalated over the decades. Data indicates that in 2025, especially in rapidly developing nations, individual electricity use has doubled or even tripled since 2000, emphasizing the profound transformations across global energy landscapes.
The decade-long journey from 2000 to 2025 showcases a complex web of technological, social, and economic factors driving changes in per capita electricity consumption. As countries continue to evolve and innovate, understanding these patterns will be crucial for crafting sustainable energy policies to meet future demands.