Select Language:
The Surprising Population Parity Between Two Global Regions
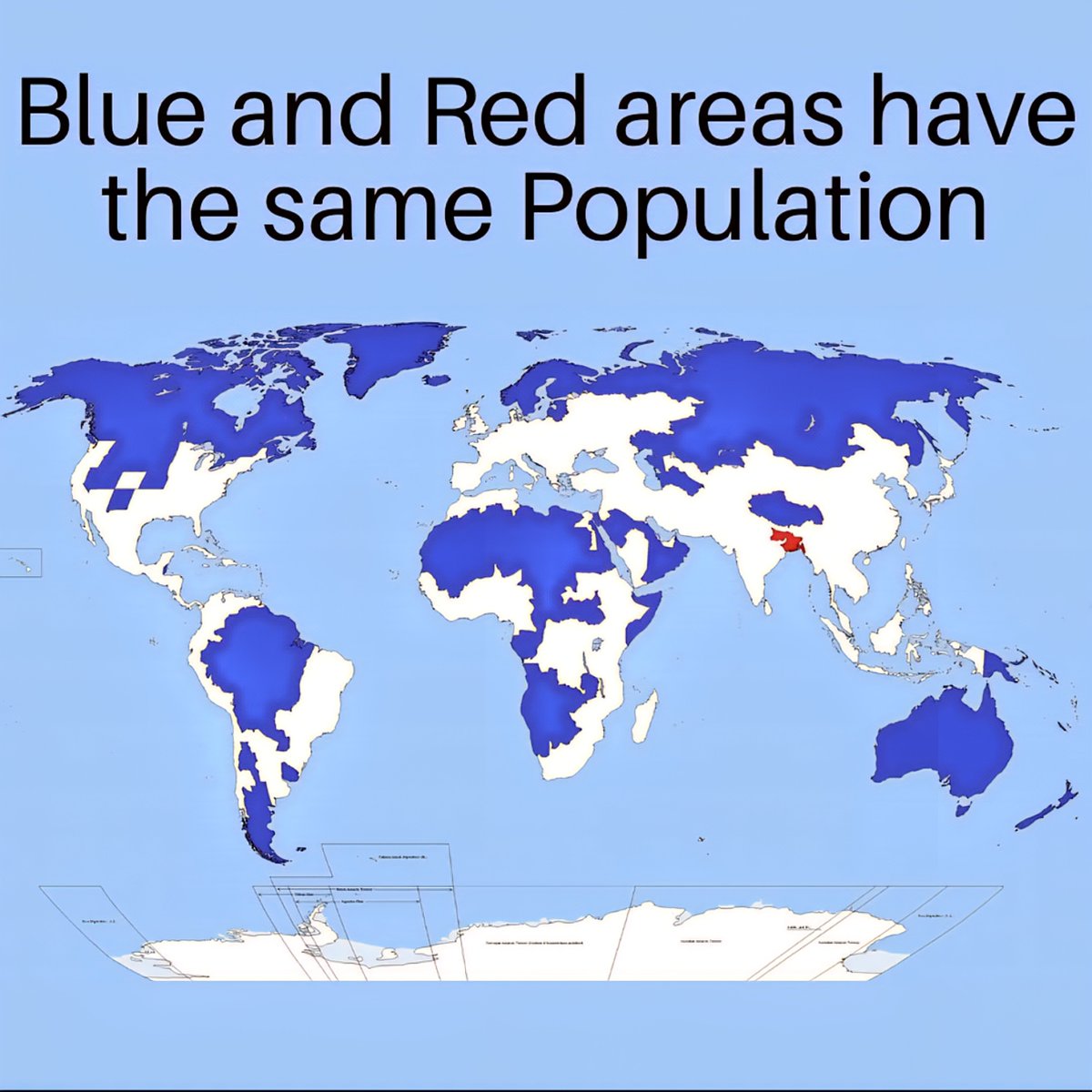
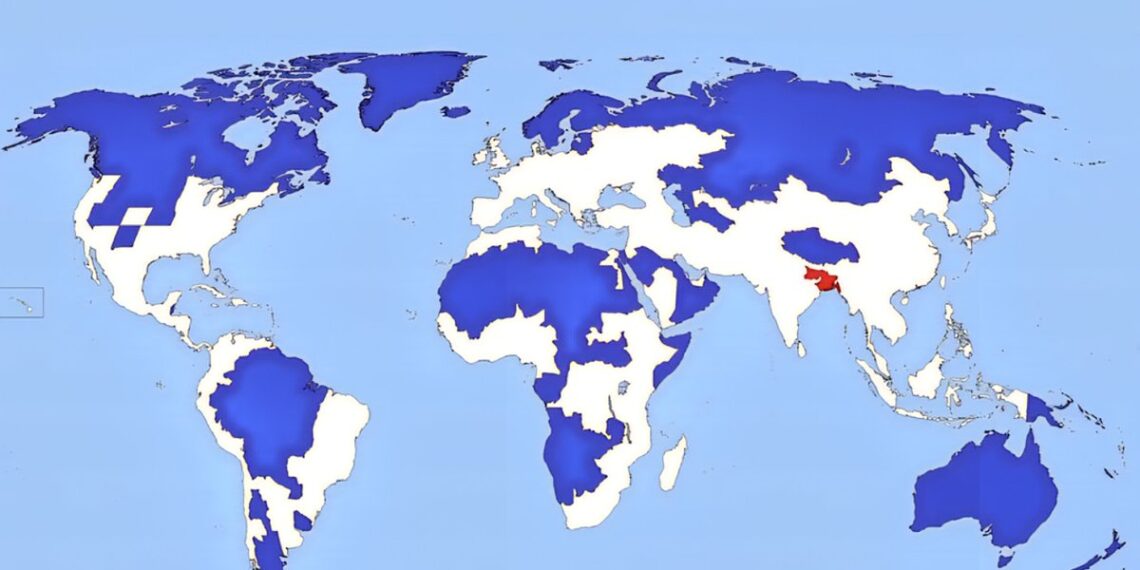
In a striking revelation made in 2025, new data shows that two distinct regions across the globe—one marked by the color red and the other by blue—each house exactly 5% of the world’s population. This finding challenges common assumptions about population distribution and highlights the importance of understanding the demographic nuances that shape our world.
The Red Zone: A Compact but Critical Population Cluster
- Represents 5% of the world’s population, making it a significant yet contained demographic segment.
- Located primarily within regions characterized by densely populated urban centers and territories with high birth rates.
- Contains countries such as India, Nigeria, and Indonesia, which are often grouped under the “fast-growth” category.
- Despite its fairly small global share, this region’s rapid population increase poses future challenges for infrastructure, resources, and environmental sustainability.
The Blue Zone: An Urban and Economic Powerhouse
- Equally accounts for 5% of the global population, yet its demographic makeup differs markedly from the red zone.
- Encompasses highly urbanized, economically developed countries, including parts of Europe, North America, and East Asia.
- Regions within the blue zone tend to have aging populations but possess significant technological, financial, and cultural influence worldwide.
- Its population density may be lower than the red zone’s in some areas, but their global impact remains substantial due to economic strength and technological innovation.
The Meaning Behind the Numbers
This parity in population figures between such contrasting regions offers a compelling glimpse into the world’s demographic diversity. It underscores the demographic shifts driven by urbanization, birth rates, mortality rates, and migration patterns—all key factors shaping the future of global population dynamics.
While the red zone continues to grow rapidly, driven by high birth rates and expanding economies in developing countries, the blue zone’s population mostly faces aging and stagnation, echoing trends observed in the early 21st century. Balancing these contrasting demographic realities will remain a pressing concern for policymakers, environmentalists, and global organizations heading into 2025.
Population Distribution: A Closer Look
- Urbanization Trends: The red area is witnessing a surge in urban populations, with megacities expanding rapidly to accommodate swelling numbers. Conversely, the blue zone is seeing aging populations leading to concerns over workforce sustainability.
- Resource Allocation: The red zone’s population boom stresses food systems, healthcare, and education infrastructure, necessitating innovative solutions for sustainable development. Meanwhile, the blue zone’s more stable population requires adjustments in pension systems, healthcare services, and social support structures.
- Migration Flows: Migration from the red to blue regions influences demographic patterns, often resulting in diverse cultural landscapes within immigrant-dense countries. This movement adds complexity to population estimations and policy planning.
Future Implications
The fact that two regions, vastly different in economy, culture, and demographic structure, each bear 5% of the world’s population emphasizes the crucial need for targeted strategies to address their unique challenges. As the global population edges towards approximately 8 billion, understanding these demographic balances becomes pivotal for sustainable growth, climate resilience, and international cooperation.
In summary, the revelation that the red and blue regions each constitute 5% of the global populace unveils a nuanced story of demographic disparity and convergence. Governments, researchers, and organizations worldwide will need to navigate these complexities over the coming years to foster equitable and sustainable development.
Note: The image provided visually emphasizes the population distribution between the two regions, making this demographic insight even more striking.