Select Language:
The Rise of Germany’s Far-Right AfD: An In-Depth Analysis
In the contemporary political landscape of Germany, the Alternative für Deutschland (AfD) party has become a significant player, capturing the attention of both citizens and political analysts alike. Recently, a poll conducted between February 11 and 13 revealed that one in five Germans expressed their willingness to vote for the AfD, placing it in a strong second position behind the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) and its Bavarian counterpart, the Christian Social Union (CSU).
Current Polling Landscape
Poll Results and Voter Sentiment
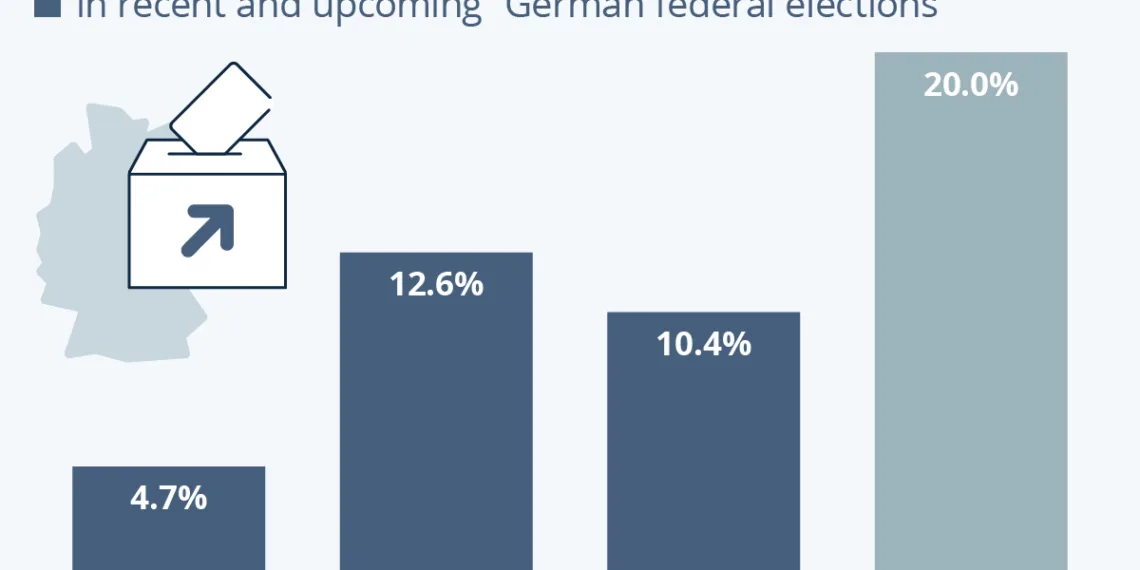
The recent polling data indicates that the AfD is gaining traction, achieving approximately 20 percent of the predicted vote share. This statistic is crucial as it underscores a shift in the political dynamics of Germany, illustrating a notable increase in support for right-wing populism. Meanwhile, the CDU/CSU coalition has garnered around 30 percent of the vote, signifying its continued dominance in the political arena.
It is essential to acknowledge that these figures are reflective of the political climate at a specific moment, and there is potential for fluctuations in support based on evolving socio-political circumstances. Polling organizations, such as YouGov, have corroborated these findings, reinforcing the notion that the AfD’s influence is on the rise.
Long-Term Implications
While the immediate future may not see the AfD forming the next government—given that current projections do not align with a majority—the party’s enhanced representation in the Bundestag (German parliament) could still play a pivotal role in shaping policy. This potential increase in seats may translate to a more profound impact on legislative proceedings, particularly in areas concerning immigration, social policy, and national identity.
Historical Context of the AfD
Founding and Evolution
The AfD was established in 2013, initially as an anti-Euro party, focusing primarily on opposing the European Union’s currency policies. However, as times have changed, so has the party’s platform. The AfD has increasingly shifted to the far-right, adopting a stance that is staunchly against immigration, particularly in light of the refugee crises and subsequent migration waves that have affected Europe over the past decade.
Accusations of Extremism
In its pursuit of political gain, the AfD has been marred with controversies, facing allegations of racism, Islamophobia, and extremism. These accusations have stemmed from various public statements made by party officials and their anti-immigration rhetoric, which often calls for measures that many consider draconian, including mass deportations.
The Broader Implications of AfD’s Rise
Societal Divisions
The ascension of the AfD points to a significant polarization within German society. The party’s populist messaging resonates with a segment of the population that feels disenfranchised or alienated by the traditional political establishment. This sentiment has fostered a growing divide, resulting in widespread protests against the party’s ideology and actions.
Response from Civil Society
In response to the increasing visibility of far-right ideologies, mass protests have erupted across Germany. These demonstrations often advocate for multiculturalism, tolerance, and the protection of human rights, indicating a robust counter-movement to the rising tide of right-wing populism. These societal responses play a critical role in shaping the narrative around the AfD’s influence and the broader implications for German democracy.
Potential Future Trajectories
Monitoring the Momentum
Looking forward, political observers are closely monitoring the AfD’s momentum, as the potential for further growth looms large. Experts warn that if the party continues to solidify its base, it could pose an even greater challenge by 2029, potentially transforming the political landscape in ways currently unimagined.
The Role of Other Political Parties
While the AfD’s ascent raises critical questions about the country’s future, it also puts pressure on traditional parties. Many have ruled out forming coalitions with the AfD, a stance that reflects both moral objections and strategic calculations. The response from these parties will be crucial in determining how the political chessboard will be laid out in the years to come, especially as they seek to combat the rise of populism and reconnect with disillusioned voters.
Conclusion (Not to be Included)
The detailed insights into the AfD’s current standing, historical evolution, societal repercussions, and potential future growth undeniably illuminate the complexities and challenges facing Germany. As a pivotal time in the nation’s political narrative unfolds, the interactions between these factors will be critical in shaping the future of German politics.