Select Language:
Jump Links
– Best Coding Practices And Advice
If you’re just starting out in programming, “The Farmer Was Replaced” serves as both a great introduction and an initial source of confusion. Designed to teach coding in a Python-like environment through a farming game, it uses a fun farming theme to motivate learning.
Learning to code is challenging, even with guidance. To make things easier, we’ve gathered the most important tips and information into this guide.
How The Game Works
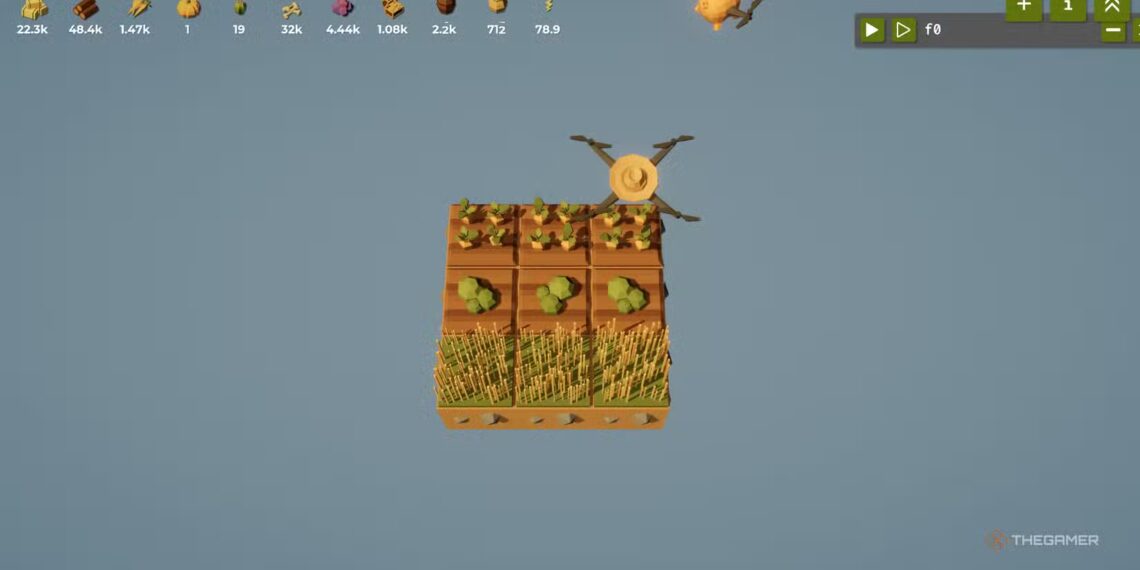
The game shows a farm with the farmer gone. You and a drone are responsible for managing the farm. Since the drone is a machine, it must be programmed with commands to perform tasks such as moving around, planting seeds, harvesting, and analyzing the land below.
Using specific commands and properly formatted commands, you tell the drone what to do. You might instruct it to move west, plant crops, or harvest mature plants. The crops you harvest can then be used to buy upgrades or unlock new types of crops.
As you grow more crops, the rules for growing them become more complex. This means you’ll need to write more advanced code to keep everything running smoothly.
The Different Crops
You can unlock and grow various crops on the farm. Each new crop adds more complexity to your code.
These crops introduce common programming challenges, like managing environmental conditions or optimizing planting strategies. Explaining how to grow each crop efficiently is a long topic, but here’s a quick summary of what to expect from each:
| Crop | What It Teaches You |
| ————–|——————————————————–|
| Grass | Using if statements for planting and harvesting |
| Bushes | Managing land space between multiple crops |
| Trees | Spatial awareness and avoiding overcrowding |
| Carrots | Tilling land and environmental conditions |
| Water | Managing resources—using water only when needed |
| Fertilizer | Toggling conditions or states in code |
| Sunflower | Picking the most petal-filled sunflower |
| Pumpkins | Combining multiple plots into larger pumpkins |
| Cactus | Sorting by height for better growth |
| Polyculture | Planting different crops next to each other |
Remember to check the in-game documentation if you forget details about a specific crop.
The Different Mini-Games
Some upgrades involve mini-games instead of more complex growth mechanics. These puzzles test your coding skills through challenges like navigating mazes or playing a game similar to Snake, where you collect apples and avoid getting stuck.
The Best Coding Practices And Advice
Some screens show open script pages. Since you have total freedom in how you program, there’s no one right way to play. Instead, here are some tips for approaching coding challenges:
This Isn’t Python
The game claims to use a Python-like language, meaning it shares some syntax rules. However, it’s quite different from Python in many ways. Look for help within the game’s own help pages rather than relying on Python resources.
Comments are important. If you type ‘#’ at the start of a line, anything after it is ignored by the game. Use comments to describe what your code does; this helps you remember later on, especially if you need to troubleshoot.
If you have to write the same code repeatedly more than three times, turn that code into a function to keep your scripts cleaner and easier to manage. For example, automating the process of checking if a crop is ready, harvesting it, and replanting can be done with a single function—saving time and reducing errors.
The Right Side of the Skill Tree Is Key
Not all programming features are available immediately. You start with basic tools and unlock more advanced features, like operators, variables, and functions, as you progress. This staged approach simplifies complexity and helps you learn step-by-step.
The most important upgrades are on the right side of the skill tree. Getting these early allows you to write more efficient code sooner.
You’re Going To Feel Stupid
It’s normal—regardless of experience—to encounter problems where the solution isn’t obvious. Don’t get discouraged. If you’re stuck, try working on a different part of the code or take a break. Often, stepping away helps you see the problem with fresh eyes.
You’ll also experience moments of triumph when your code finally works—that feeling of solving a tricky problem is part of the learning process.
Efficiency Is Optional
While optimizing your code and farming strategies can improve productivity, it’s not required. If you need a steady supply of certain crops like pumpkins or cacti, just harvesting normally works fine. The game allows you to focus on resource collection at your own pace and priority.