Select Language:
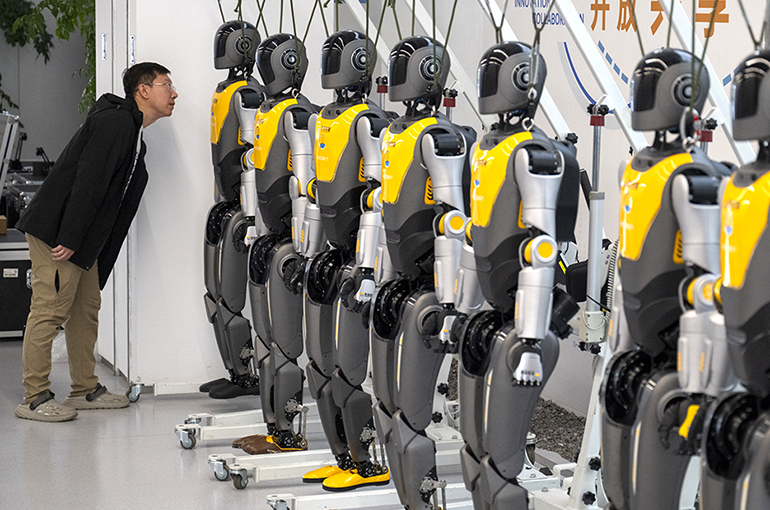
A recent report from Goldman Sachs has raised concerns about potential oversupply in China’s expanding humanoid robot industry, but industry insiders have emphasized that such worries are currently unfounded. The report, based on a survey of nine Chinese supply chain companies—including Sanhua Intelligent Controls and Tuopu Group—indicated that none of these firms have confirmed receiving significant orders, nor have they provided a clear timeline for mass production.
These companies are actively increasing their production capacities, with estimated annual output ranging from 100,000 to one million units. The report cautioned that this level of confidence could be overly optimistic, especially considering that global shipments of humanoid robots are expected to hit only 1.38 million units by 2035.
A representative from Tuopu, headquartered in Ningbo, Zhejiang Province, explained that the company currently has no confirmed orders from major North American clients but is planning its production capacity based on client guidance. Tuopu specializes in manufacturing automotive parts and intends to set up production lines for humanoid robot components in Thailand, Mexico, and the United States, with a potential annual capacity of up to one million units at the Thailand facility.
The company’s representative added, “Since suppliers need to prepare sufficient capacity to meet future demands, we plan according to our clients’ requirements. If future orders are lower or higher than expected, it’s uncertain at this stage,”.
Industry analysts pointed out that globally, application scenarios and technological development pathways for humanoid robots remain in early exploration stages. They also emphasized that it’s premature to dismiss the medium- and long-term growth potential of humanoid robots simply because of a lack of immediate large orders.
While oversupply is common in mature industries, humanoid robotics is still in its initial development phase. Supply chain companies are proactively expanding capacity in anticipation of future demand, and concerns over overcapacity ahead of actual orders are considered premature.
Notably, confidence in the sector is shared internationally. Elon Musk, CEO of Tesla, recently stated at an annual shareholders meeting that humanoid robots could become the most widely produced product in history, with a potential market reaching billions of units. Musk announced that Tesla plans to launch a production line next year with an annual capacity of one million robots, and future facilities in Austin could reach an output of ten million annually.
Domestic confidence also remains strong. A report from the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology predicts that the number of humanoid robots in use within China will surpass 100 million units by 2045, with the market valued at around 10 trillion yuan (approximately 1.4 trillion USD).
Furthermore, the economic impact of humanoid robots extends beyond hardware manufacturing. Jiang Lei, chief scientist at the National and Local Co-Built Humanoid Robotics Innovation Center, noted that developing embodied intelligence models for robots and accumulating data during their operation will likely become primary areas of innovation in the future.