Select Language:
The number of newly installed industrial robots in China increased by 5% in 2024 compared to the previous year, while global installations declined by 3%, primarily due to reduced demand in the automotive sector.
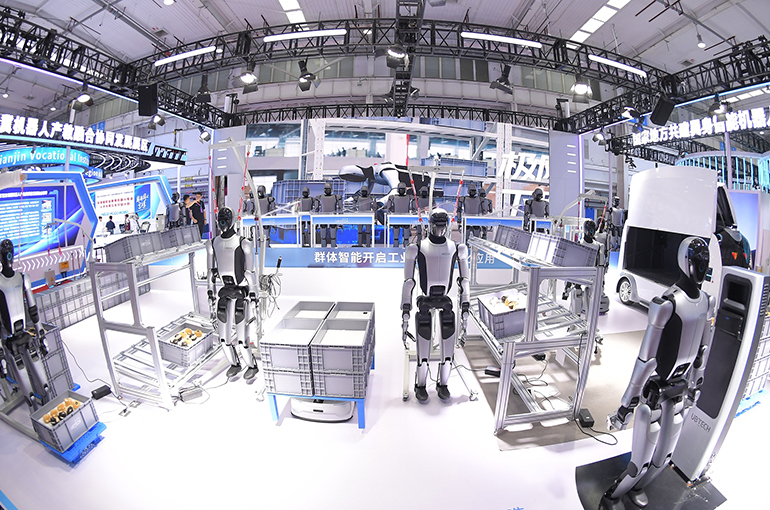
Over the past year, approximately 290,000 industrial robots were put into operation across China, according to Takayuki Ito, president of the International Federation of Robotics, during the World Robot Conference in Beijing on August 9. China now accounts for 54% of the global market, up from 51% in 2023.
Meanwhile, other key markets experienced a drop in new robot installations: the United States saw a 9% decrease, Japan a 7% decline, and Europe a 6% fall, Ito reported.
China has also surpassed Japan and Germany in robot density—a measure of automation that calculates the number of industrial robots per 10,000 workers—reaching 470 units. Only South Korea with 1,012 units and Singapore with 770 units rank higher, according to data from the International Federation of Robotics.
Despite ongoing geopolitical tensions and tariff disputes, robot orders in Asia increased modestly—by a single digit—during the first quarter of this year, driven mainly by a partial recovery in the electronics industry. Ito emphasized that China is expected to continue leading global robotics demand.
Last year, China’s industrial robot sales exceeded 302,000 units, making it the top market worldwide for the 12th consecutive year, according to data from the Chinese Institute of Electronics. The nation is also the world’s largest producer of industrial robots, with output reaching 556,000 units in 2024.
Since 2015, China has hosted the annual World Robotics Conference to foster industry development and technological advancements. This five-day event, concluding tomorrow, drew more than 200 prominent Chinese and international robotics firms, including Unitree Robotics, ABB Group, and KUKA, showcasing over 1,500 products.