Select Language:
AI agents are action-oriented systems powered by artificial intelligence designed to execute tasks on behalf of users. Currently, most AI agents need human oversight to ensure that they complete tasks accurately and reliably. However, autonomous AI agents elevate this concept by functioning entirely independently, eliminating the need for human guidance. In this guide, I will explore what Autonomous AI agents are, how they operate, and provide a real-world example to illustrate their capabilities.
What Are Autonomous AI Agents?
Autonomous AI agents are cutting-edge AI systems capable of executing actions without any human intervention. Unlike traditional AI agents, which often require some degree of human monitoring, autonomous AI agents are designed to plan, decide, and act independently. Essentially, these agents are self-directed and possess their own form of autonomy.
These advanced AI agents can interpret their environment by using sensors and data to construct an internal representation of the world. They possess memory, enabling them to remember past data and enhance their performance over time.
Generally, autonomous AI agents are categorized as model-based and goal-based agents, designed to achieve specific targets independently of human oversight. In simple terms, they can navigate complex, multi-step tasks by making decisions without needing human input.
How Do Autonomous AI Agents Work?
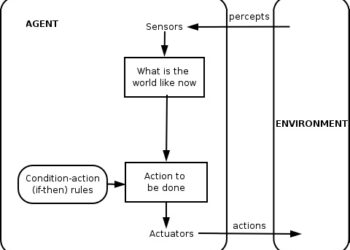
Since autonomous AI agents operate independently, their architecture is sophisticated enough to handle a wide range of scenarios. Initially, they contain a perception module that analyzes input data from sensors, APIs, or databases, which helps create an internal representation of the constantly changing environment.
In addition, they leverage a trained knowledge base for reasoning, planning, and decision-making. These systems also perform self-monitoring to identify and rectify errors. Depending on the task, autonomous AI agents may create hierarchical plans to manage uncertainty. Once a goal is established, they execute actions and monitor the outcomes.
This process repeats autonomously until the target is reached. That’s how autonomous AI agents function without requiring human intervention.
Real-World Example of an Autonomous AI Agent
To illustrate the concept of autonomous AI agents, let’s consider AI-powered self-driving cars. Waymo, which began as Google’s Self-Driving Car Project, is a technology that enables fully autonomous vehicles. Waymo cars operate without any human drivers at the wheel, making them a leading example of a completely autonomous ride-hailing service.
Waymo vehicles utilize a sophisticated perception system that collects and processes data from LiDAR, cameras, and radar to create a real-time map of their surroundings. This information empowers the cars to make decisions about stopping, accelerating, steering, and more—completely independently. They navigate through dense traffic and change lanes without any human assistance.
As mentioned earlier, autonomous AI agents prepare for uncertainty, allowing Waymo cars to respond to unpredictable situations, such as pedestrians crossing the road or vehicles making sudden U-turns. Over time, these cars learn from various situations and edge cases, demonstrating their capacity for continuous improvement.
Waymo vehicles operate in real-world environments where passenger safety is paramount. Decisions are made in milliseconds and aren’t always explicitly programmed into the system. According to Google, waymo cars have traveled over 25 million miles autonomously in cities like Phoenix, San Francisco, Los Angeles, and Austin.
Remarkably, Waymo’s self-driving cars have achieved a 92% reduction in bodily injury claims compared to human-operated vehicles. In terms of property damage, there’s an 88% reduction in claims against traditional, human-driven cars.
This represents a physical instance of an autonomous AI agent, but similar concepts apply in digital domains. For example, autonomous AI agents can manage extensive IT systems, identifying security threats and ensuring resources keep a website operational. They can also conduct autonomous financial trading based on risk assessments or serve as digital assistants to schedule meetings and make reservations, all without human intervention.